An overview of NetScaler kerberos SSO
To use the NetScaler Kerberos SSO feature, users first authenticate with Kerberos or a supported third-party authentication server. Once authenticated, the user requests access to a protected web application. The web server responds with a request for proof that the user is authorized to access that web application. The user’s browser contacts the Kerberos server, which verifies that the user is authorized to access that resource, and then provides the user’s browser with a service ticket that provides proof. The browser resends the user’s request to the web application server with the service ticket attached. The web application server verifies the service ticket, and then allows the user to access the application.
Authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management implements this process as shown in the following diagram. The diagram illustrates the flow of information through the NetScaler appliance and authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management, on a secure network with LDAP authentication and Kerberos authorization. Authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management environments that use other types of authentication have essentially the same information flow, although they might differ in some details.
Figure 1. A Secure Network with LDAP and Kerberos
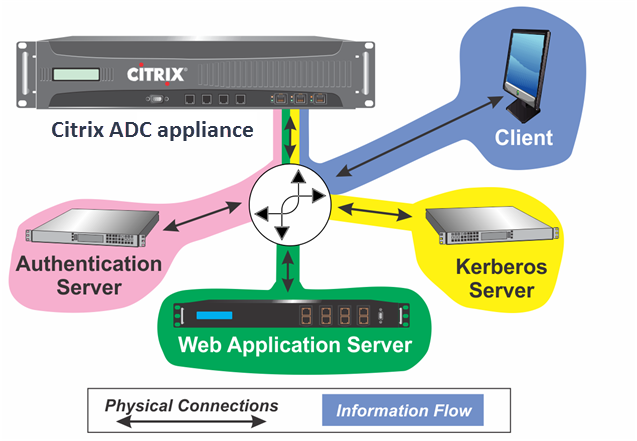
The authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management with authentication and authorization in a Kerberos environment requires that the following actions take place.
- The client sends a request for a resource to the traffic management virtual server on the NetScaler appliance.
- The traffic management virtual server passes the request to the authentication virtual server, which authenticates the client and then passes the request back to the traffic management virtual server.
- The traffic management virtual server sends the client’s request to the web application server.
- The web application server responds to the traffic management virtual server with a 401 Unauthorized message that requests Kerberos authentication, with fallback to NTLM authentication if the client does not support Kerberos.
- The traffic management virtual server contacts the Kerberos SSO daemon.
- The Kerberos SSO daemon contacts the Kerberos server and obtains a ticket-granting ticket (TGT) allowing it to request service tickets authorizing access to protected applications.
- The Kerberos SSO daemon obtains a service ticket for the user and sends that ticket to the traffic management virtual server.
- The traffic management virtual server attaches the ticket to the user’s initial request and sends the modified request back to the web application server.
- The web application server responds with a 200 OK message.
These steps are transparent to the client, which just sends a request and receives the requested resource.
Integration of NetScaler Kerberos SSO with authentication methods
All authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management authentication mechanisms support NetScaler Kerberos SSO. Authentication, authorization, and auditing traffic management supports the Kerberos SSO mechanism with the Kerberos, CAC (Smart Card) and SAML authentication mechanisms with any form of client authentication to the NetScaler appliance. It also supports the HTTP-Basic, HTTP-Digest, Forms-based, and NTLM (versions 1 and 2) SSO mechanisms if the client uses either HTTP-Basic or Forms-Based authentication to log on to the NetScaler appliance.
The following table shows each supported client-side authentication method, and the supported server-side authentication method for that client-side method.
Table 1. Supported Authentication Methods
| Basic/Digest/NTLM | Kerberos Constrained Delegation | User Impersonation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAC (Smart Card): at SSL/T LS Layer | X | X | |
| Forms-Based (LDAP/RADIUS/TACACS) | X | X | X |
| HTTP Basic (LDAP/RADIUS/TACACS) | X | X | X |
| Kerberos | X | ||
| NT LM v1/v2 | X | X | |
| SAML | X | ||
| SAML Two-Factor | X | X | X |
| Certificate Two-Factor | X | X | X |