This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
How HTML5 works
HTML5 uses HTTP, which is a request/response protocol for communication between clients and servers. A client initiates a TCP connection and uses it to send HTTP requests to the server. The server responds to these requests by granting access rights for the available resources. After the client and server establish a connection, the messages exchanged between them contain only WebSocket headers, not HTTP headers.
The infrastructure of HTML5 consists of WebSockets, which further use the existing HTTP infrastructure to provide a lightweight mechanism for communication between a client and a web server. You typically implement the WebSocket protocol in a browser and web servers. However, you can use this protocol with any client or server application.
When a client attempts to make a connection using WebSockes, web servers treat the WebSocket handshake as an upgrade request, and the server switches to the WebSocket protocol. The WebSocket protocol enables frequent interaction between the browser and the web servers. Therefore, you can use this protocol for live updates, such as stock indexes and score cards, and even live games. This is possible because of a standardized way for the server to send unsolicited responses to the client while maintaining an open connection for two-way ongoing communication between the client browser and the server.
Note
You can also achieve this effect, in non-standardized ways, by using various other technologies, such as Comet. For more information about Comet, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comet_(programming).
The WebSocket protocol communicates over TCP ports 80 and 443. This facilitates communication in environments that use firewalls to block non-web Internet connections. Additionally, WebSocket has its own fragmentation mechanism. A WebSocket message can be sent as multiple WebSocket frames.
Note
You cannot use WebSocket if the web applications on the servers do not support it.
How HTML5 establishes a webSocket session
A browser supporting HTML5 uses JavaScript APIs to perform the following tasks:
-
Open a WebSocket connection.
-
Communicate over the WebSocket connection.
-
Close the WebSocket connections.
To open a WebSocket connection, the browser sends an HTTP upgrade message to the server for switching to the WebSocket protocol. The server either accepts or rejects this request. Following are snippets of a sample client request and server response:
-
Sample client request
pre codeblock GET /HTTP/1.1 Upgrade: websocket Sec-websocket-protocol: <List of protocols that the client supports over this websocket session, such as an application level protocol, for example ICA.> Sec-websocket-extensions: <List of extensions client wants applied to this session, such as compression.> Sec-Websocket-version: <Version of websocket protocol that the client intends to use.> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Sample server response
pre codeblock HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-Websocket-Protocol: <One from the list of protocols in the client request.> Sec-Websocket-extensions: <List of extensions server accepts for session.> Sec-Websocket-version: <Version of websocket protocol that the server supports.> <!--NeedCopy-->
The following figure shows the sequence of messages exchanged between a client and a server:
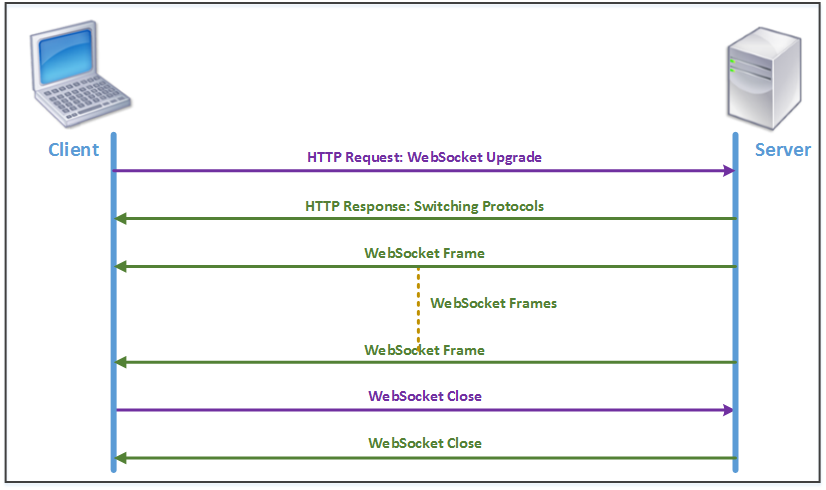
During an HTML5 connection, the following messages are exchanged between the client and the server:
- Client sends an HTTP request to upgrade WebSocket.
- Server responds to the client request and switches to WebSocket protocol.
- Server sends WebSocket frames to the client.
- Client sends a request to close the WebSocket.
- Server closes the WebSocket.
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.