This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Group Mode
In group mode, two or more appliances become a single virtual appliance. This mode is one solution to the problem of asymmetric routing, which is defined as any case in which some packets in a given connection pass through a given appliance but others do not. A limitation of the appliance architecture is that acceleration cannot take place unless all packets in a given connection pass through the same two appliances. Group mode overcomes this limitation.
Group mode can be used with multiple or redundant links without reconfiguring your routers.
Note
Group mode is not supported on the SD-WAN 4000 or 5000 appliances.
Group mode applies only to the appliances on one side of the WAN link; the local appliances neither know nor care whether the remote appliances are using group mode.
Group mode uses a heartbeat mechanism to verify that other members of the group are active. Packets are forwarded to active group members only.
Avoiding asymmetric routing is the main reason to use group mode, but group mode is not the only method available for that purpose. If you decide that it is the best method for your environment, you can enable it by setting a few parameters. If the default mechanism for determining which appliance is responsible for a particular connection does not provide optimal acceleration, you can change the forwarding rules.
Figure 1. Group Mode With Redundant Links
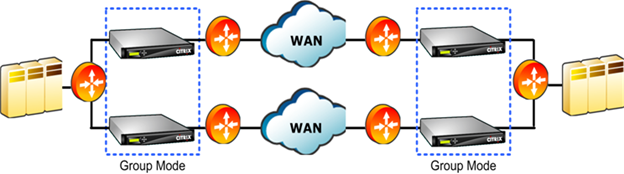
Figure 2. Group Mode With Non-Redundant Links with Possible Asymmetric Routing
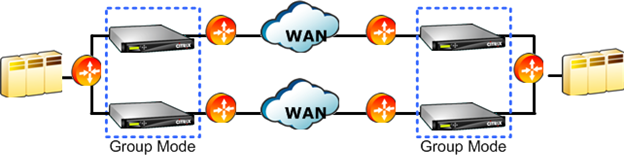
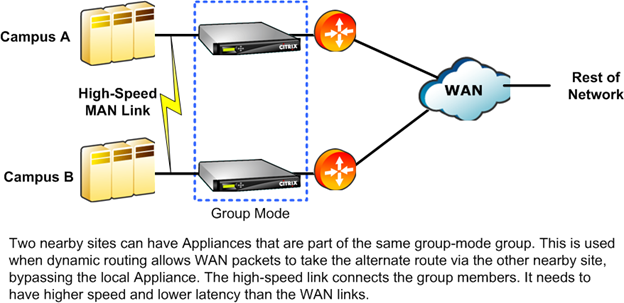
Figure 3. Group Mode On Nearby Campuses
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.