Configure a NetScaler VPX on ESX hypervisor to use Intel QAT for SSL acceleration in SR-IOV mode
The NetScaler VPX instance on the VMware ESX hypervisor can use the Intel QuickAssist Technology (QAT) to accelerate the NetScaler SSL performance. Using Intel QAT, all heavy-latency crypto processing can be offloaded to the chip thus freeing up one or more host CPUs to do other tasks.
Previously, all NetScaler data path crypto processing was done in the software using host vCPUs.
Note:
Currently, NetScaler VPX supports only the C62x chip model under Intel QAT family. This feature is supported starting from NetScaler release 14.1 build 8.50.
Prerequisites
- The ESX host is provisioned with one or more Intel C62x (QAT) chips.
- NetScaler VPX meets the VMware ESX hardware requirements. For more information, see Install a NetScaler VPX instance on VMware ESX.
Limitations
There’s no provision to reserve crypto units or bandwidth for individual VMs. All the available crypto units of any Intel QAT hardware are shared across all VMs using the QAT hardware.
Set up the host environment for using Intel QAT
-
Download and install the Intel-provided VMware driver for the C62x series (QAT) chip model in the VMware host. For more information on the Intel package downloads and installation instructions, see Intel QuickAssist Technology Driver for VMware.
-
Enable SR-IOV on the ESX host.
-
Create virtual machines. When creating a VM, assign the appropriate number of PCI devices to meet the performance requirements.
Note:
Each C62x (QAT) chip can have up to three separate PCI endpoints. Each endpoint is a logical collection of VFs, and shares the bandwidth equally with other PCI endpoints of the chip. Each endpoint can have up to 16 VFs that show up as 16 PCI devices. You can add these devices to the VM to do the crypto acceleration using the QAT chip.
Points to note
- If the VM crypto requirement is to use more than one QAT PCI endpoint/chip, it’s recommended to pick the corresponding PCI devices/VFs in a round-robin fashion to have a symmetric distribution.
-
It’s recommended that the number of PCI devices picked is equal to the number of licensed vCPUs (without including the management vCPU count). Adding more PCI devices than the available number of vCPUs does not necessarily improve the performance.
Example:
Consider an ESX host with one Intel C62x chip that has 3 endpoints. While provisioning a VM with 6 vCPUs, pick 2 VFs from each endpoint, and assign them to the VM. This kind of assignment ensures an effective and equal distribution of crypto units for the VM. From the total available vCPUs, by default, one vCPU is reserved for the management plane, and the rest of the vCPUs are available for the data plane PEs.
Assign QAT VFs to VPX using the vSphere web client
-
In the vSphere web client, navigate to the ESX host where the virtual machine is located and click Power off.
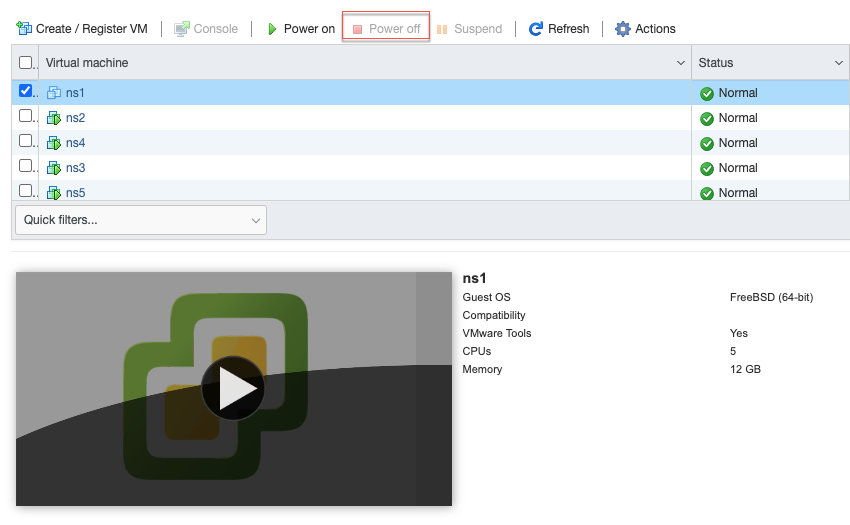
-
Navigate to Actions > Edit settings > Add other device, and select PCI device.
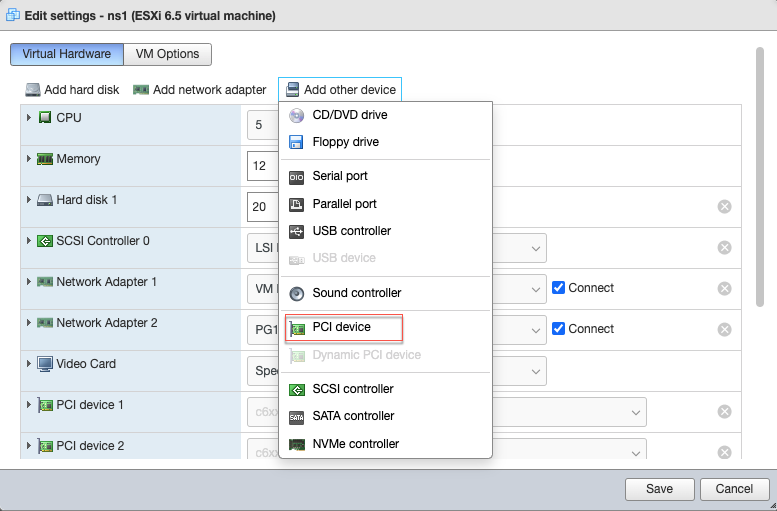
-
For the newly added PCI device, assign the c6xx QAT VF, and save the configuration.
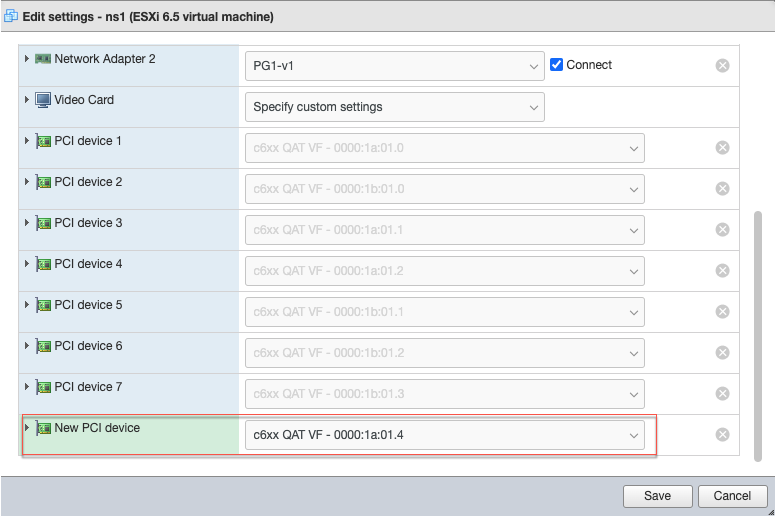
-
Power on the VM again.
-
Run the
stat sslcommand in the NetScaler CLI to display the SSL summary, and verify the SSL cards after assigning QAT VFs to VPX.
About the deployment
This deployment was tested with the following component specifications:
- NetScaler VPX version and build: 14.1–8.50
- VMware ESXi version: 7.0.3 (build 20036589)
- Intel C62x QAT driver version for VMware: 1.5.1.54