App-based provisioning in Azure
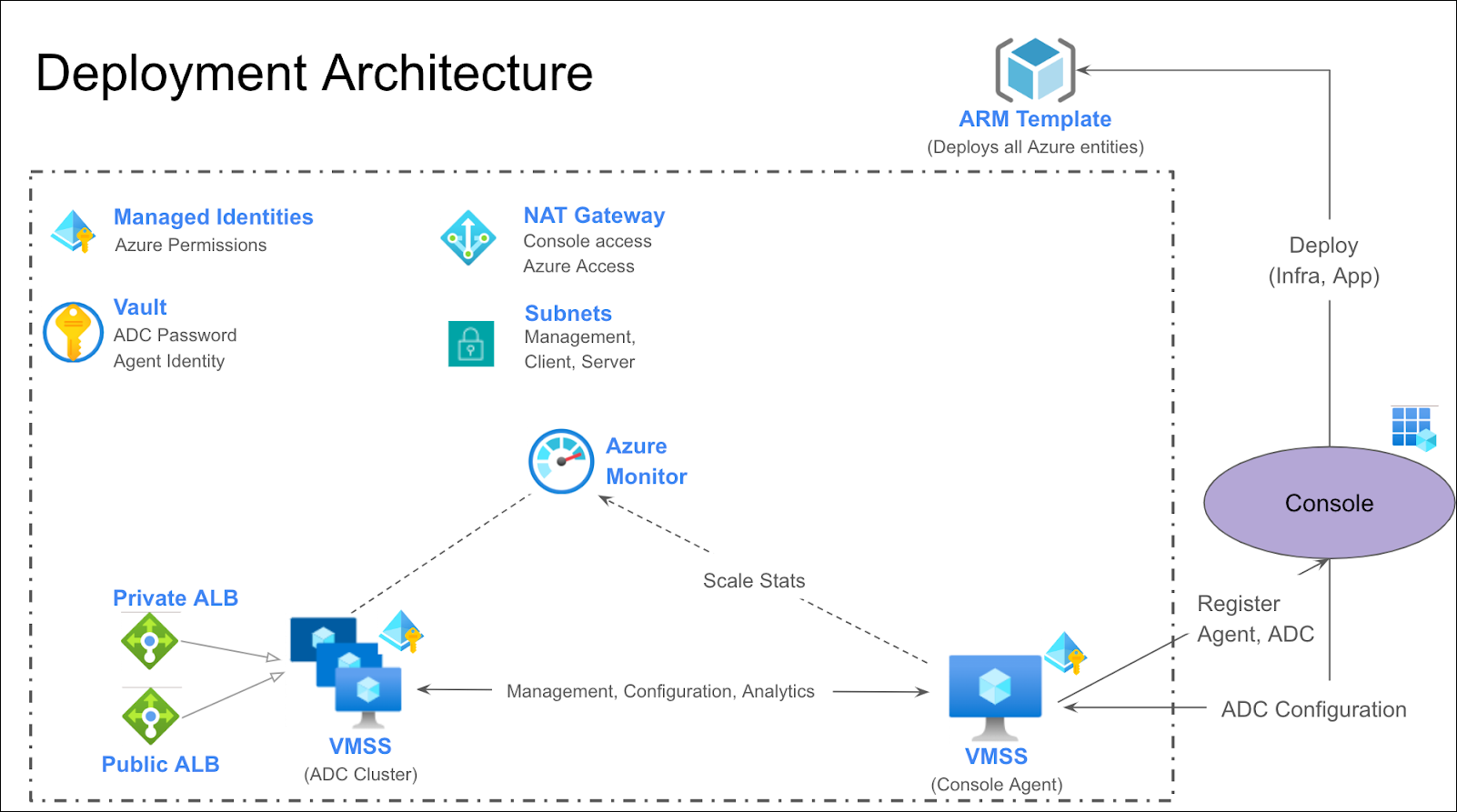
NetScaler Console service introduces “App based” provisioning, designed to streamline and simplify NetScaler deployments on cloud data centers and deliver applications from them.
NetScaler Console service accepts the customer’s cloud credentials and sets up the infrastructure required for application delivery by orchestrating the launching of NetScaler instances, NetScaler Console Agents and the necessary cloud entities in Azure. NetScaler administrators can leverage both Flexed and Cloud Marketplace licenses for their NetScaler instances, ensuring flexibility in licensing options.
Administrators can then deliver applications present in their cloud by defining delivery settings in a straightforward, app centric manner from NetScaler Console service. The service then takes care of configuring both ADCs and Azure infrastructure to deliver their applications. Once the applications are delivered, NetScaler administrators gain access to the rich analytics, and monitoring features of NetScaler Console service to effectively manage and monitor their applications.
Prerequisites
Configure programmatic deployment for the following products in Azure Marketplace:
- NetScaler VPX - Configure programmatic deployment for one of the following variants:
- NetScaler VPX BYOL - Subscribe if you have purchased flexed licenses and they are available in NetScaler Console service for licensing NetScaler instances.
- NetScaler VPX Premium - 1 Gbps - Subscribe if you want a subscription based license from the Azure Marketplace.
- NetScaler Agent Service
- Select a VNet - Select a VNet for setting up the infrastructure for application delivery.
The VNet should have a CIDR of /22 or more. During the infrastructure deployment process, dedicated subnets for ADC infrastructure are created consuming /24 address space. Select a VNet from the list based on your deployment:
- Dedicated VNet that is separate from the applications, if you want your deployment to be similar to a DMZ.
- Same VNet where the applications are also present.
Cloud access profile
A cloud access profile is used to give permissions of the customer’s Azure account to NetScaler Console service. While creating a cloud access profile the administrator must download and run a powershell script in Azure CLI. The script creates Service Principals in the customer’s Azure account with owner permissions at the subscription level.
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Provisioning > App based > Cloud Access Profiles.
- Follow the on-screen directions to create a cloud access profile for your subscription.
Note:
To create this profile, the NetScaler administrator must also be the Azure subscription owner.
App environment
App Environment represents the delivery infrastructure set up in a VNet for delivering the applications. When an administrator creates an App Environment in the NetScaler Console service, all the resources for delivering and monitoring applications, including gateways, security groups, subnets, NetScaler instances, and NetScaler Console agents, are deployed as part of an App Environment. See the FAQ section for more information.
- Navigate to InfraStructure > Provisioning > App based > Environments.
- Follow the on-screen directions to create an App environment.
Application delivery
Application delivery is the core component of the App-based provisioning feature and contains the mandatory application delivery and security information. As part of application delivery configuration you define the following entities:
- The endpoint representing how the application is accessed by the clients, such as protocol, port, certificates, and ciphers. For example, an SSL profile of an endpoint represents the set of SSL configurations that includes the supported ciphers and protocols. A predefined A+ SSL profile is available by default.
- The services that represent an application’s component, which must be accessed based on the specific HTTP request. For example, a component for an ecommerce application could be an order service, a catalog service, or a payment service that are installed in different application servers and requests must be routed based on the URL accessed. The service profile of an application service represents how the delivery infrastructure can access and monitor the application service, such as load balancing, SSL, and health check settings.
- The content policy that defines how the L7 content is inspected and modified when a request or a response arrives for a specific service. It is used to take a predefined action on the HTTP requests based on headers, URLs, or IP addresses. Some of the actions could be header enrichment, redirecting requests, or dropping requests.
- Navigate to InfraStructure > Provisioning > App based > App Delivery.
- Follow the on-screen directions to create a new application.
FAQs
What are the entities created by NetScaler Console service for delivering an application in the cloud?
NetScaler Console service creates the following entities in the customer’s VNet:
- NetScaler VPX cluster.
- The VPX instances are deployed as a Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS).
- A single node cluster is created during App Environment creation. This cluster can scale up to a maximum of 10 nodes.
- A NetScaler Console agent.
- Subnets: One subnet each for management, client, and server.
- Security groups: One security group each for management, client, and server NICs of NetScaler.
- Management security group: This security group is associated with the management NICs of the NetScaler instances and NetScaler Console agents. It consists of rules to allow communication between NetScaler instances, NetScaler Console agents, and any other control plane traffic.
- Client security group: This security group is associated with the client NICs of the NetScaler instances and is used to allow the data traffic to the NetScaler virtual servers.
- Server security group: This security group is associated with the server NICs of the NetScaler instances and does not contain any default rules.
- NAT gateway: A NAT gateway enables NetScaler Console agent to access NetScaler Console service and NetScaler instances to access the internet.
- Azure Key Vault: Store any NetScaler and agent secrets in the vault.
What are the metrics used to Autoscale NetScaler?
The following metrics are used to Autoscale NetScaler:
- The minimum number of instances in the VMSS is 1 and the maximum is 10.
- Scale-Out by 1 capacity unit. That is, cpu_use > 70% or throughput > 70% for 5 consecutive periods of 60 seconds.
- Scale-In by 1 capacity unit. That is, cpu_use =< 30% and throughput =< 30% for 5 consecutive periods of 60 seconds.
How can an administrator identify the resources created by NetScaler Console service in the cloud?
All Azure resources are created with the tag “UsedFor: AppDeliveryByNetScaler” by default. In addition, the resources are tagged using the tags specified during the App Environment creation workflow.
How can a NetScaler administrator upgrade NetScaler in an App Environment?
Perform the following steps to upgrade NetScaler:
-
From the Azure console, disable scaling for the VMSS by setting the scaling policy values to the current number of instances in the VMSS for the App Environment.
Naming convention:
vmss-adc-<App Environment Name>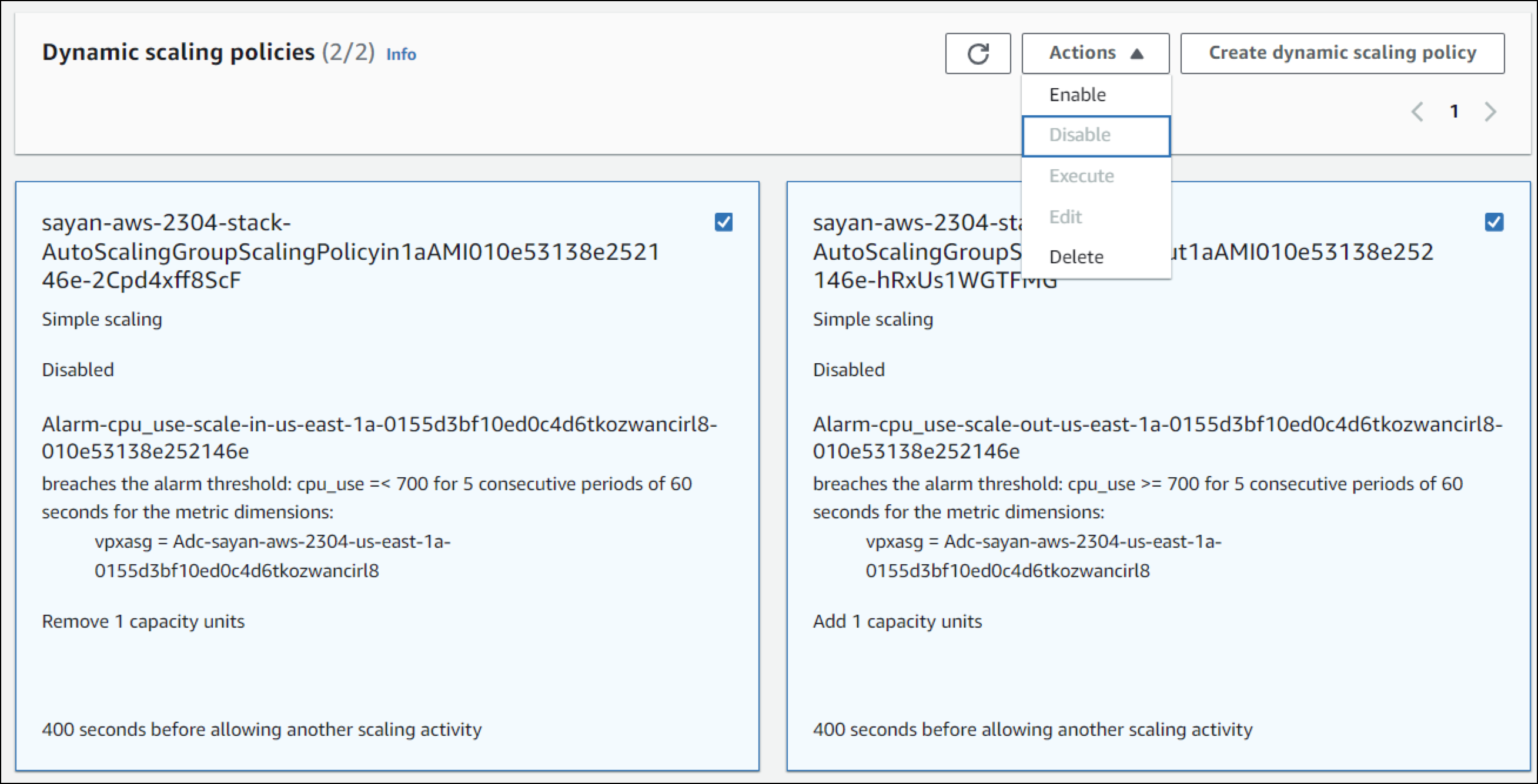
-
From the NetScaler Console service, edit the App Environment and select the version to upgrade to.
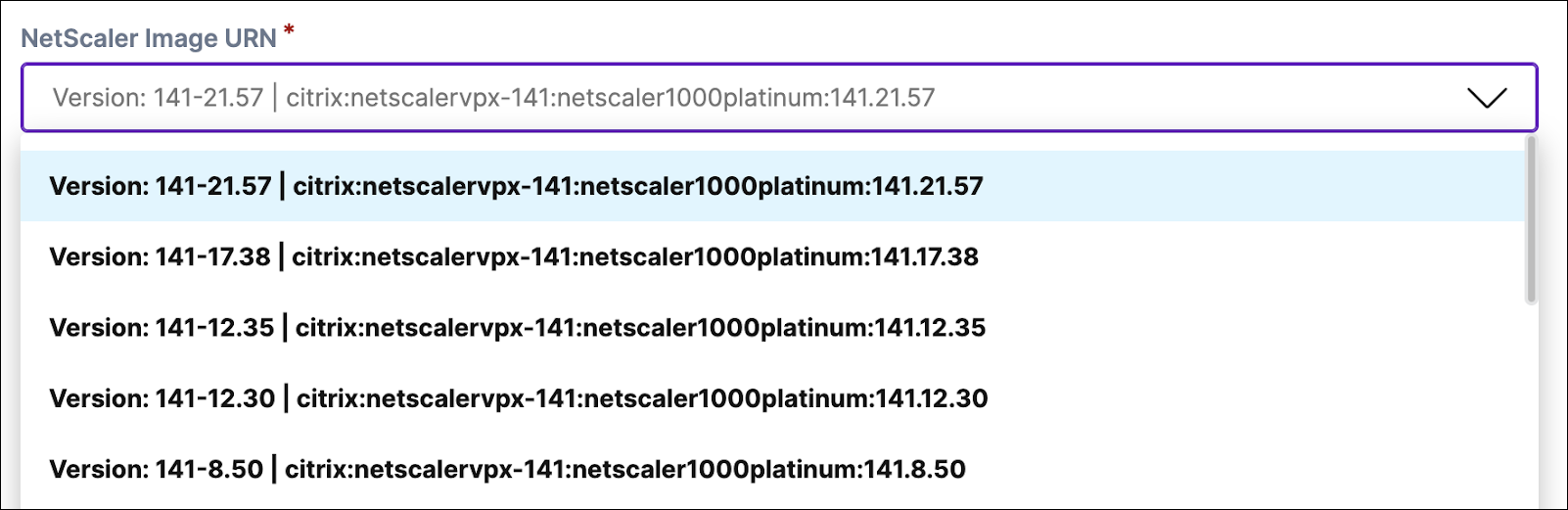
-
From NetScaler Console service, upgrade ADCs to the version selected in the pervious step by using the Upgrade Job feature.
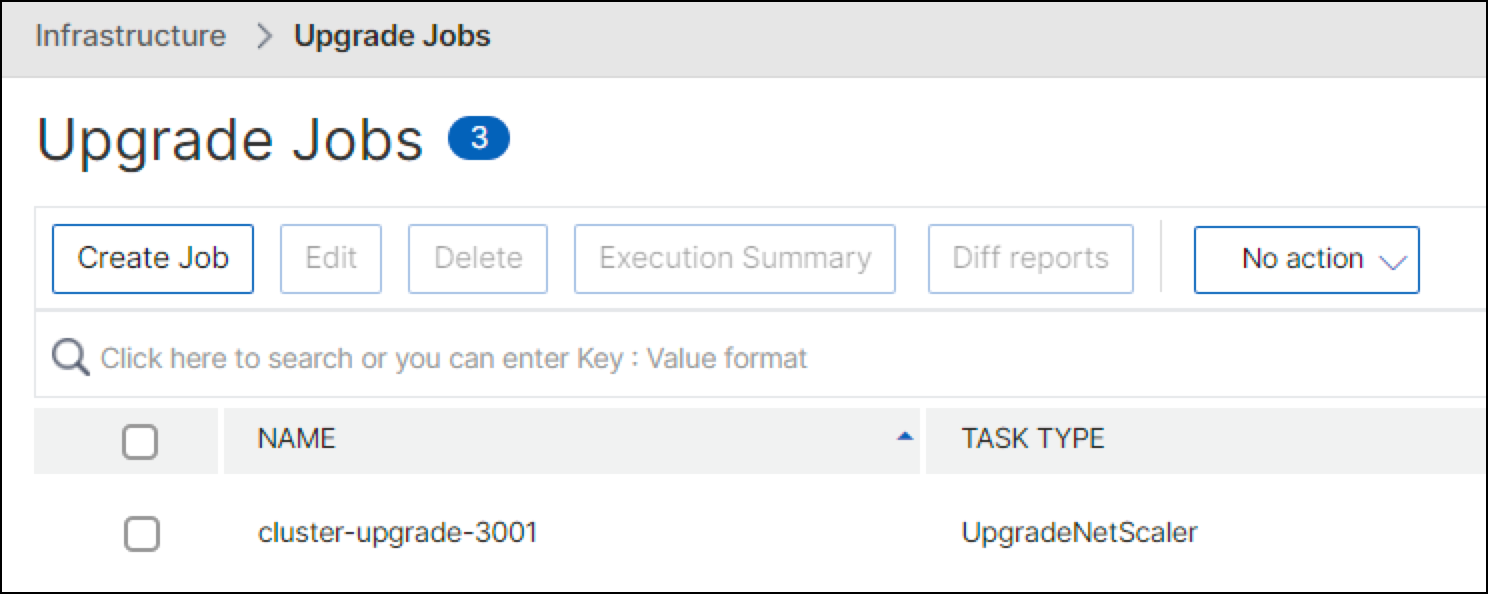
-
From the Azure Console, re-enable dynamic scaling for the VMSS. The instance limit must be set to the initial values. That is, minimum=1, maximum=10, default=1.