Configuring SNMP on SDX Appliances
You can configure an SNMP agent on the NetScaler SDX appliance to generate asynchronous events, which are called traps. The traps are generated whenever there are abnormal conditions on the SDX appliance. The traps are then sent to a remote device called a trap listener, which signals the abnormal condition on the SDX appliance.
In addition to configuring an SNMP trap destination, downloading MIB files, and configuring one or more SNMP managers, you can configure the NetScaler SDX appliance for SNMPv3 queries.
The following figure illustrates a network with an SDX appliance that has SNMP enabled and configured. In the figure, each SNMP network management application uses SNMP to communicate with the SNMP agent on the SDX appliance.
Figure 1. SDX Appliance Supporting SNMP
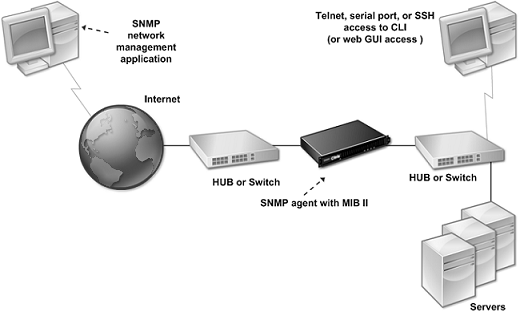
The SNMP agent on the SDX appliance generates traps that are compliant with SNMPv2 only. The supported traps can be viewed in the SDX MIB file. You can download this file from the Downloads page in the SDX user interface.
To add an SNMP trap destination
-
On the configuration tab, in the navigation pane, expand System > SNMP, and then click SNMP Trap Destinations.
-
In the SNMP Trap Destinations pane, click Add.
-
In the Configure SNMP Trap Destination page, specify values for the following parameters:
- Destination Server—IPv4 address of the trap listener to which to send the SNMP trap messages.
- Port—UDP port at which the trap listener listens for trap messages. Must match the setting on the trap listener, or the listener drops the messages. Minimum value: 1. Default: 162.
- Community—Password (string) sent with the trap messages, so that the trap listener can authenticate them. Can include letters, numbers, and hyphen (-), period (.) hash (#), space ( ), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters. Note: Specify the same community string on the trap listener device, or the listener drops the messages. Default: public.
-
Click Add, and then click Close. The SNMP trap destination that you added appears in the SNMP Traps pane.
To modify the values of the parameters of an SNMP trap destination, in the SNMP Trap Destinations pane, select the trap destination that you want to modify, and then click Modify. In the Modify SNMP Trap Destination dialog box, modify the parameters.
To remove an SNMP trap, in the SNMP Trap Destinations pane, select the trap destination that you want to remove, and then click Delete. In the Confirm message box, click to remove the SNMP trap destination.
Downloading MIB Files
You must download the following file before you start monitoring an SDX appliance.
SDX-MIB-smiv2.mib. This file is used by SNMPv2 managers and SNMPv2 trap listeners.
The file includes a NetScaler enterprise MIB that provides SDX-specific events.
To download MIB files
- Log on to the Downloads page of the SDX appliance user interface.
- Under SNMP Files, click SNMP v2 - MIB Object Definitions. You can open the file by using a MIB browser.
Adding an SNMP Manager Community
Configure SNMP managers on the SDX appliance to query and monitor the appliance and managed devices hosted on the appliance. Also, you must provide the SNMP manager with the required appliance-specific information. For an IPv4 SNMP manager you can specify a host name instead of the manager’s IP address. If you do so, you must add a DNS name server that resolves the host name of the SNMP manager to its IP address.
Configure at least one SNMP manager. If you do not configure an SNMP manager, the appliance does not accept or respond to SNMP queries from any IP address on the network. If you configure one or more SNMP managers, the appliance accepts and responds only to SNMP queries from those specific IP addresses.
To configure an SNMP manager
- On the Configuration tab, in the navigation pane, expand System, and then expand SNMP.
- Click Managers.
- In the details pane, click Add.
- In the Create SNMP Manager Community page, set the following parameters:
- SNMP Manager—IPv4 address of the SNMP manager. Alternatively, instead of an IPv4 address, you can specify a host name that has been assigned to an SNMP manager. If you do so, you must add a DNS name server that resolves the host name of the SNMP manager to its IP address.
- Community—The SNMP community string. Can consist of 1 to 31 characters that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-), period (.) pound (#), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters.
- Select the Enable Management Network check box to specify the SNMP managers by using the netmask.
- In the Netmask field, enter the netmask of the SNMP community.
- Click Add, and then click Close.
Configuring the SDX Appliance for SNMPv3 Queries
SNMPv3 is based on the basic structure and architecture of SNMPv1 and SNMPv2. However, SNMPv3 enhances the basic architecture to incorporate administration and security capabilities, such as authentication, access control, data integrity check, data origin verification, message timeliness check, and data confidentiality.
The NetScaler SDX appliance supports the following entities that enable you to implement the security features of SNMPv3:
- SNMP Views
- SNMP Users
These entities function together to implement the SNMPv3 security features. Views are created to allow access to subtrees of the MIB.
Adding an SNMP Manager
Configure the SDX appliance to allow the appropriate SNMP managers to query it. Also provide the SNMP manager with the required appliance-specific information. For an IPv4 SNMP manager you can specify a host name instead of the manager’s IP address. If you do so, you must add a DNS name server that resolves the host name of the SNMP manager to its IP address.
Configure at least one SNMP manager. If you do not configure an SNMP manager, the appliance does not accept or respond to SNMP queries from any IP address on the network. If you configure one or more SNMP managers, the appliance accepts and responds only to SNMP queries from those specific IP addresses.
To configure an SNMP manager:
- Navigate to the System > Configuration page.
- On the Configuration tab, in the navigation pane, expand System, and then expand SNMP.
- Click Managers.
- In the details pane, click Add.
- In the Add SNMP Manager Community dialog box, set the following parameters:
- SNMP Manager—IPv4 address of the SNMP manager. Alternatively, instead of an IPv4 address, you can specify a host name that has been assigned to an SNMP manager. If you do so, you must add a DNS name server that resolves the host name of the SNMP manager to its IP address.
- Community—The SNMP community string. Can consist of 1 to 31 characters that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-), period (.) pound (#), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters.
- Click Add, and then click Close.
Configuring an SNMP View
SNMP views restrict user access to specific portions of the MIB. SNMP views are used to implement access control.
To configure a view
- On the Configuration tab, in the navigation pane, expand System, and then expand SNMP.
- Click Views.
- In the details pane, click Add.
- In the Add SNMP View dialog box, set the following parameters:
- Name—Name for the SNMPv3 view. Can consist of 1–31 characters that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-), period (.) pound (#), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters. Choose a name that helps identify the SNMPv3 view.
- Subtree—A particular branch (subtree) of the MIB tree, which you want to associate with this SNMPv3 view. Specify the subtree as an SNMP OID.
- Type—Include or exclude the subtree, specified by the subtree parameter, in or from this view. This setting can be useful when you have included a subtree, such as A, in an SNMPv3 view and you want to exclude a specific subtree of A, such as B, from the SNMPv3 view.
Configuring an SNMP User
After you have created an SNMP view, add SNMP users. SNMP users have access to the MIBs that are required for querying the SNMP managers.
To configure a user
- On the Configuration tab, in the navigation pane, expand System, and then expand SNMP.
- Click Users.
- In the details pane, click Add.
- In the Create SNMP User page, set the following parameters:
- Name—Name for the SNMPv3 user. Can consist of 1–31 characters that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-), period (.) pound (#), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters.
- Security Level—Security level required for communication between the appliance and the SNMPv3 users. Select from one of the following options:
- noAuthNoPriv—Require neither authentication nor encryption.
- authNoPriv—Require authentication but no encryption.
- authPriv—Require authentication and encryption.
- Authentication Protocol—Authentication algorithm used by the appliance and the SNMPv3 user for authenticating the communication between them. Specify the same authentication algorithm when you configure the SNMPv3 user in the SNMP manager.
- Authentication Password—Pass phrase to be used by the authentication algorithm. Can consist of 1–31 characters that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-), period (.) pound (#), space ( ), at (@), equals (=), colon (:), and underscore (_) characters.
- Privacy Protocol—Encryption algorithm used by the appliance and the SNMPv3 user for encrypting the communication between them. Specify the same encryption algorithm when you configure the SNMPv3 user in the SNMP manager.
- View Name—Name of the configured SNMPv3 view that you want to bind to this SNMPv3 user. An SNMPv3 user can access the subtrees that are bound to this SNMPv3 view as type INCLUDED, but cannot access the ones that are type EXCLUDED.
Configuring an SNMP Alarm
The appliance provides a predefined set of condition entities called SNMP alarms. When the condition set for an SNMP alarm is met, the appliance generates SNMP trap messages that are sent to the configured trap listeners. For example, when the deviceAdded alarm is enabled, a trap message is generated and sent to the trap listener whenever a device (instance) is provisioned on the appliance. You can assign a severity level to an SNMP alarm. When you do so, the corresponding trap messages are assigned that severity level.
Following are the severity levels defined on the appliance, in decreasing order of severity:
- Critical
-
Major
- Minor
- Warning
- Informational (default)
For example, if you set a Warning severity level for the SNMP alarm named deviceAdded, the trap messages generated when a device is added are assigned with the Warning severity level.
You can also configure an SNMP alarm to log the corresponding trap messages generated whenever the condition on that alarm is met.
To modify a predefined SNMP alarm, click System > SNMP > Alarms.
Alarm for monitoring discrepancies in Management Service inventory
The Management Service monitors all interfaces and channels within its inventory, checking for discrepancies between the Management Service database, Xen server, and VPX. If any mismatches in channel or interface details are found, it triggers a “VPXInterfacesNotInSync” alarm. This feature is available in versions 14.1-34.x and later.