Deploy NetScaler® Kubernetes Gateway Controller
The deployment process involves deploying the Gateway Controller, which monitors and manages Gateway CRDs that define traffic routing rules. The Gateway Controller then configures the NetScaler VPX™ to direct external requests to the sample application.
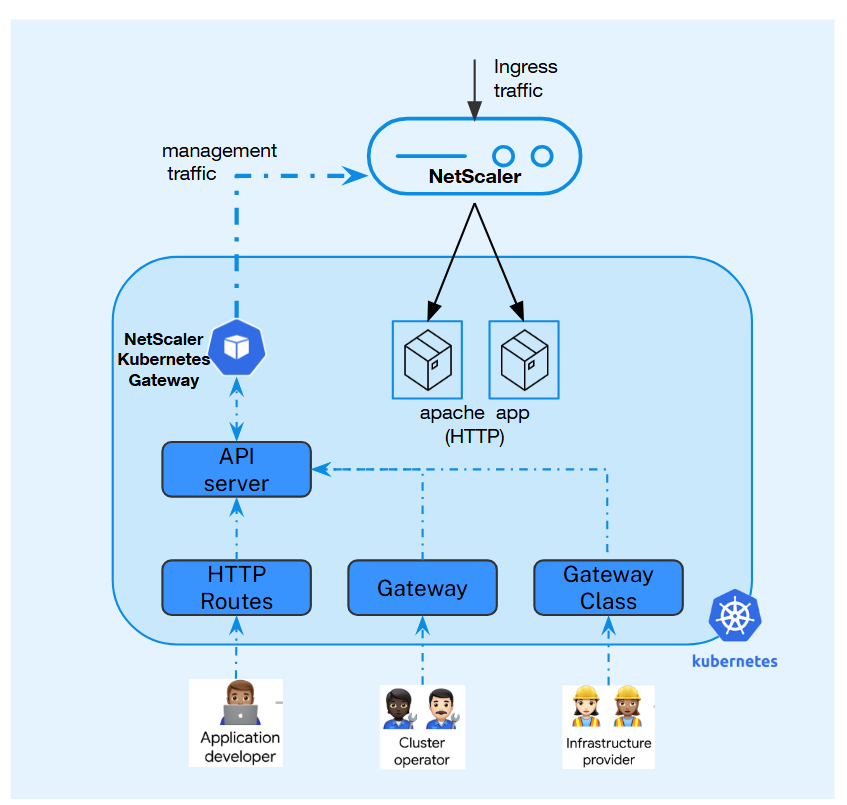
-
Deploy a sample application to get started.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: cnn-website labels: name: cnn-website app: cnn-website spec: selector: matchLabels: app: cnn-website replicas: 2 template: metadata: labels: name: cnn-website app: cnn-website spec: containers: - name: cnn-website image: quay.io/sample-apps/cnn-website:v1.0.0 ports: - name: http-80 containerPort: 80 - name: https-443 containerPort: 443 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: cnn-website labels: app: cnn-website spec: type: NodePort ports: - name: http-80 port: 80 targetPort: 80 - name: https-443 port: 443 targetPort: 443 appProtocol: https selector: name: cnn-website <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install the Gateway API CRDs from the official standard channel if they are not already installed.
-
Generate
values.yamlbased on your use case. For information about the mandatory and optional parameters that you can configure during NetScaler Kubernetes Gateway Controller installation, see Configurations.netscaler: adcCredentialSecret: "nslogin" nsIP: "4.4.4.10" # NetScaler Management IP or SNIP with Management access enabled for HA and CLIP for NetScaler Cluster gatewayController: entityPrefix: gwy gatewayControllerName: "citrix.com/nsgw-controller" license: accept: yes <!--NeedCopy-->The user name and password of a system user account on NetScaler MPX or NetScaler VPX are required for the Kubernetes Gateway. Ensure that NetScaler has a non-default system user account with the necessary privileges to allow the NetScaler Kubernetes Gateway Controller to configure NetScaler MPX or VPX. For instructions on creating a system user account on NetScaler, refer to the Create a system user account for NetScaler Ingress Controller in NetScaler.
You can provide the user name and password directly or use Kubernetes secrets. To use Kubernetes secrets, create a secret for the user name and password with the following command:
kubectl create secret generic nslogin --from-literal=username=<username> --from-literal=password=<password> <!--NeedCopy-->Note:
entityPrefixandgatewayControllerNameare mandatory and must be unique for every deployment of NetScaler Kubernetes Gateway Controller. -
Deploy the NetScaler Kubernetes Gateway controller using the Helm charts and the
values.yamlgenerated in previous step. For more information, see NetScaler Kubernetes Gateway Controller deployment using Helm Chart.helm repo add netscaler https://netscaler.github.io/netscaler-helm-charts/ helm install gateway-controller netscaler/netscaler-kubernetes-gateway-controller -f values.yaml <!--NeedCopy-->
Exposing an application by using HTTP Using Gateway and HTTPRoute CRDs
The following is an example of a GatewayClass, Gateway, and an HTTPRoute definition.
-
Create a GatewayClass resource to define the controller handling Gateway objects.
Sample GatewayClass
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: GatewayClass metadata: name: example-gateway-class spec: controllerName: citrix.com/nsgw-controller <!--NeedCopy--> -
Define a Gateway resource to expose services based on defined listeners.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: example-gateway spec: gatewayClassName: example-gateway-class listeners: - name: http protocol: HTTP port: 80 addresses: - type: IPAddress value: 4.4.4.4 <!--NeedCopy-->Notes:
- Verify that the gatewayClassName defined in the Gateway matches the GatewayClass resource that was created in the previous step.
-
Apply HTTPRoute or other route CRDs to route traffic to backend services.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: example-route spec: parentRefs: - name: example-gateway hostnames: - "example.com" rules: - matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: / backendRefs: - name: cnn-website namespace: default port: 80 <!--NeedCopy-->Notes:
- Ensure that the gateway name specified in
parentRefsmatches with the Gateway CRD established in the previous step. - Currently, the HTTPRoute CRD only supports a single
parentRef.
- Ensure that the gateway name specified in
-
Verify the gatewayClass status. If the status shows
ACCEPTED: True, then the controller has accepted the resource.kubectl get gatewayclass NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE example-gateway-class citrix.com/nsgw-controller True 2d <!--NeedCopy-->kubectl describe gatewayclass ... Spec: Controller Name: citrix.com/nsgw-controller Status: Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2025-03-21T09:15:32Z Message: Accepted by the controller. Reason: Accepted Status: True Type: Accepted Events: <none> <!--NeedCopy-->Verify the Gateway resource status. If the status shows
PROGRAMMED : True, then controller has successfully pushed the configuration to NetScaler.kubectl get gateway example-gateway NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE example-gateway example-gateway-class 4.4.4.4 True 6d3h <!--NeedCopy-->kubectl describe gateway example-gateway ... Status: Addresses: Type: IPAddress Value: 4.4.4.4 Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2025-03-24T08:53:07Z Message: Accepted by the controller. Reason: CreatedCRDInstance Status: True Type: Accepted Last Transition Time: 2025-03-24T08:53:18Z Message: Config pushed by the controller. Reason: ConfigPushedToNetscaler Status: True Type: Programmed Events: <none> <!--NeedCopy-->
Exposing an application by using HTTPS/SSL Using Gateway and HTTPRoute CRDs
The following is an example of a GatewayClass, Gateway, and an HTTPRoute definition.
-
Create a GatewayClass resource to define the Gateway objects handled by the controller.
Sample GatewayClass
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: GatewayClass metadata: name: example-gateway-class spec: controllerName: citrix.com/nsgw-controller <!--NeedCopy--> -
(Optional) Create a self-signed SSL certificate and a key to be used with the Gateway-Listener for TLS configuration. The following command is just a sample command to create a self-signed certificate and assumes that the host name of the application is
example.comopenssl genrsa -out cnnwebsite_key.pem 2048 openssl req -new -key cnnwebsite_key.pem -out cnnwebsite_csr.pem -subj "/CN=example.com" openssl x509 -req -in cnnwebsite_csr.pem -sha256 -days 365 -extensions v3_ca -signkey cnnwebsite_key.pem -CAcreateserial -out cnnwebsite_cert.pem <!--NeedCopy-->Note:
If you already have an SSL certificate, you can create a Kubernetes secret using the same.
-
Create a Kubernetes Secret to store the SSL certificate and key (TLS pair).
kubectl create secret tls app1-secret --key cnnwebsite_key.pem --cert cnnwebsite_cert.pem <!--NeedCopy--> -
Create the Gateway resource with listeners for HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443). The Gateway exposes the application on 4.4.4.4. Refer the SSL certificate Secret created in the preceding step within the HTTPS listener.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: example-gateway spec: gatewayClassName: example-gateway-class listeners: - name: http protocol: HTTP port: 80 - name: https protocol: HTTPS port: 443 tls: mode: Terminate certificateRefs: - kind: Secret name: app1-secret addresses: - type: IPAddress value: 4.4.4.4 <!--NeedCopy--> -
Apply the HTTPRoute resource to route incoming traffic to one or more backend services.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: example-route spec: parentRefs: - name: example-gateway hostnames: - "example.com" rules: - matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: / backendRefs: - name: cnn-website namespace: default port: 443 <!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
The application is exposed on both port 80 (HTTP) and port 443 (HTTPS).
- To expose the application on HTTPS only, exclude the HTTP listener configuration in the Gateway resource.
- To redirect HTTP to HTTPS, use the
requestRedirectHTTPRoute Filter.If your backend service expects HTTPS traffic from the Gateway, ensure the appProtocol is set to https on the corresponding port (for example, port 443) in your Service definition. Reference: Consult the Gateway API documentation for details on backend protocols.