Configure AWS IAM roles on NetScaler VPX instance
Applications that run on an Amazon EC2 instance must include AWS credentials in the AWS API requests. You can store AWS credentials directly within the Amazon EC2 instance and allow applications in that instance to use those credentials. But you then have to manage the credentials and ensure that they securely pass the credentials to each instance and update each Amazon EC2 instance when it’s time to rotate the credentials. That’s a lot of additional work.
Instead, you can and must use an Identity and Access Management (IAM) role to manage temporary credentials for applications that run on an Amazon EC2 instance. When you use a role, you don’t have to distribute long-term credentials (such as a user name and password or access keys) to an Amazon EC2 instance. Instead, the role provides temporary permissions that applications can use when they make calls to other AWS resources. When you launch an Amazon EC2 instance, you specify an IAM role to associate with the instance. Applications that run on the instance can then use the role-supplied temporary credentials to sign API requests.
The IAM role associated with your AWS account must have the following IAM permissions for various scenarios.
HA pair with IPv4 addresses in the same AWS zone:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:AssignPrivateIpAddresses",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
HA pair with IPv6 addresses in the same AWS zone:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:AssignIpv6Addresses",
"ec2:UnassignIpv6Addresses",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
HA pair with both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses in the same AWS zone:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:AssignPrivateIpAddresses",
"ec2:AssignIpv6Addresses",
"ec2:UnassignIpv6Addresses",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
HA pair with elastic IP addresses across different AWS zones:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
HA pair with private IP addresses across different AWS zones:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DeleteRoute",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
HA pair with both private IP and elastic IP addresses across different AWS zones:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DeleteRoute",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
AWS backend autoscaling:
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"autoscaling:*",
"sns:CreateTopic",
"sns:DeleteTopic",
"sns:ListTopics",
"sns:Subscribe",
"sqs:CreateQueue",
"sqs:ListQueues",
"sqs:DeleteMessage",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:SetQueueAttributes",
"iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy",
"iam:GetRole"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Points to note:
- If you use any combination of the preceding features, use the combination of IAM permissions for each of the features.
- If you use the Citrix CloudFormation template, the IAM role is automatically created. The template does not allow selecting an already created IAM role.
- When you log on to the VPX instance through the GUI, a prompt to configure the required privileges for the IAM role appears. Ignore the prompt if you’ve already configured the privileges.
- An IAM role is mandatory for both standalone and high availability deployments.
Create an IAM role
This procedure describes how to create an IAM role for the AWS back-end autoscaling feature.
Note:
You can follow the same procedure to create any IAM roles corresponding to other features.
- Log on to the AWS Management Console for EC2.
-
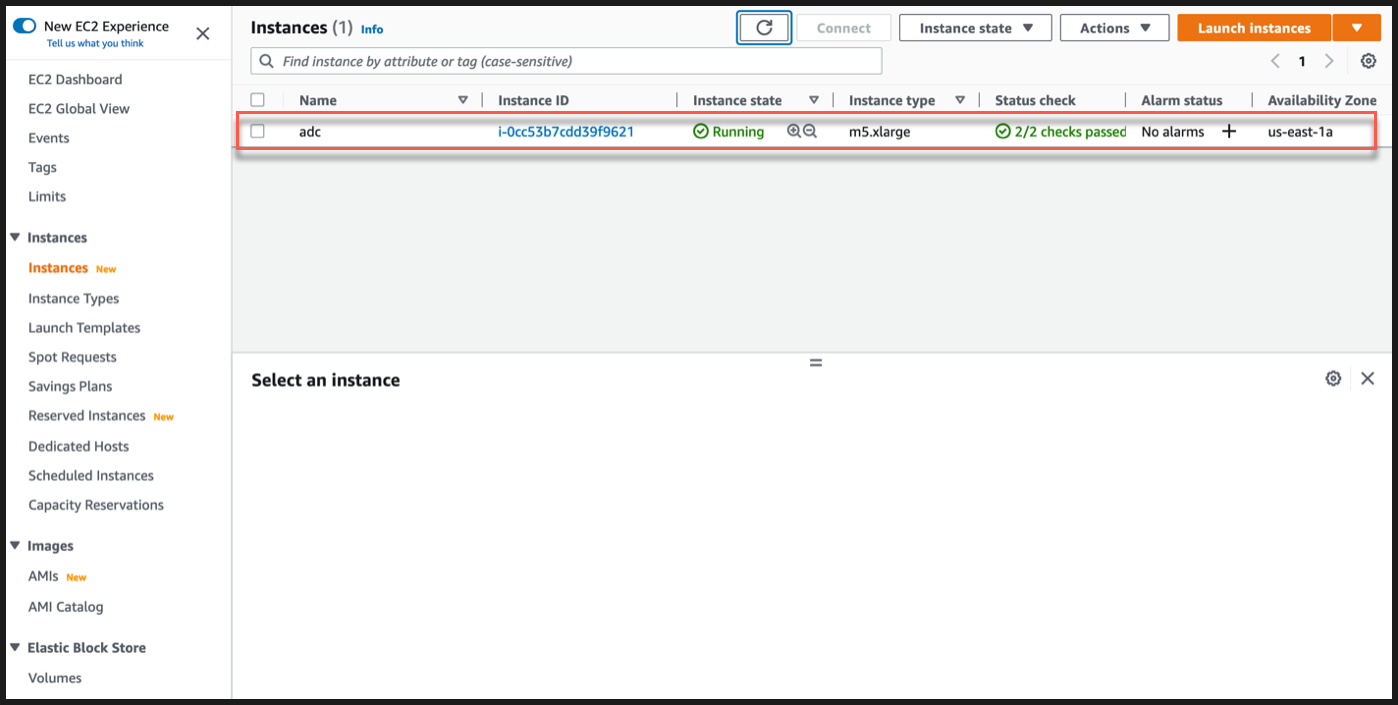
Go to EC2 instance page, and select your ADC instance.
-
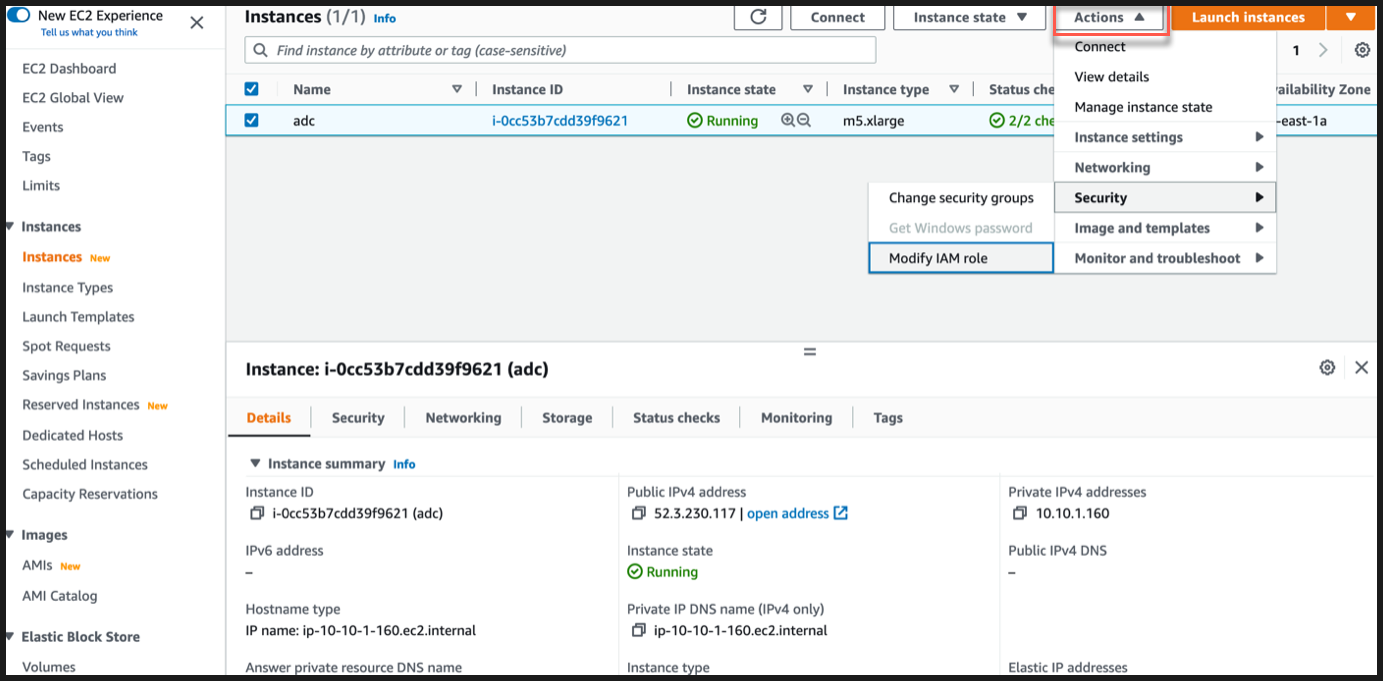
Navigate to Actions > Security > Modify IAM role.
-
In the Modify IAM role page, you can either choose an existing IAM role or create a IAM role.
-
To create a IAM role, follow these steps:
-
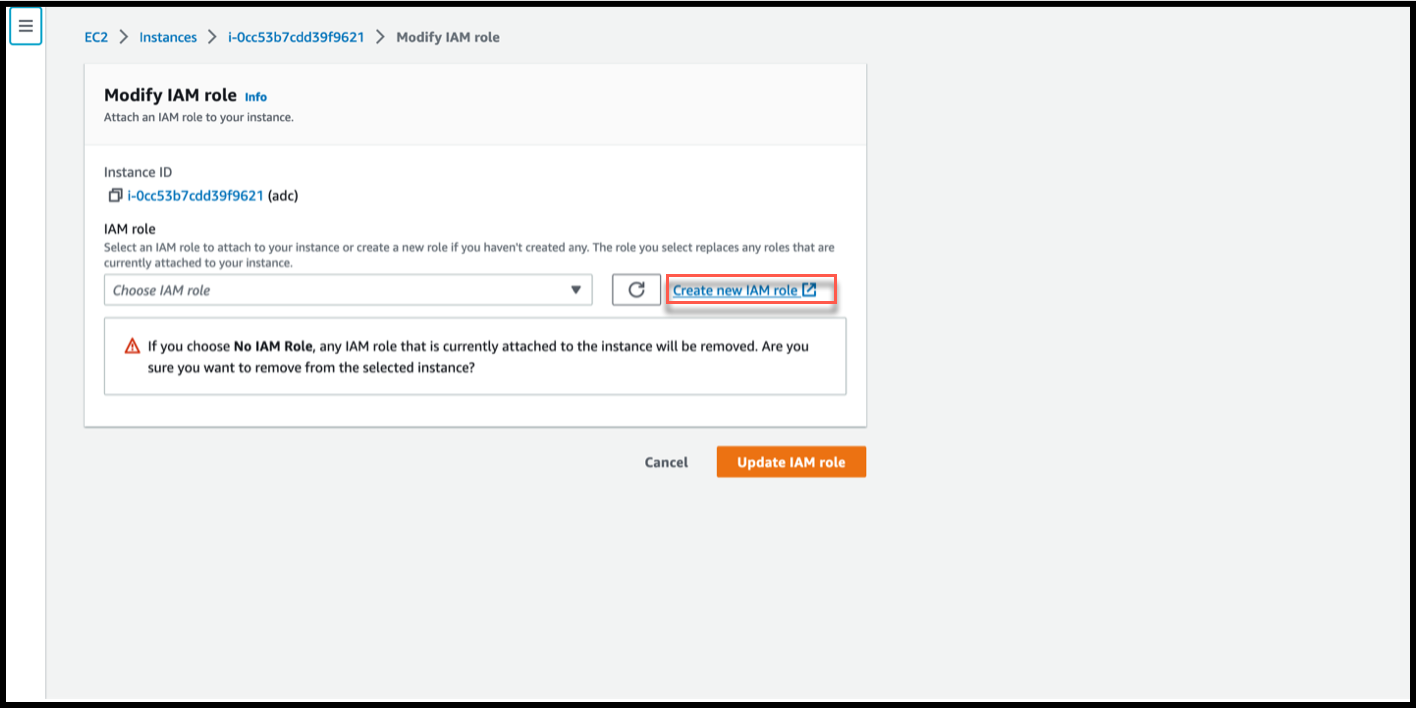
In the Modify IAM role page, click Create new IAM role.
-
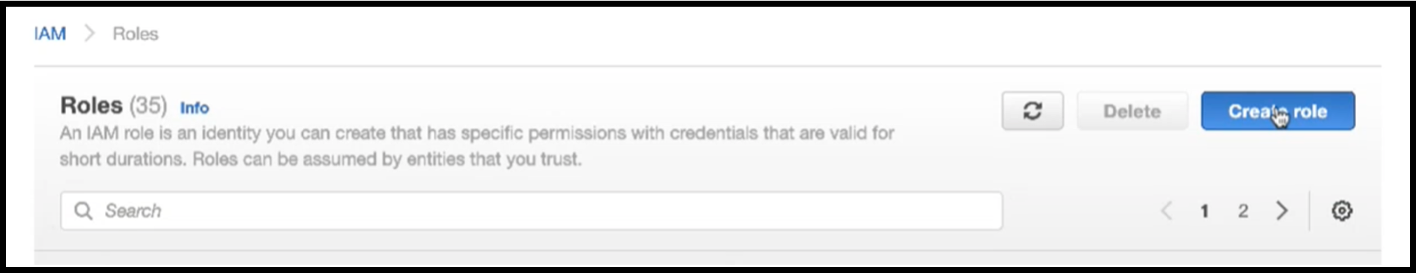
In the Roles page, click Create role.
-
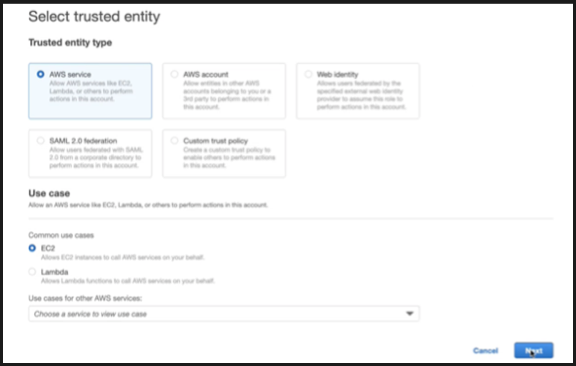
Select AWS service under Trusted entity type and EC2 under Common use cases and then click Next.
-
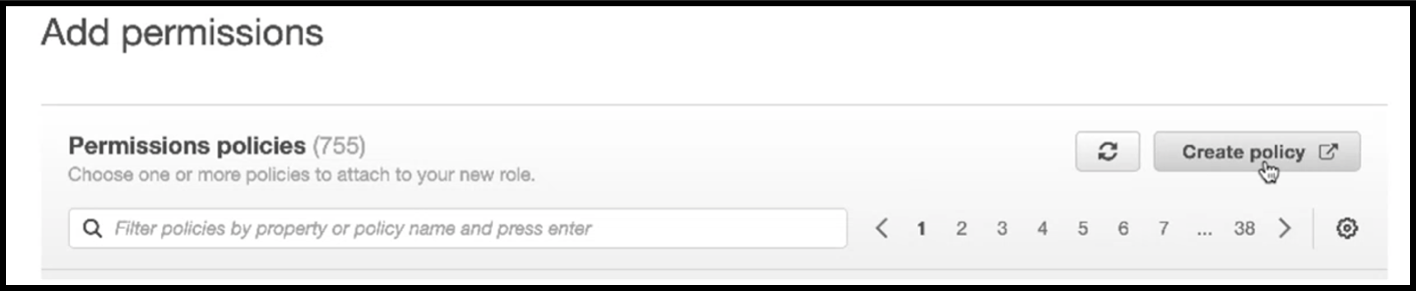
In the Add permissions page, click Create policy.
-
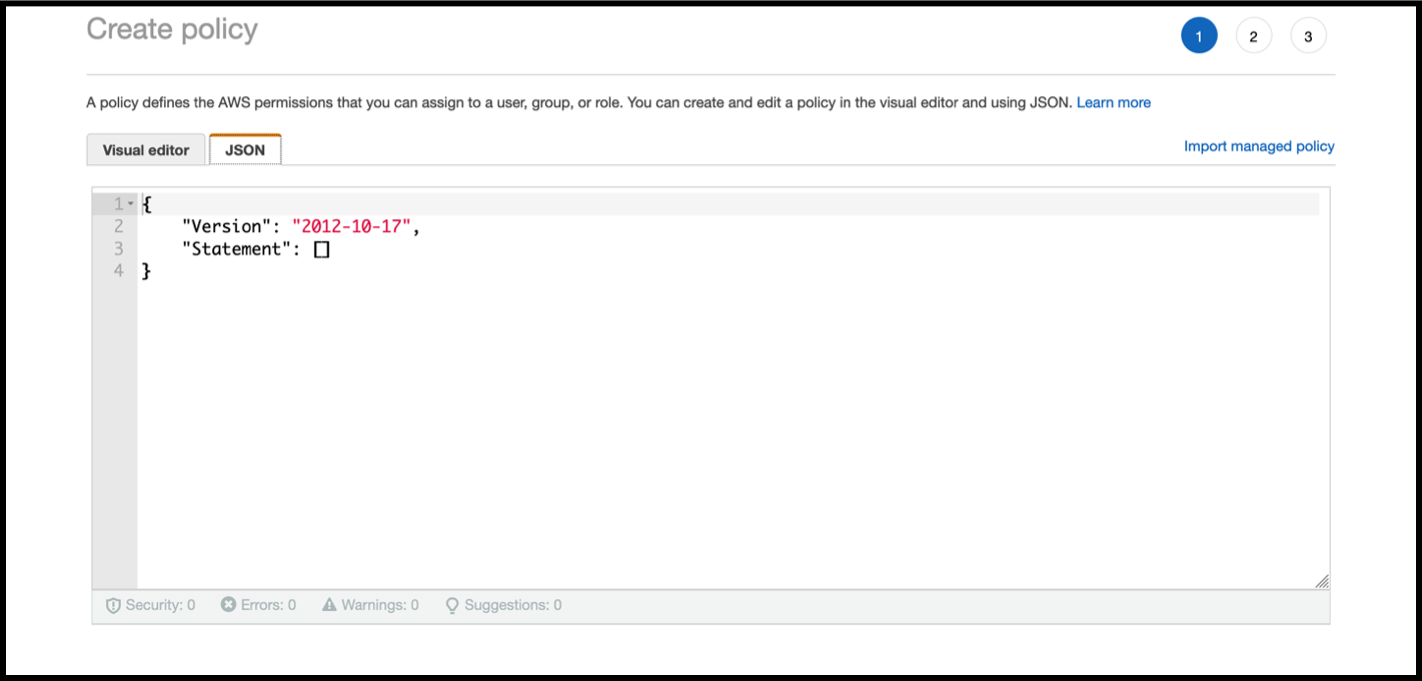
Click the JSON tab to open the JSON editor.
-
In the JSON editor, delete everything and paste the IAM permissions for the feature that you want to use.
For example, paste the following IAM permissions for the AWS back-end autoscaling feature:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:DescribeInstances", "autoscaling:*", "sns:CreateTopic", "sns:DeleteTopic", "sns:ListTopics", "sns:Subscribe", "sqs:CreateQueue", "sqs:ListQueues", "sqs:DeleteMessage", "sqs:GetQueueAttributes", "sqs:SetQueueAttributes", "iam:SimulatePrincipalPolicy", "iam:GetRole" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } <!--NeedCopy-->Ensure that the “Version” key-value pair that you provide is the same as the one automatically generated by AWS.
-
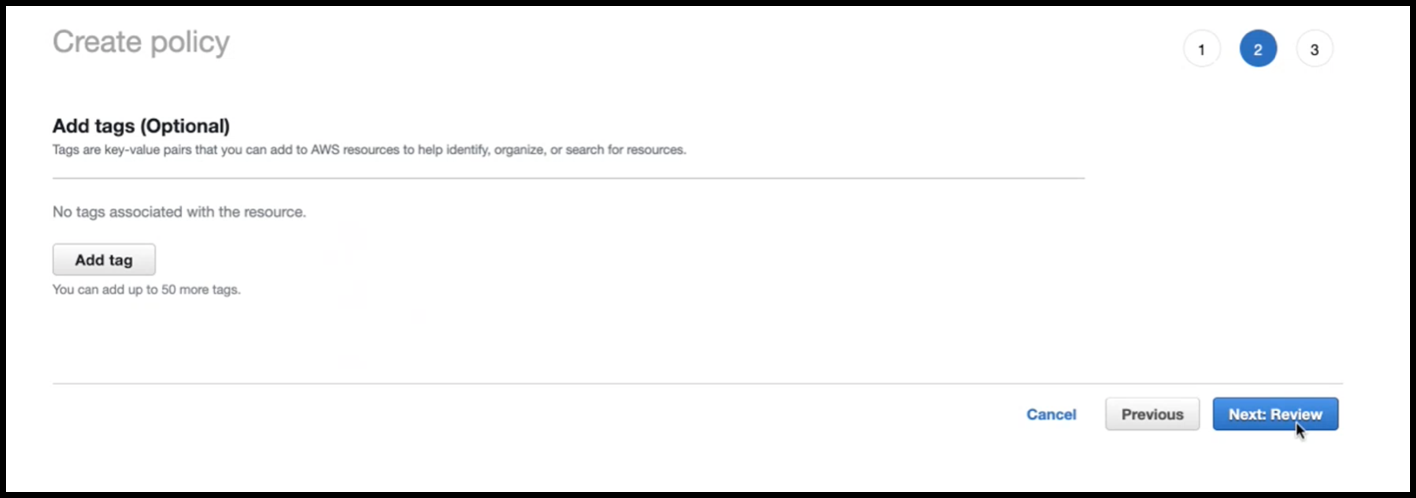
Click Next: Review.
-
In the Review policy tab, give a valid name to the policy, and click Create Policy.
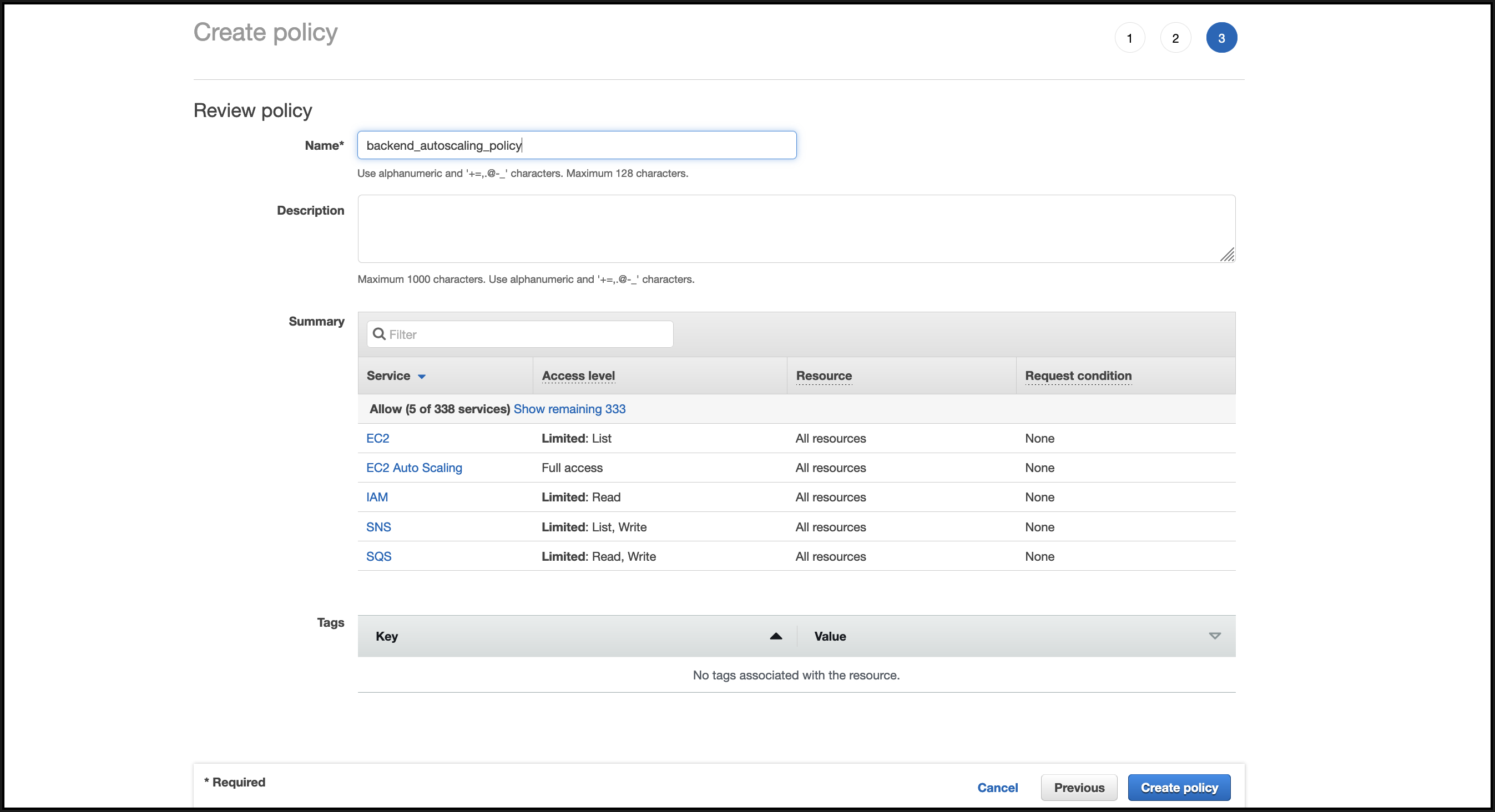
-
In the Identity Access Management page, click the policy name that you created. Expand the policy to check the entire JSON, and click Next.
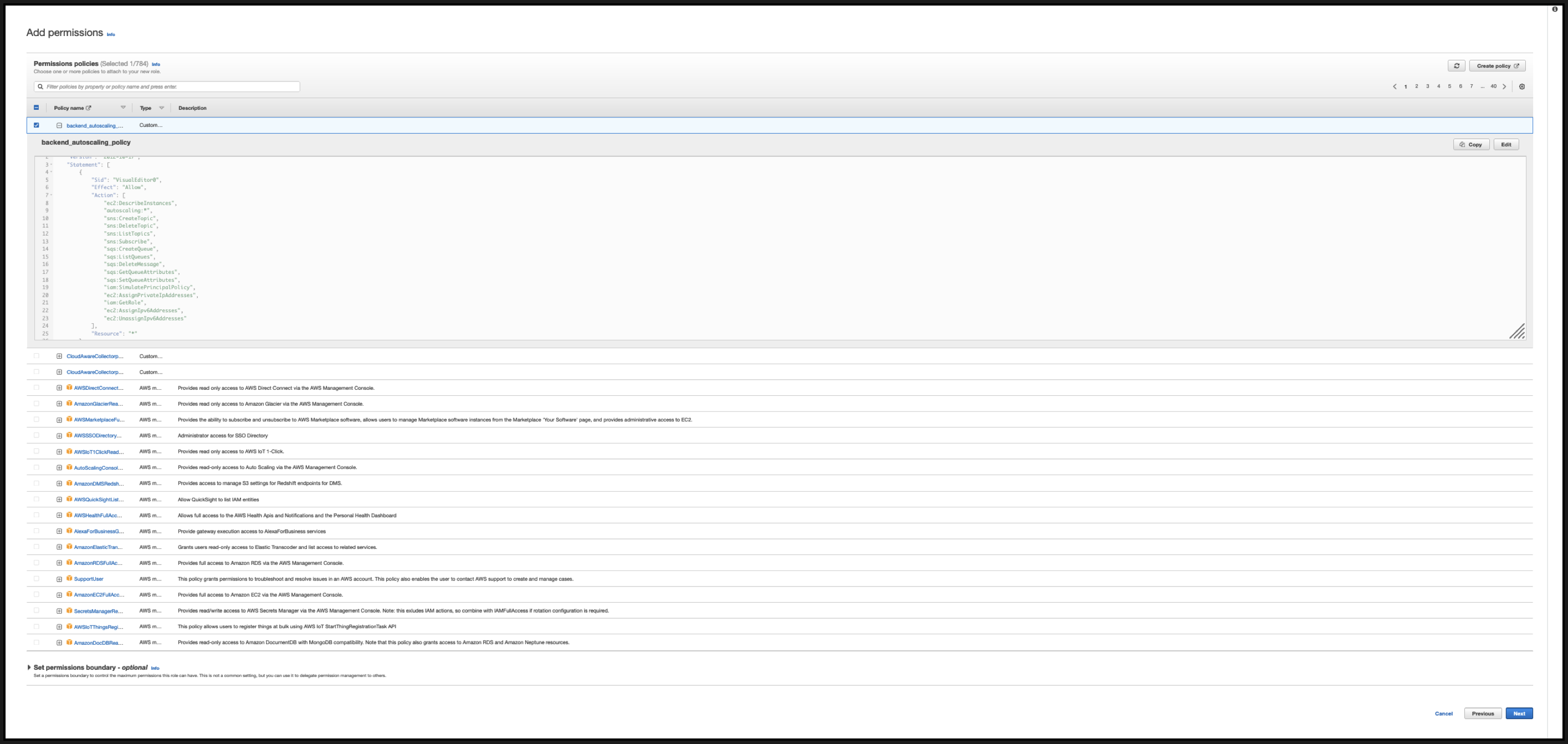
-
In the Name, review, and create page, give a valid name to the role.
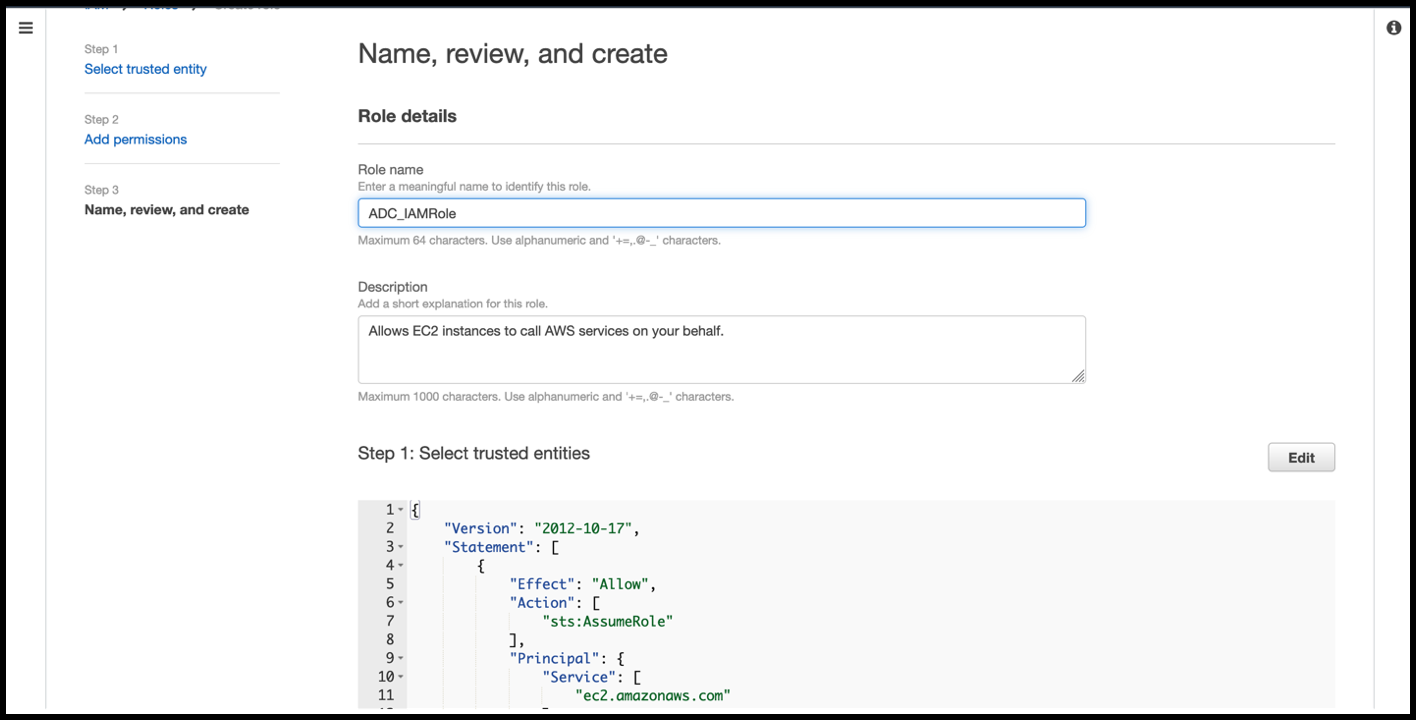
-
Click Create role.
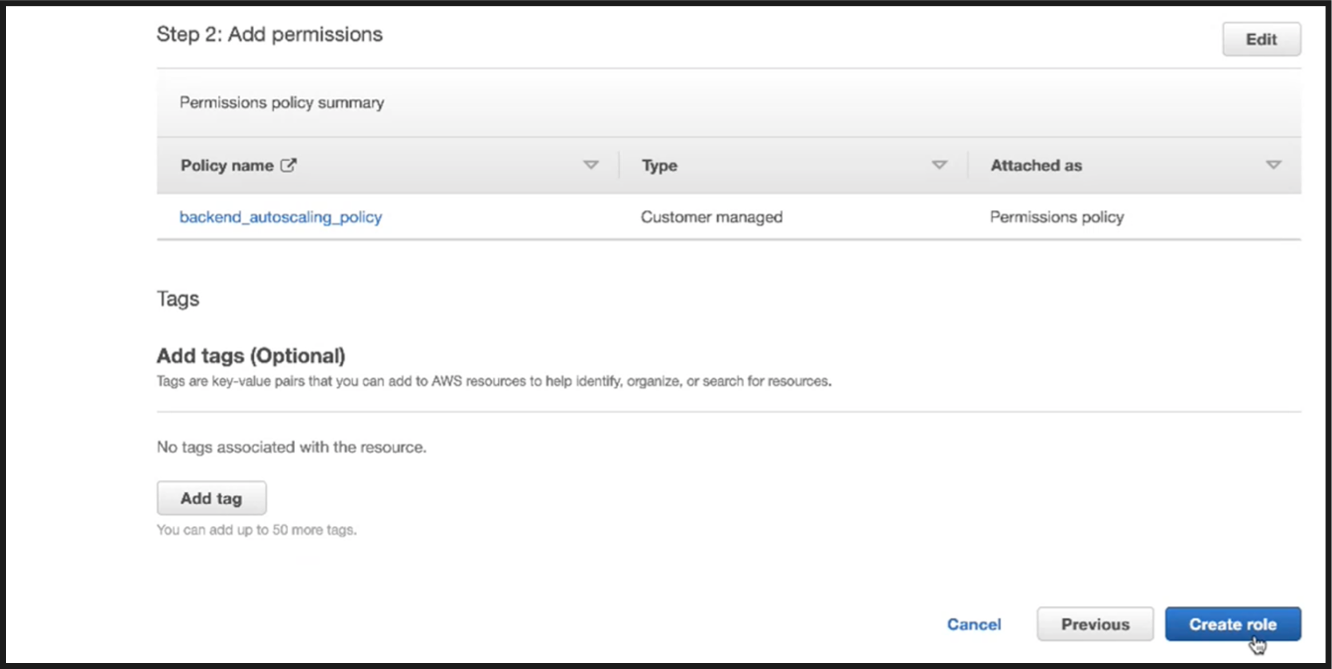
-
-
Repeat steps: 1, 2 and 3. Select the Refresh button and select the drop-down menu to see the role that you created.
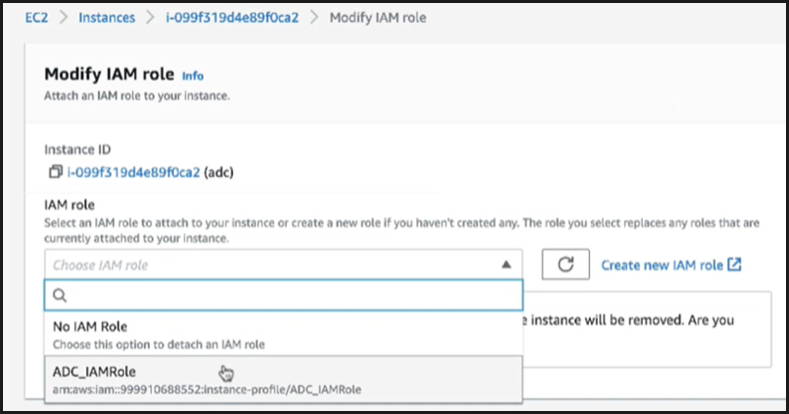
-
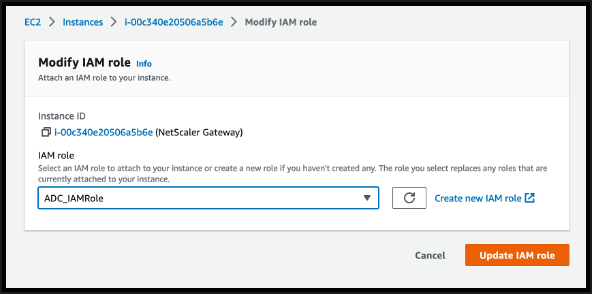
Click Update IAM role.
Test IAM policies with the IAM policy simulator
The IAM policy simulator is a tool that enables you to test the effects of IAM access control policies before committing them into production. It is easier to verify and troubleshoot permissions.
-
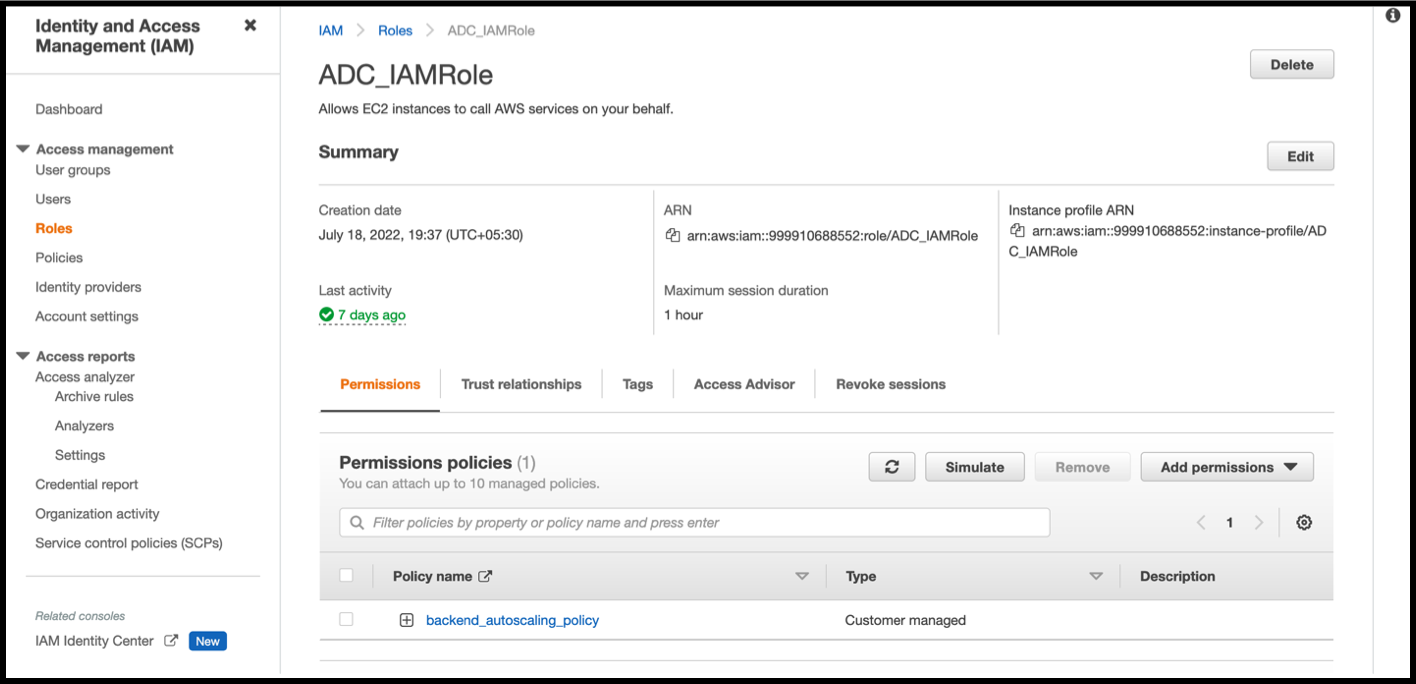
In the IAM page, select the IAM role that you want to test, and click Simulate. In the following example, “ADC_IAMRole” is the IAM role.
-
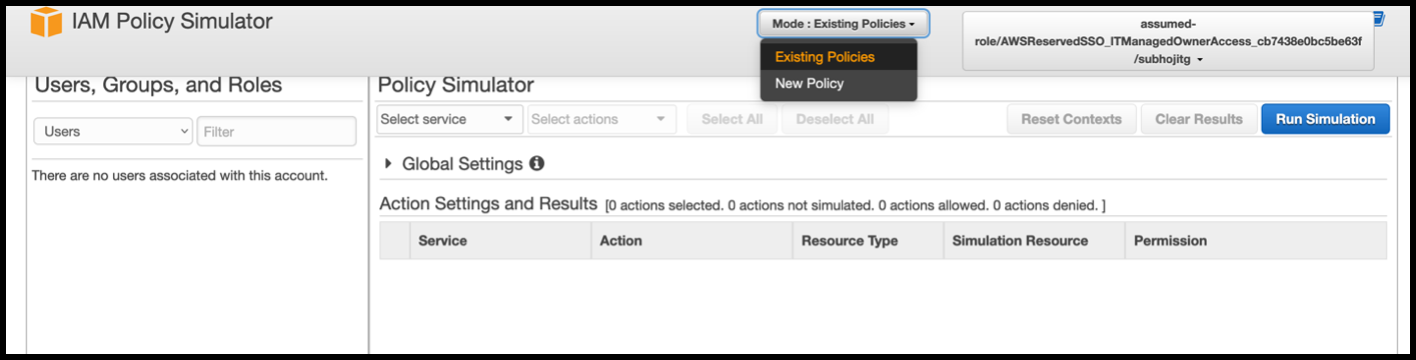
In the IAM policy simulator console, select Existing Policies as the Mode.
-
In the Users, Groups and Roles tab, select Roles from the drop-down menu and choose an existing role.
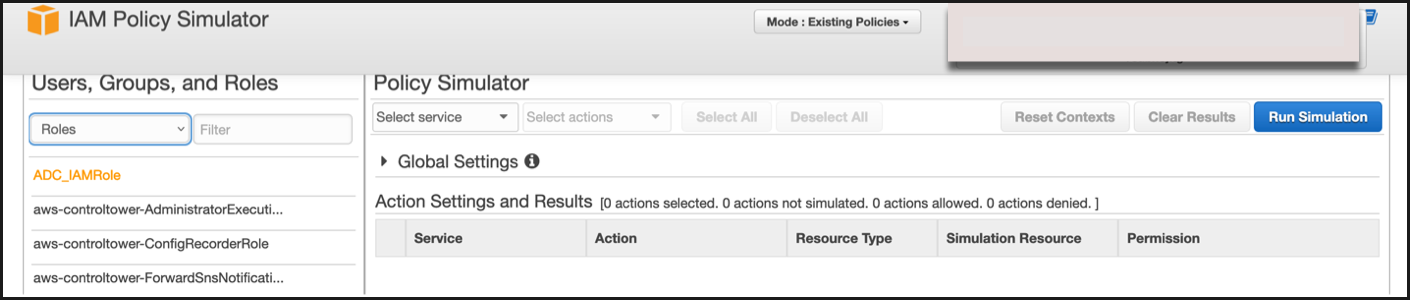
-
After selecting the existing role, select the existing policy under it.
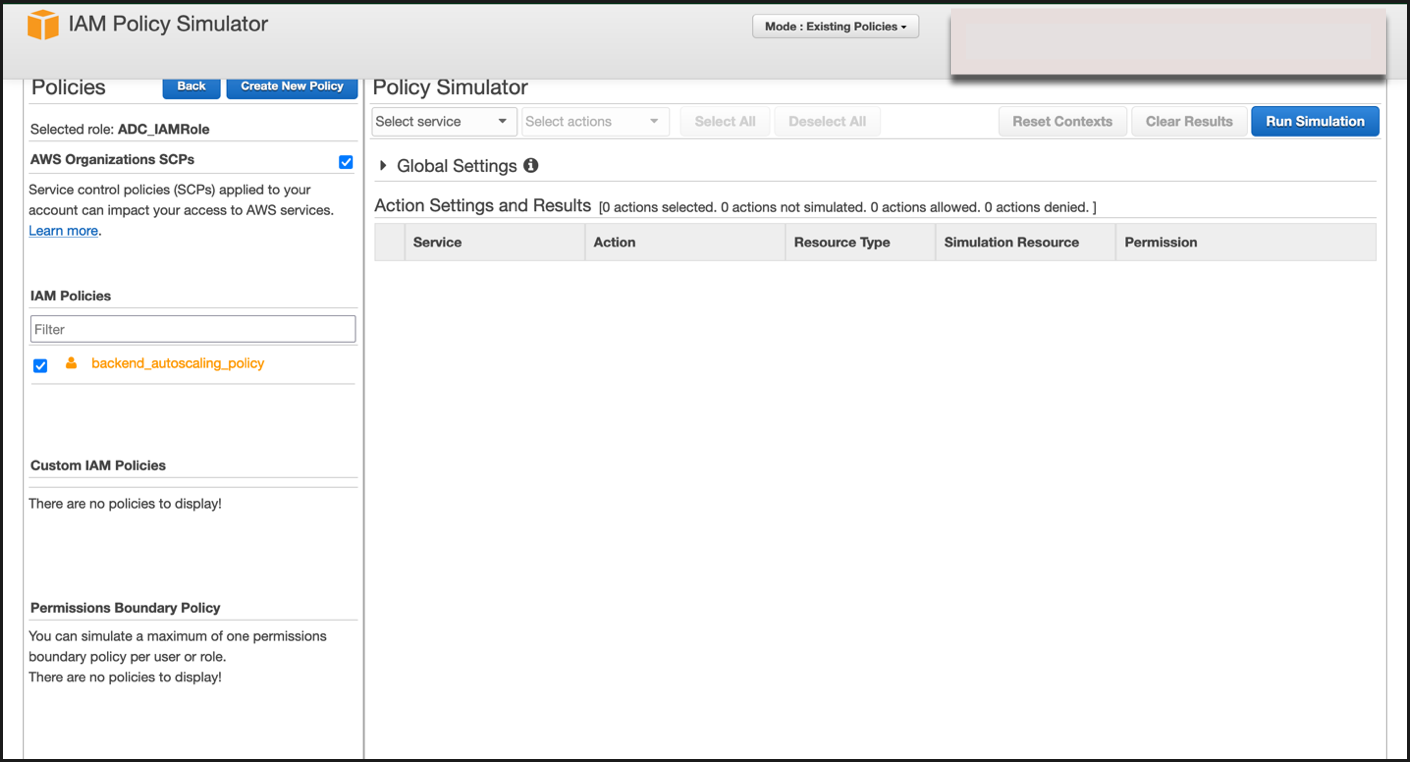
-
After you select the policy, you can see the exact JSON on the left-hand side of the screen. Select the desired actions in the Select actions drop-down menu.
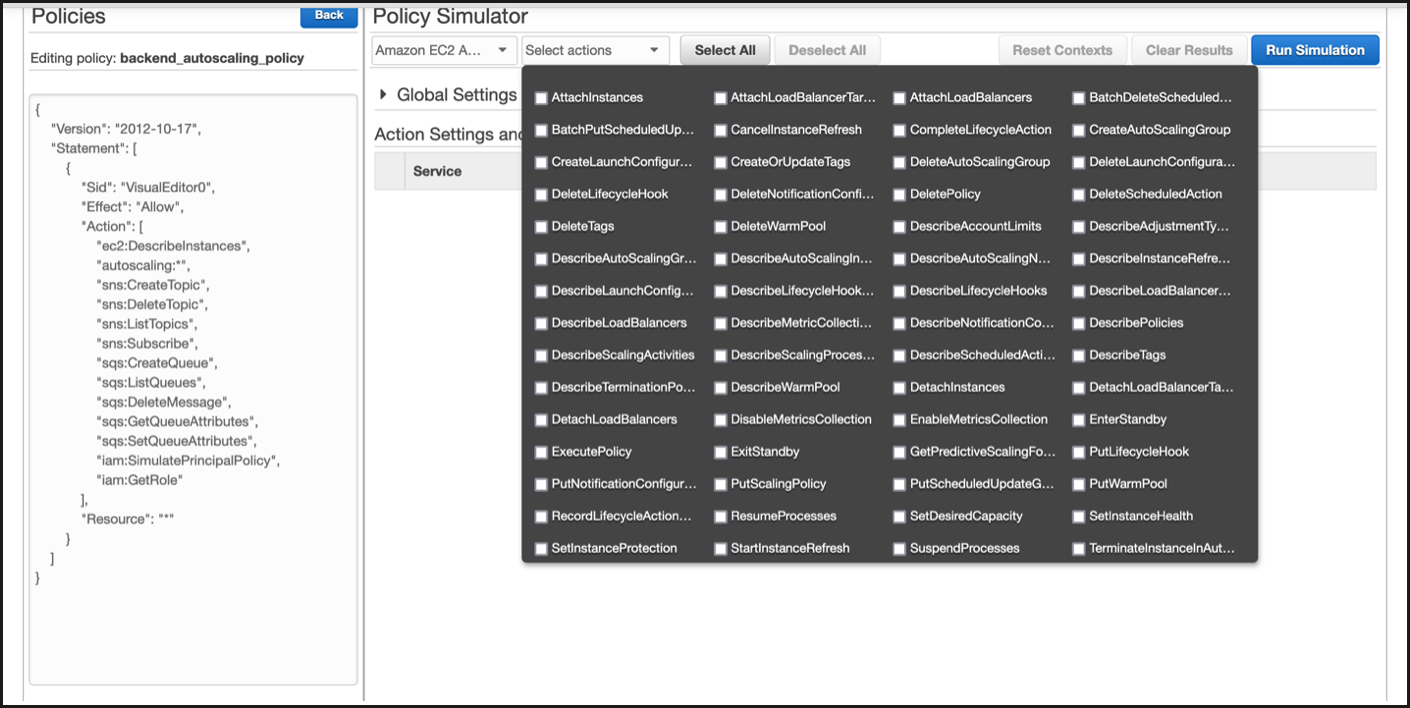
-
Click Run simulation.
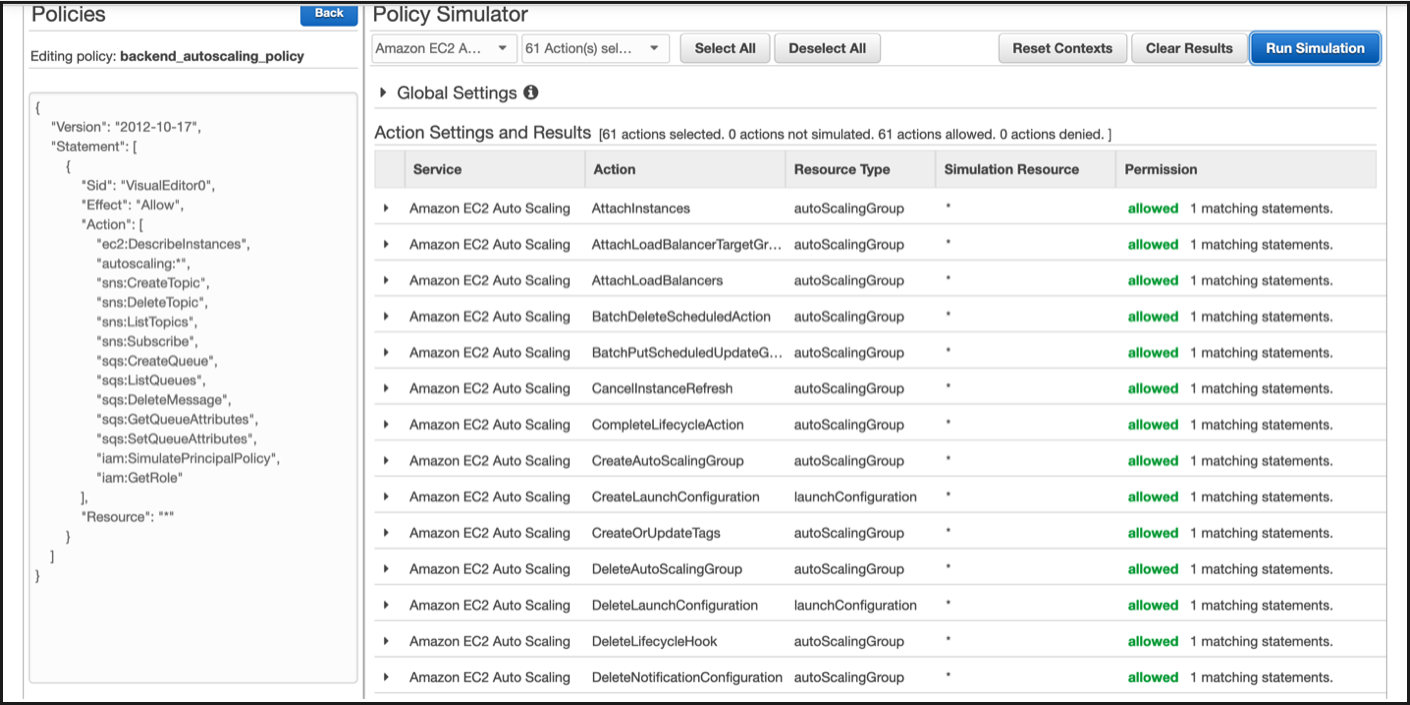
For detailed information, see AWS IAM documentation.
Other references
Using an IAM role to grant permissions to applications running on Amazon EC2 instances