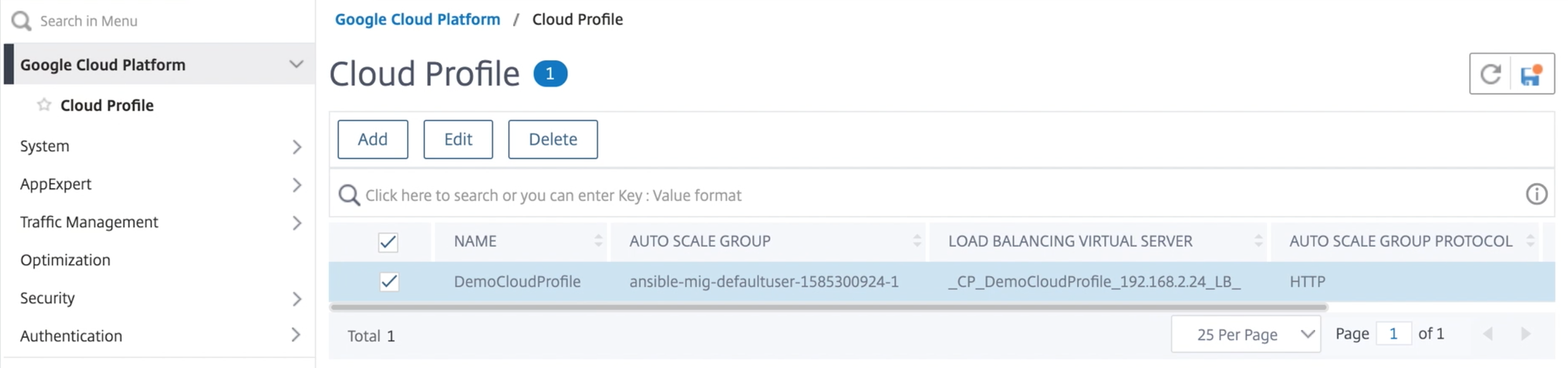
Add back-end GCP Autoscaling service
Efficient hosting of applications in a cloud requires easy and cost-effective management of resources, depending on the application demand. To meet the increasing demand, you have to scale network resources upward. When demand subsides, you need to scale down to avoid the unnecessary cost of underutilized resources. To minimize the cost of running the application, you have to constantly monitor traffic, memory and CPU use, and so on. However, monitoring traffic manually is cumbersome. For the application environment to scale up or down dynamically, you must automate the processes of monitoring traffic and of scaling resources up and down whenever necessary.
Integrated with the GCP Autoscaling service, the NetScaler VPX instance provides the following advantages:
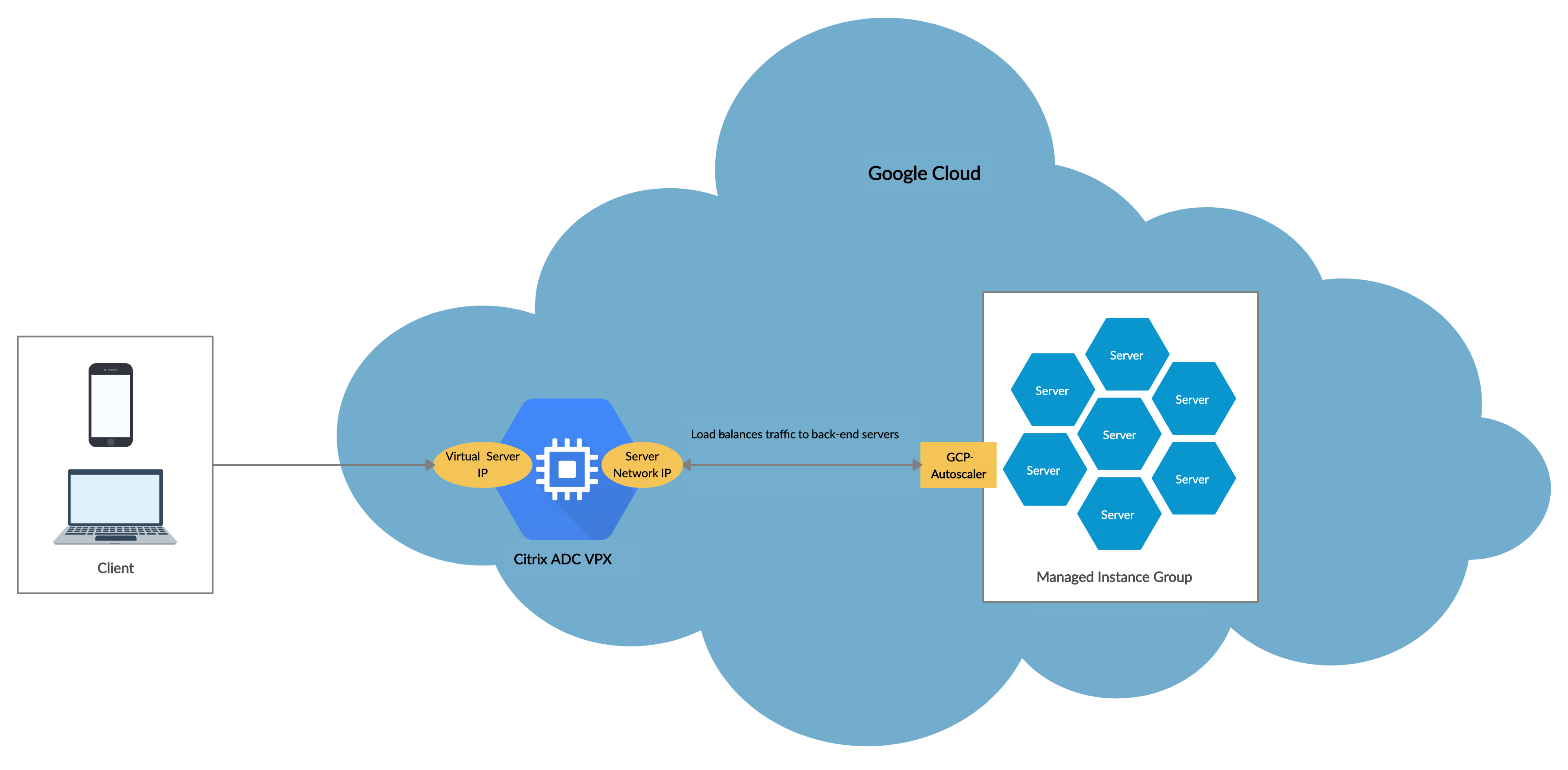
- Load balance and management: Auto configures servers to scale up and scale down, depending on demand. The VPX instance auto detects managed instance groups in the back-end subnet and allows you to select the managed instance groups to balance the load. The virtual and subnet IP addresses are auto configured on the VPX instance.
- High availability: Detects managed instance groups that span multiple zones and load-balance servers.
-
Better network availability: The VPX instance supports:
- Back-end servers on same placement groups
- Back-end servers on different zones
This diagram illustrates how the GCP Autoscaling service works in a NetScaler VPX instance acting as the load balancing virtual server.
Before you begin
Before you start using Autoscaling with your NetScaler VPX instance, you must complete the following tasks.
-
Create a NetScaler VPX instance on GCP according to your requirement.
- For more information about how to create a NetScaler VPX instance, see Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on the Google Cloud Platform.
- For more information about how to deploy VPX instances in HA mode, see Deploy a VPX high-availability pair on the Google Cloud Platform.
-
Enable Cloud Resource Manager API for your GCP project.
-
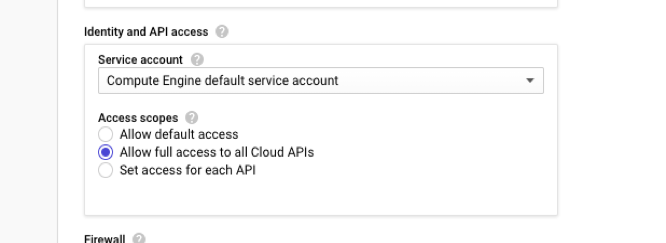
Allow full access to all Cloud APIs while creating the instances.
-
Make sure that your GCP service account has the following IAM permissions:
REQUIRED_INSTANCE_IAM_PERMS = [ "compute.instances.get", "compute.instanceGroupManagers.get", "compute.instanceGroupManagers.list", "compute.zones.list", "logging.sinks.create", "logging.sinks.delete", "logging.sinks.get", "logging.sinks.list", "logging.sinks.update", "pubsub.subscriptions.consume", "pubsub.subscriptions.create", "pubsub.subscriptions.delete", "pubsub.subscriptions.get", "pubsub.topics.attachSubscription", "pubsub.topics.create", "pubsub.topics.delete", "pubsub.topics.get", "pubsub.topics.getIamPolicy", "pubsub.topics.setIamPolicy", ] <!--NeedCopy--> -
To set up Autoscaling, ensure the following are configured:
- Instance template
- Managed Instance group
- Autoscaling policy
Add the GCP Autoscaling service to a NetScaler VPX instance
You can add the Autoscaling service to a VPX instance with a single click by using the GUI. Complete these steps to add the Autoscaling service to the VPX instance:
-
Log on to the VPX instance by using your credentials for
nsroot. -
When you log on to the NetScaler VPX instance for the first time, you see the default Cloud Profile page. Select the GCP managed instance group from the drop-down menu and click Create to create a cloud profile.
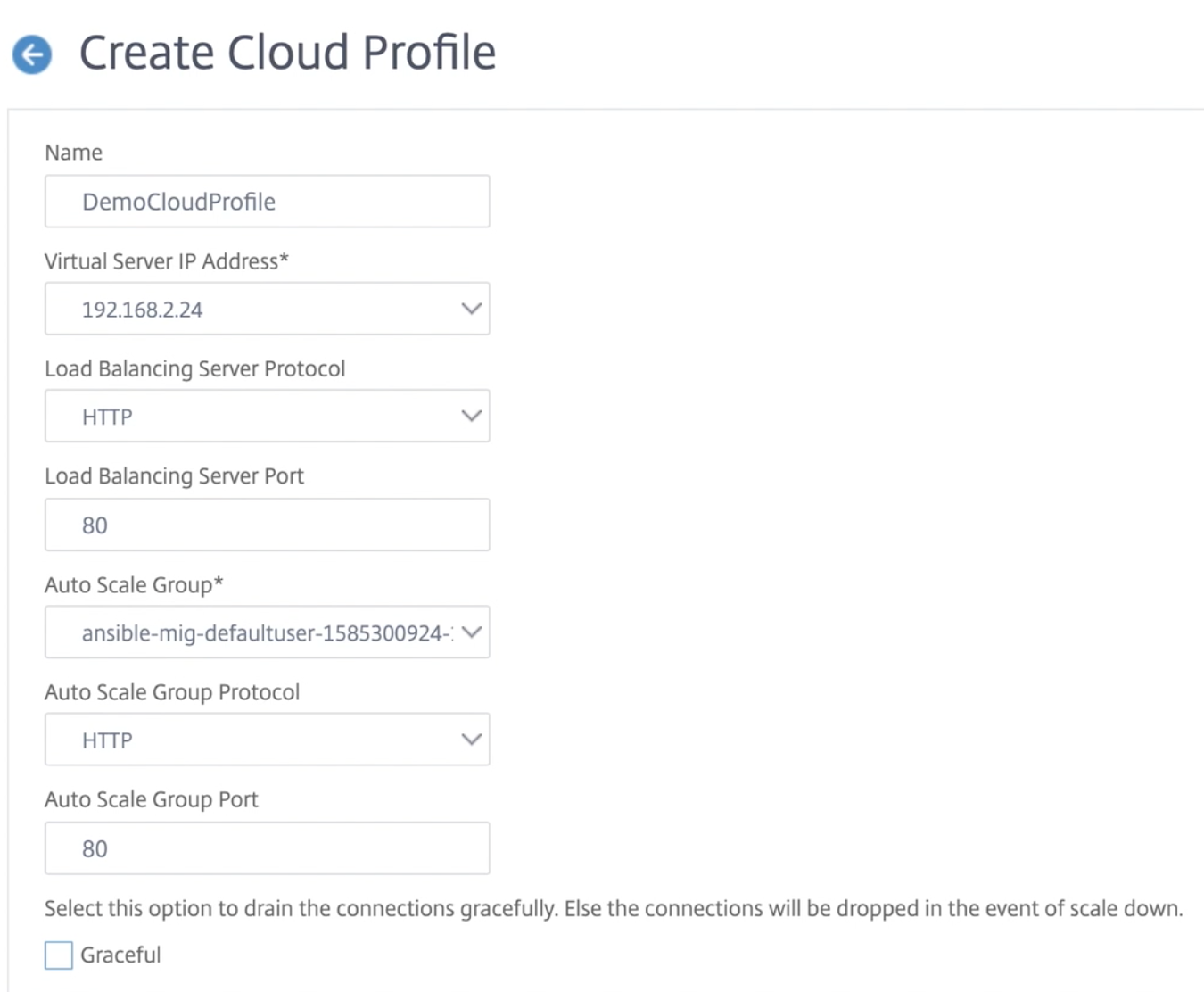
- The Virtual Server IP Address field is auto-populated from all the IP addresses associated with the instances.
- The Autoscale™ Group is prepopulated from the managed instance group configured on your GCP account.
- When selecting the Autoscale Group Protocol and Autoscale Group Port, ensure that your servers listen on the configured protocol and ports. Bind the correct monitor in the service group. By default, the TCP monitor is used.
- Clear the Graceful checkbox because it is not supported.
Note:
For SSL Protocol type Autoscaling, after you create the Cloud Profile, the load balance virtual server or service group is down because of a missing certificate. You can bind the certificate to the virtual server or service group manually.
-
After the first time logon if you want to create Cloud Profile, on the GUI go to System > Google Cloud Platform > Cloud Profile and click Add.
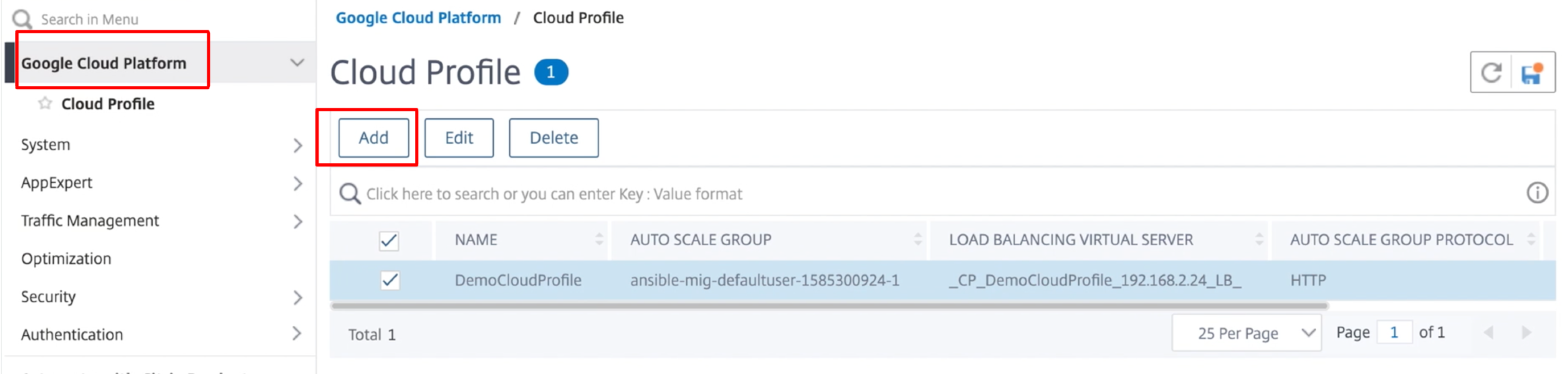
The Create Cloud Profile configuration page appears.

Cloud Profile creates a NetScaler load-balancing virtual server and a service group with members as the servers of the managed instance group. Your back-end servers must be reachable through the SNIP configured on the VPX instance.
Note:
From NetScaler release 13.1-42.x onwards, you can create different cloud profiles for different services (using different ports) with the same managed instance group in GCP. Thus, the NetScaler VPX instance supports multiple services with the same Autoscaling group in public cloud.