Deploy a VPX high-availability pair with external static IP address on the Google Cloud Platform
You can deploy a VPX high-availability pair on GCP using an external static IP address. The client IP address of the primary node must be bound to an external static IP address. Upon failover, the external static IP address is moved to the secondary node for traffic to resume.
A static external IP address is an external IP address that is reserved for your project until you decide to release it. If you use an IP address to access a service, you can reserve that IP address so that only your project can use it. For more information, see Reserving a Static External IP Address.
For more information on HA, see High Availability.
Before you start
-
Read the Limitation, Hardware requirements, Points to note mentioned in Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on Google Cloud Platform. This information applies to HA deployments also.
- Enable Cloud Resource Manager API for your GCP project.
-
Allow full access to all Cloud APIs while creating the instances.
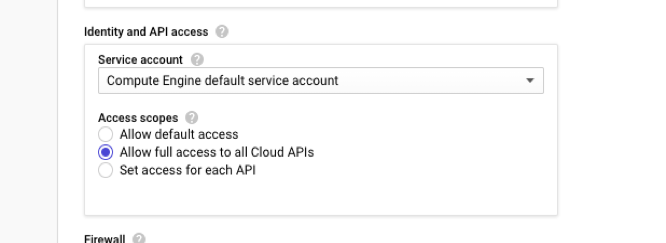
-
Ensure that the IAM role associated with your GCP service account has the following IAM permissions:
REQUIRED_INSTANCE_IAM_PERMS = [ "compute.addresses.use", "compute.forwardingRules.list", "compute.forwardingRules.setTarget", "compute.instances.setMetadata" "compute.instances.addAccessConfig", "compute.instances.deleteAccessConfig", "compute.instances.get", "Compute.instances.list", "compute.networks.useExternalIp", "compute.subnetworks.useExternalIp", "compute.targetInstances.list", "compute.targetInstances.use", "compute.targetInstances.create", "compute.zones.list", "compute.zoneOperations.get", ] <!--NeedCopy--> -
If you have configured alias IP addresses on an interface other than the management interface, ensure that your GCP service account has the following additional IAM permissions:
"compute.instances.updateNetworkInterface" <!--NeedCopy--> - If you have configured GCP forwarding rules on the primary node, read the limitations and requirements mentioned in Forwarding rules support for VPX high-availability pair on GCP to update them to new primary on failover.
How to deploy a VPX HA pair on Google Cloud Platform
Here’s a summary of the HA deployment steps:
- Create VPC networks in the same region. For example, Asia-east.
- Create two VPX instances (primary and secondary nodes) on the same region. They can be in the same zone or different zones. For example Asia east-1a and Asia east-Ib.
- Configure HA settings on both instances by using the NetScaler GUI or ADC CLI commands.
Step 1. Create VPC networks
Create VPC networks based on your requirements. Citrix® recommends you to create three VPC networks for associating with management NIC, client NIC, and server NIC.
To create a VPC network, perform these steps:
- Log on the Google console > Networking > VPC network > Create VPC Network.
- Complete the required fields, and click Create.
For more information, see the Create VPC Networks section in Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on Google Cloud Platform.
Step 2. Create two VPX instances
Create two VPX instances by following the steps given in Scenario: deploy a multi-NIC, multi-IP standalone VPX instance.
Important:
Assign a static external IP address to client IP address (VIP) of the primary node. You can use an existing reserved IP address or create a new one. To create a static external IP address, navigate to Network interface > External IP, click Create IP address.
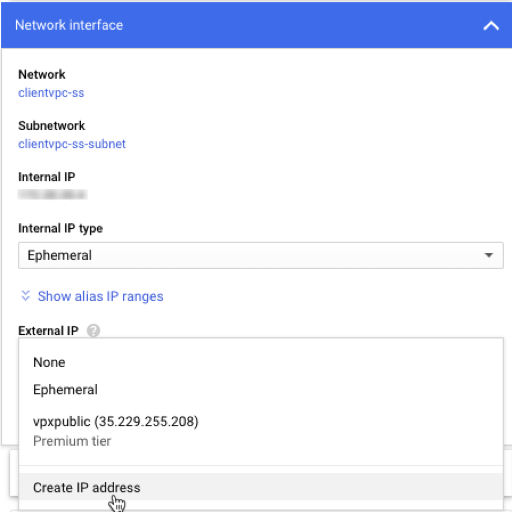
After the failover, when the old primary becomes the new secondary, the static external IP address moves from the old primary and is attached to the new primary. For more information, see the Google cloud document Reserving a Static External IP Address.
After you’ve configured the VPX instances, you can configure the VIP and SNIP addresses. For more information, see Configuring NetScaler-owned IP addresses.
Step 3. Configure high availability
After you’ve created the instances on Google Cloud Platform, you can configure HA by using the NetScaler GUI for CLI.
Configure HA by using the GUI
Step 1. Set up high availability in INC mode on both the instances.
On the primary node, perform the following steps:
- Log on to the instance with user name
nsrootand instance ID of the node from GCP console as the password. - Navigate to Configuration > System > High Availability > Nodes, and click Add.
- In the Remote Node IP address field, enter the private IP address of the management NIC of the secondary node.
- Select the Turn on INC (Independent Network Configuration) mode on self node check box.
- Click Create.
On the secondary node, perform the following steps:
- Log on to the instance with user name
nsrootand instance ID of the node from GCP console as the password. - Navigate to Configuration > System > High Availability > Nodes, and click Add.
- In the Remote Node IP address field, enter the private IP address of the management NIC of the primary node.
- Select the Turn on INC (Independent Network Configuration) mode on self node check box.
- Click Create.
Before you proceed further, ensure that the Synchronization state of the secondary node is shown as SUCCESS in the Nodes page.
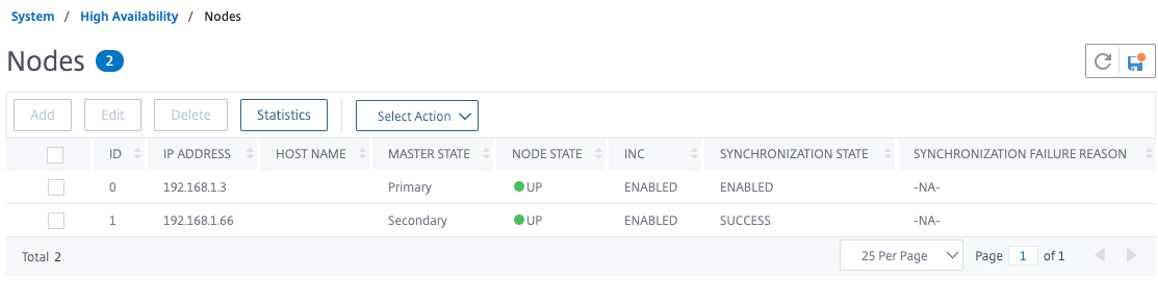
Note:
Now, the secondary node has the same log-on credentials as the primary node.
Step 2. Add Virtual IP address and Subnet IP address on both the nodes.
On the primary node, perform the following steps:
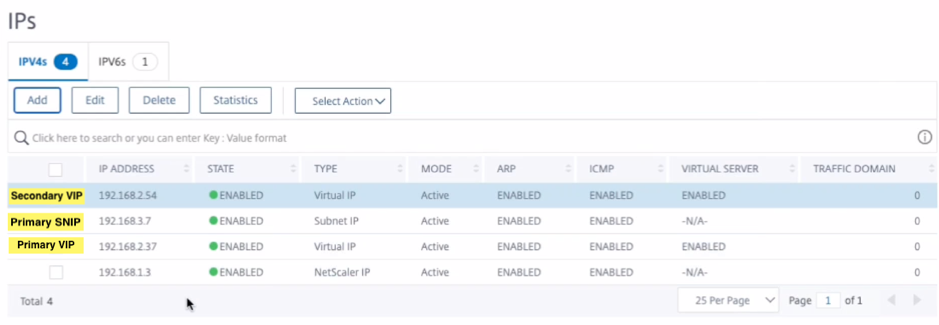
- Navigate to System > Network > IPs > IPv4s, and click Add.
- Add a primary VIP address by following these steps:
- Enter the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the primary instance and netmask configured for the client subnet in the VM instance.
- In the IP Type field, select Virtual IP from the drop-down menu.
- Click Create.
- Add a primary SNIP address by following these steps:
- Enter the internal IP address of the server-facing interface of the primary instance and netmask configured for the server subnet in the primary instance.
- In the IP Type field, select Subnet IP from the drop-down menu.
- Click Create.
- Add a secondary VIP address by following these steps:
- Enter the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the secondary instance and netmask configured for the client subnet in the VM instance.
- In the IP Type field, select Virtual IP from the drop-down menu.
- Click Create.
On the secondary node, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to System > Network > IPs > IPv4s, and click Add.
- Add a secondary VIP address by following these steps:
- Enter the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the secondary instance and netmask configured for the client subnet in the VM instance.
- In the IP Type field, select Virtual IP from the drop-down menu.
- Add a secondary SNIP address by following these steps:
- Enter the internal IP address of the server-facing interface of the secondary instance and netmask configured for the server subnet in the secondary instance.
- In the IP Type field, select Subnet IP from the drop-down menu.
- Click Create.
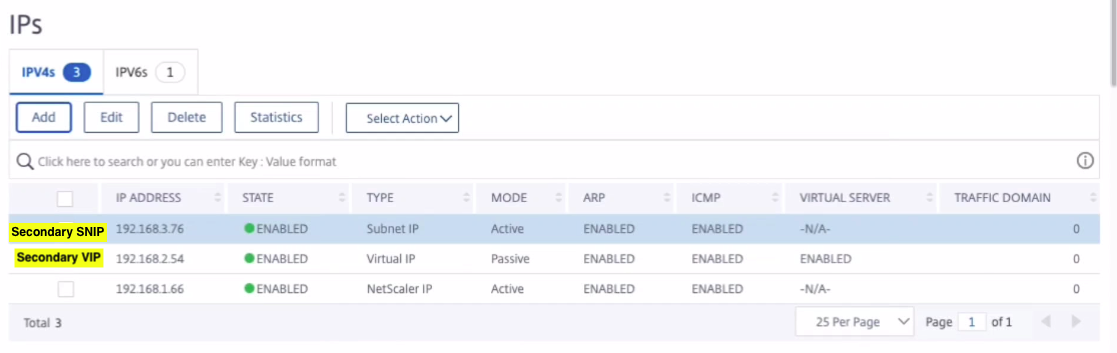
Step 3. Add IP set and bind IP set to the secondary VIP on both the instances.
On the primary node, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to System > Network > IP Sets > Add.
- Add an IP set name and click Insert.
- From the IPV4s page, select the virtual IP (secondary VIP) and click Insert.
- Click Create to create the IP set.
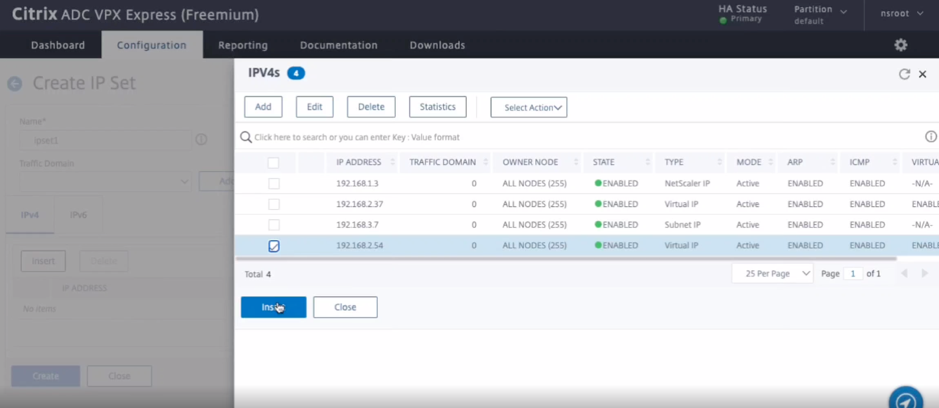
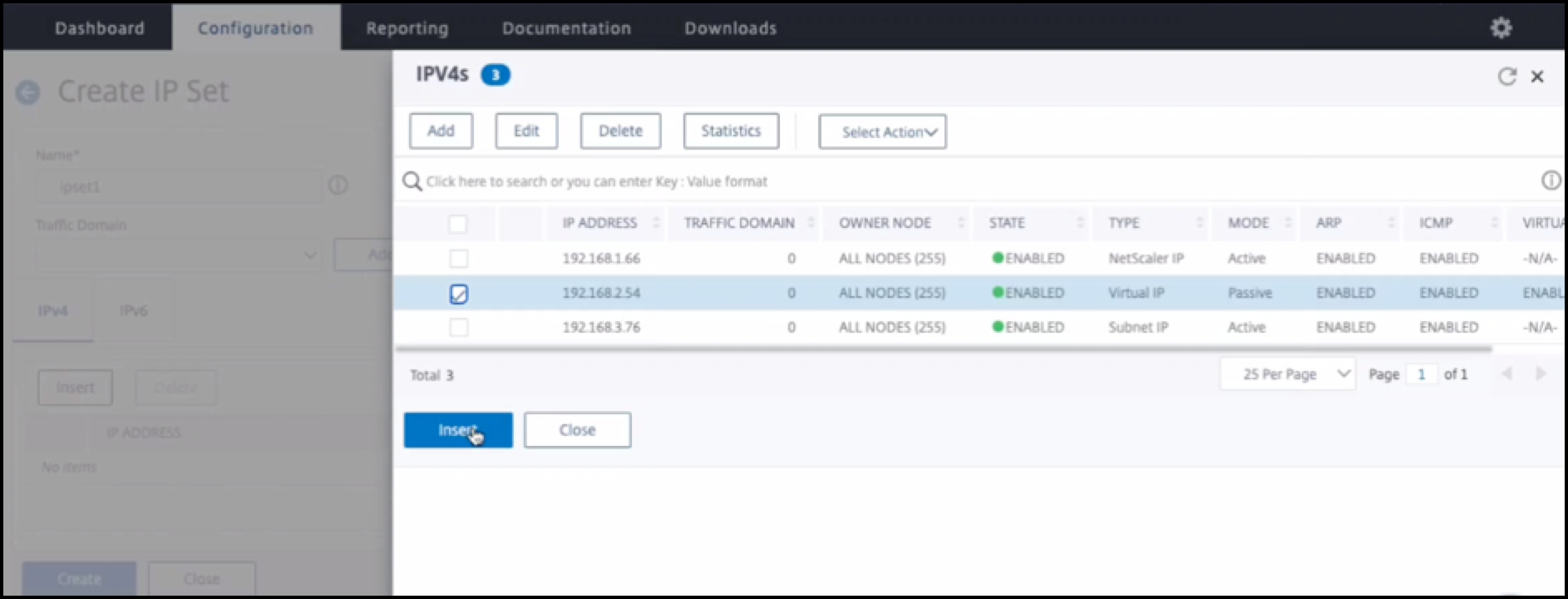
On the secondary node, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to System > Network > IP Sets > Add.
- Add an IP set name and click Insert.
- From the IPV4s page, select the virtual IP (secondary VIP) and click Insert.
- Click Create to create the IP set.
Note:
IP set name must be same on both the instances.
Step 4. Add a load balancing virtual server on the primary instance.
- Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers > Add.
-
Add the required values for Name, Protocol, IP Address Type (IP Address), IP address (primary VIP), and Port.
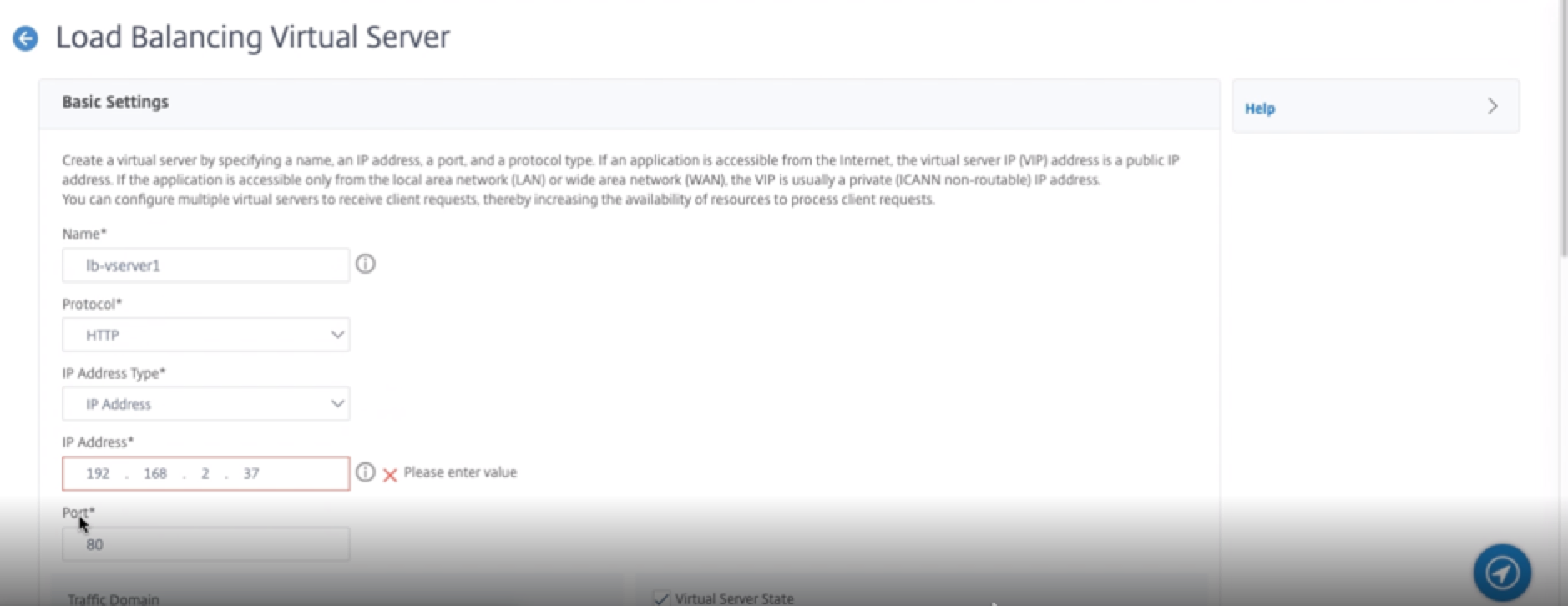
- Click More. Navigate to IP Range IP Set Settings, select IPset from the drop-down menu, and provide the IPset created in Step 3.
- Click OK to create the load balancing virtual server.
Step 5. Add a service or service group on the primary node.
- Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Services > Add.
- Add the required values for Service Name, IP Address, Protocol and Port, and click OK.
Step 6. Bind the service or service group to the load balancing virtual server on the primary node.
- Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers.
- Select the load balancing virtual server configured in Step 4, and click Edit.
- In the Service and Service Groups tab, click No Load Balancing Virtual Server Service Binding.
- Select the service configured in the Step 5, and click Bind.
Save the configuration. After a forced failover, the secondary becomes the new primary. The external static IP of the old primary VIP moves to the new secondary VIP.
Configure high availability using CLI
Step 1. Set up high availability in INC mode in both the instances.
On the primary node, type the following command.
add ha node 1 <sec_ip> -inc ENABLED
<!--NeedCopy-->
On the secondary node, type the following command.
add ha node 1 <prim_ip> -inc ENABLED
<!--NeedCopy-->
sec_ip refers to the internal IP address of the management NIC of the secondary node.
prim_ip refers to the internal IP address of the management NIC of the primary node.
Step 2. Add Virtual and Subnet IPs on both the nodes.
On the primary node, type the following command.
add ns ip <primary_vip> <subnet> -type VIP
add ns ip <secondary_vip> <subnet> -type VIP
add ns ip <primary_snip> <subnet> -type SNIP
<!--NeedCopy-->
primary_vip refers to the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the primary instance.
secondary_vip refers to the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the secondary instance.
primary_snip refers to the internal IP address of the server-facing interface of the primary instance.
On the secondary node, type the following command.
add ns ip <secondary_vip> <subnet> -type VIP
add ns ip <secondary_snip> <subnet> -type SNIP
<!--NeedCopy-->
secondary_vip refers to the internal IP address of the client-facing interface of the secondary instance.
secondary_snip refers to the internal IP address of the server-facing interface of the secondary instance.
Step 3. Add IP set and bind IP set to secondary VIP on both the instances.
On the primary node, type the following command:
add ipset <ipsetname>
bind ipset <ipsetname> <secondary VIP>
<!--NeedCopy-->
On the secondary node, type the following command:
add ipset <ipsetname>
bind ipset <ipsetname> <secondary VIP>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
IP set name must be same on both the instances.
Step 4. Add a virtual server on the primary instance.
Type the following command:
add <server_type> vserver <vserver_name> <protocol> <primary_vip> <port> -ipset <ipset_name>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 5. Add a service or service group on the primary instance.
Type the following command:
add service <service_name> <service_ip_address> <protocol> <port>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 6. Bind the service/service group to the load balancing virtual server on the primary instance.
Type the following command:
bind <server_type> vserver <vserver_name> <service_name>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
To save your configuration, type the command
save config. Otherwise, the configurations are lost after you restart the instances.
Step 7. Verify the configuration.
Ensure that the external IP address attached to the primary client NIC moves to the secondary on a failover.
- Make a cURL request to the external IP address and make sure that it is reachable.
-
On the primary instance, perform failover:
From GUI, navigate to Configuration > System > High Availability > Action > Force Failover.
From CLI, type the following command:
force ha failover -f <!--NeedCopy-->On the GCP console, goto the Secondary instance. The external IP address must have moved to the client NIC of secondary after failover.
- Issue a cURL request to the external IP and ensure it is reachable again.