Zero-Touch Certificate Management
Zero-Touch Certificate Management automates the installation and management of SSL certificates, eliminating the need for manual configuration. By uploading certificates to NetScaler® Console, administrators can centralize certificate management. NetScaler has a certificate fetcher that periodically polls NetScaler Console and packet engine. This ensures that the packet engine remains synchronized with the zero-touch certificate store on NetScaler Console. Through this process, the packet engine automatically handles the otherwise tedious tasks of adding, binding, and linking certificates, streamlining the certificate management process.
Benefits of Zero-Touch Certificate Management
The Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature automates the following processes:
- Adding, binding, and linking certificates.
- Installing and using the best suitable certificate during a TLS handshake.
- Removing expired certificates from the packet engine.
- Pushing certificates with a future issue date to the packet engine from NetScaler Console once the date is valid.
With the Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature, you can prevent the following errors commonly associated with manual processes:
- Overwriting certificates or keys. If you upload another certificate or key with the same certificate and key name that exists on NetScaler, it overwrites the existing one. This might cause applications to go down after a reboot.
- Accidental certificate deletion that can lead to application downtime after a reboot.
To enable the Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature, see Zero-Touch Certificate Management.
Note:
The Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature is activated on an application solely when there are no manual bindings of certificate-key pairs to that application. This means that the application or virtual server will automatically choose the correct server certificate from the zero touch management pool if an application does not have a specific server certificate associated with it. The same holds true for Certificate Authority certificates.
How it works
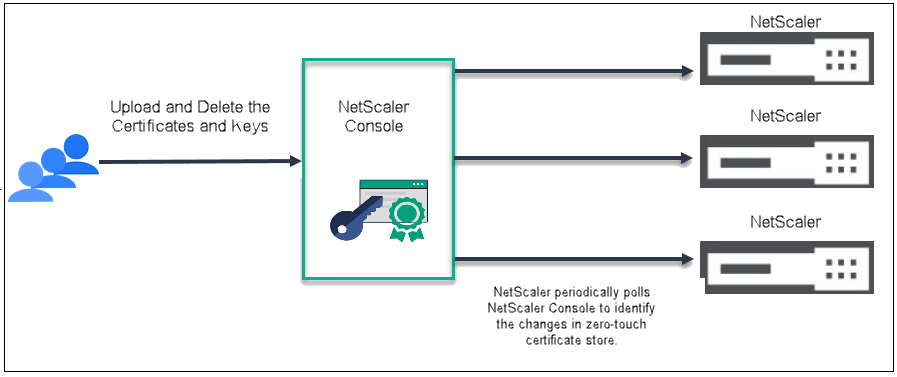
The following picture shows the workflow of Zero-Touch Certificate Management:
Prerequisite
- Ensure that the instance is managed by NetScaler Console. Enable the Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature in NetScaler Console. For more information, see Zero-Touch Certificate Management.
- Ensure that port 443 is open on all firewalls to allow communication between the certificate fetcher and NetScaler Console.
The following are the high-level steps involved in Zero-Touch Certificate Management.
- An admin uploads all certificates and keys, in any format, to NetScaler Console. For more information on uploading certificates and keys, see Zero-Touch Certificate Management.
- NetScaler Console validates and stores the certificates and keys in the database.
- The zero-touch certificate store validates and discards the files that are in an incorrect format. The supported file formats are:
- Certificate (PEM or DER)
- Private Keys
- Password-protected private keys
- CA certificates (Root or Intermediate certificates)
- PFX files
- Certificate bundle
- Certificates and keys are physically present in the NetScaler console and are available in the memory of the packet engine. NetScaler pulls the certificates and keys from NetScaler Console and also creates a local cache of the certificate and key metadata fetched. It then pushes them to the memory of the packet engine. NetScaler polls every 10 minutes for updates.
- The packet engine then handles tasks such as installing, deleting, adding, binding, and linking the certificates and keys.
- During each polling, NetScaler compares the packet engine and NetScaler console to identify any certificates and keys that are present in the packet engine but not in NetScaler Console. In such cases, it deletes these certificates and keys from the memory of the packet engine, ensuring the system remains synchronized with NetScaler Console.
Note:
- By default, certificates are fetched every 10 minutes. After a NetScaler reboot, the initial fetch happens within one minute. When NetScaler Console is unreachable and NetScaler reboots, it uses the local cache’s certificate and key metadata to serve traffic, ensuring high resiliency.
Certificates states in NetScaler
Certificates in NetScaler can be active or inactive.
- Active Certificates: Certificates that are available for immediate use. NetScaler selects server certificates for TLS transactions based on the received SNI or the default SNI configured on an SSL virtual server.
- Inactive Certificates: The certificates in NetScaler might become inactive due to any of the following reasons.
- The private key for the server certificate is not present on NetScaler Console.
- The server certificate contains SAN entries that conflict with multiple other active certificates.
- The server certificate contains SAN entries that conflict with one of the active certificates but do not cover all the SAN entries of the active certificate.
- The server certificate contains SAN entries conflicting with an active certificate and has an earlier expiry date than the active certificate.
- The server certificate contains a SAN that exceeds the maximum allowed entries.
- The server certificate does not have a common name.
- The SSL certificate has a common name or SAN name that exceeds the maximum allowed length.
- The server certificate is inactive due to a lack of memory in the packet engine.
- The CA certificate is inactive because its property increases the request message length beyond 14 KB.
- The CA certificate is inactive because its distinguished name cannot be encoded for the certificate request message.
CA certificate management
CA certificates uploaded to NetScaler Console are used to authenticate both the client and server once installed on the packet engine. The maximum length of the certificate request message is 14 KB. CA certificates included in the certificate request message remain in an active state and participate in the TLS authentication process, while others are in an inactive state. If any active CA certificate is deleted, NetScaler reassesses the list of active certificates.
CA certificates fetched from NetScaler Console are used for the TLS handshake if the Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature is enabled and no server certificate is bound to a virtual server.
Note:
- Uploaded certificates are classified as CA certificates if the basic constraints extension has the CA field set to true. Otherwise, they are considered as server certificates.
- Certificates and keys are available in memory of the packet engine and not physically stored on NetScaler.
TLS handshake process
During the TLS handshake, the server certificate is selected based on the Server Name Indication (SNI) received from the client. To support clients that do not include the SNI extension in their request, NetScaler provides an option to configure a default SNI. To configure the default SNI, use the following command:
set ssl vserver -defaultSNI <sni_name>
Notes:
- The administrator must ensure that the certificate corresponding to the default SNI is uploaded to NetScaler Console.
- The server certificates fetched from NetScaler Console are used for the TLS handshake if the Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature is enabled and no server certificate is bound to a virtual server.
View the certificate and key list
NetScaler displays the source of the certificates and keys as remote if they are fetched from NetScaler Console.
Also, you can verify whether the zero touch certificate management feature is enabled using the show command.
To view the status of Zero-Touch Certificate Management using the CLI
At the command prompt, type:
show ssl zerotouchparam
Example:
show ssl zerotouchparam
SSL Zerotouch Config Params: ENABLED
Remoteserver IP : 10.146.111.81
Keyfile Name : sslparam.key
Zerotouch Certfetcher Polled Status:
Request Status : SUCCESS
Request Type : GET-LIST
HTTP Status Code : 200
Time-Stamp : 2024-10-08T09:15:56Z
Next Polling At : 2024-10-08T09:25:56Z
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
To view the certificate source by using CLI
At the command prompt, type:
show ssl certkey
Example(Certificate which is in active state):
show ssl certkey
Name: 023a2b9d-de07-b53a-70b8-b925fc09efe8
Certificate Source: REMOTE Certkey Status: ACTIVE
Cert Path: entity654_ec.crt
Key Path: entity654_ec.key
Format: PEM
Status: Valid, Days to expiration:3635
Certificate Expiry Monitor: DISABLED
Certificate Type: "Client Certificate" "Server Certificate"
Version: 3
Serial Number: 12494655570E02CA2B5CCCB1DC317C41271B8BD1
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: CN=Intermediate5.Root4
Validity
Not Before: Oct 1 10:15:53 2024 GMT
Not After : Sep 29 10:15:53 2034 GMT
Subject: CN=Entity6.Intermediate5.Root4
Public Key Algorithm: id-ecPublicKey
Digest:
Public Key size: 256
Ocsp Response Status: NONE
deleteCertKeyFilesOnRemoval:
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example(Certificate which is in inactive state):
show ssl certkey
Name: ed9d7c90-6f28-5407-8073-346440044e34
Certificate Source: REMOTE Certkey Status: INACTIVE(No Private Key)
Cert Path: server_rsa_4096_9.crt
Format: PEM
Status: Valid, Days to expiration:280
Certificate Expiry Monitor: DISABLED
Certificate Type: "Server Certificate"
Version: 3
Serial Number: 04B5502077AFC2EF9581F49BDFA104C9360CA6D2
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=US,ST=InterState2,L=InterCity2,O=InterOrganization2,OU=InterUnit2,CN=IntermediateCA2_9/emailAddress=intermediate29@example.com
Validity
Not Before: Jul 23 09:47:54 2024 GMT
Not After : Jul 23 09:47:54 2025 GMT
Subject: C=US,ST=ServerState,L=ServerCity,O=ServerOrganization,OU=ServerUnit,CN=Server9/emailAddress=server9@example.com
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Digest:
Public Key size: 4096
Ocsp Response Status: NONE
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
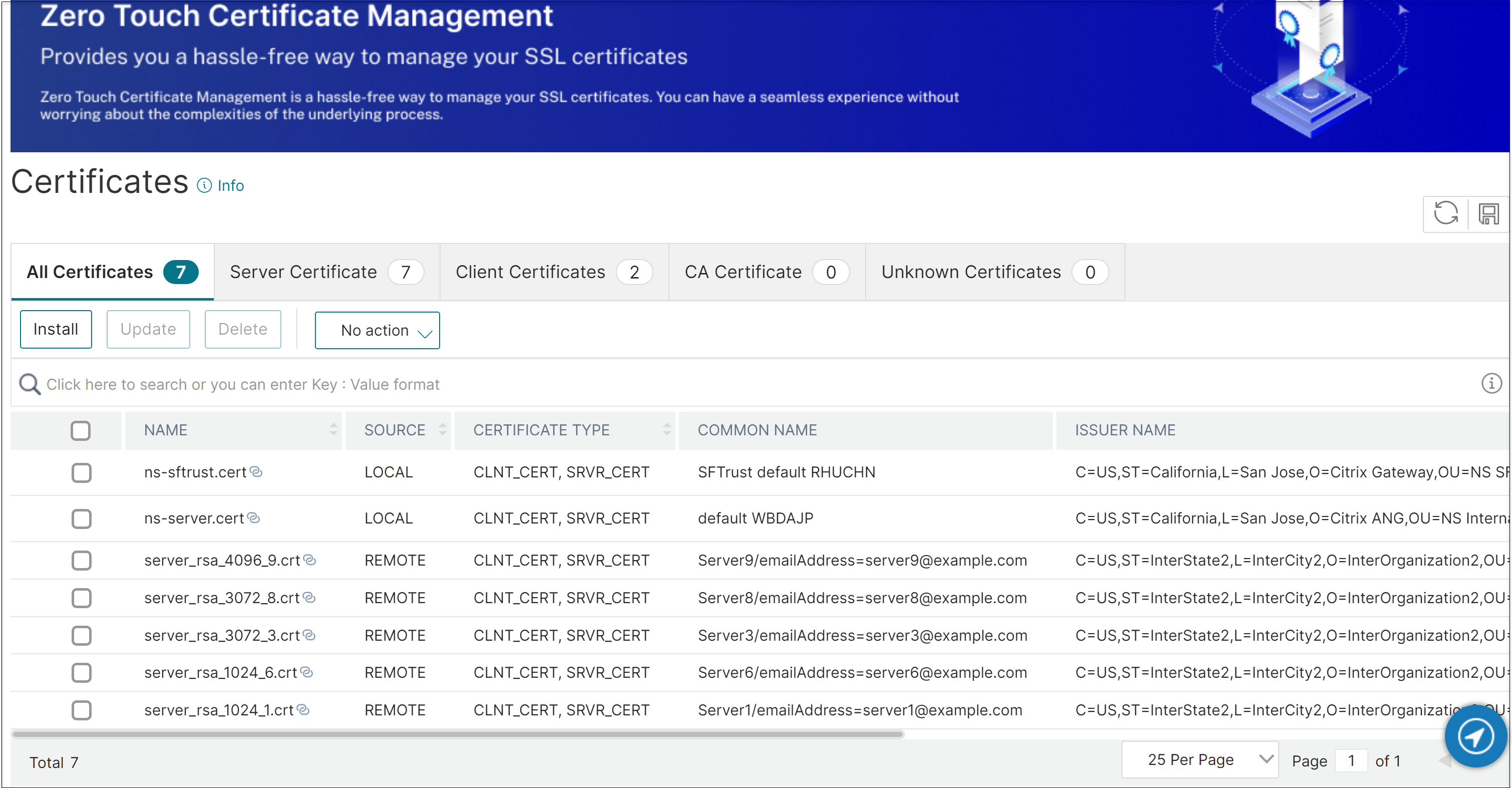
To view the certificate source using the GUI
-
Navigate to Traffic Management > SSL > Certificates
-
On the Certificates page, the list of certificates and keys is displayed along with the source.
Restrict virtual servers with a limited domain
The virtual servers configured on NetScaler can access all the domains using the server certificates uploaded in NetScaler Console. You have the option to restrict access by configuring the virtual server with a limited domain.
Restrict the virtual servers with a limited domain by using CLI
At the command prompt, type:
add policy patset <name> [-patsetFile <string>]
bind policy patset <name> <string> [-index <positive_integer>]
add ssl policy <name> -rule <expression>
bind ssl vserver <vServerName> (-policyName <string> [-priority <positive_integer>] [-type <type>])
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add policy patset pat_sni_list
bind policy patset pat_sni_list abc.com -index 1
bind policy patset pat_sni_list xyz.com -index 2
bind policy patset pat_sni_list example.com -index 3
add ssl policy pol_ssl_sni_allowed -rule "client.ssl.client_hello.sni.equals_any(\"pat_sni_list\").not" -action RESET
bind ssl vserver v1 -policyName pol_ssl_sni_allowed -priority 1 -type CLIENTHELLO_REQ
<!--NeedCopy-->
Restrict the virtual servers with a limited domain by using the GUI
-
Create the patterns and bind them to the pattern set.
For information on creating and binding, see Configure a pattern set.
-
Configure an SSL policy to restrict virtual servers with a limited domain.
For information on configuring an SSL policy, see Configure an SSL policy by using the GUI.
-
Bind an SSL policy to a virtual server.
For more information, see Bind an SSL policy to a virtual server by using the GUI.
Support for verbose logging in NetScaler for Zero Touch Certificate Management
Zero Touch Certificate Management (ZTCM) is designed as a fully automated, hand-off system. Due to the lack of manual intervention points for tasks like certkey binding, troubleshooting issues (such as certificate serving failures or metadata fetching errors) can be challenging.
To address this, NetScaler introduces comprehensive verbose logging across the ZTCM automated workflow. This feature requires no explicit user configuration and provides granular, real-time diagnostic insight into the ZTCM process.
The following are the benefits:
-
Gain visibility into the automated decisions and logic within the ZTCM workflow.
-
Quickly pinpoint the exact stage where a failure occurred, expediting issue resolution.
Logged Workflow Touchpoints
Verbose logs are generated for successful operations, warnings, and errors at the following critical stages of the ZTCM workflow:
| Category | Description | |
| NetScaler Console Communication | Records periodic polling, synchronization, and the success or failure of fetching certificate and key metadata from NetScaler Console. | |
| Certificate Serving Logic | Detailed tracking of the dynamic certificate selection and serving based on runtime context (for example, SNI matching, non-SNI traffic, client/server authentication). | |
| Automated Lifecycle Tasks | Tracking records for automated processes such as certkey pair generation, certificate chaining, and activation/deactivation status changes. | |
Viewing ZTCM Diagnostic Logs
All verbose ZTCM logs are automatically written to the standard System Log stream.
-
Log Destination: ns.log
-
Log Format: Syslog format
Sample Log Messages
The following examples demonstrate the level of detail available for troubleshooting:
| Scenario | Sample Log Message | |
| Failure while fetching files from the Cert Store (Console Communication) | Sep 25 08:35:43 |
|
| Failure due to certificate filename exceeding the system limit of 64 characters | Sep 25 10:04:30 |
|
| Status: New Zero Touch certificate marked INACTIVE due to the absence of a private key | Sep 25 10:15:04 |
|
| Status: Zero Touch certificate is successfully updated and marked ACTIVE | Sep 25 11:50:51 |
|
Support for HDX or ICA Proxy virtual servers
Zero-touch Certificate Management (ZTCM) feature is now supported on VPN virtual servers. This support currently limited to deployments using the VPN virtual server specifically for HDX or ICA Proxy traffic.
Note:
ZTCM support is not available for Full VPN or clientless VPN use cases. For double-hop deployments, use the configuration setting related to Zero Touch Certificate Management on NetScaler Gateway in the second DMZ.
The Default-SNI configuration is also mandatory in a deployment scenario where a single NetScaler acts as both the VPN front end and the Load Balancing backend. The requirement applies when a NetScaler has a VPN virtual server on the front end (connecting the client) and a load balancing virtual server on the backend (connecting to StoreFront or Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops components).
For more information on Default-SNI configuration, see TLS handshake process.
Limitations
- The Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature is not supported for authentication virtual servers.
- The following features are not supported in the release 14.1 build 34. x:
- CRL
- Admin partition
- All NetScaler devices managed by a single NetScaler Console have access to all the certificates in the zero-touch certificate store.
- If the NetScaler Console is configured with IPv6, the certificate fetcher is unable to communicate with it.
- The Zero-Touch Certificate Management feature cannot be enabled in MPX 14 K(N3 FIPS) and SDX 14 K(N3 FIPS).
In this article
- Benefits of Zero-Touch Certificate Management
- How it works
- Certificates states in NetScaler
- CA certificate management
- TLS handshake process
- View the certificate and key list
- Restrict virtual servers with a limited domain
- Support for verbose logging in NetScaler for Zero Touch Certificate Management
- Support for HDX or ICA Proxy virtual servers
- Limitations