VIP scaling support for NetScaler VPX instance on GCP
A NetScaler appliance resides between the clients and the servers, so that client requests and server responses pass through it. In a typical installation, virtual servers configured on the appliance provide connection points that clients use to access the applications behind the appliance. The number of public virtual IP (VIP) addresses needed for a deployment varies on a case-by-case basis.
The GCP architecture restricts each interface on the instance to be connected to a different VPC. A VPC on GCP is a collection of subnets, and each subnet can span across zones of a region. In addition, GCP imposes the following limitation:
- There is a 1:1 mapping of number of public IP addresses to number of NICs. Only one public IP address can be assigned to a NIC.
- A maximum of only 8 NICs can be attached on a higher capacity instance type.
For example, an n1-standard-2 instance can have only 2 NICs, and the Public VIPs that can be added is limited to 2. For more information, see VPC resource quotas.
To achieve higher scales of public virtual IP addresses on a NetScaler VPX instance, you can configure the VIP addresses as part of the metadata of the instance. The NetScaler VPX instance internally uses forwarding rules provided by the GCP to achieve VIP scaling. The NetScaler VPX instance also provides high availability to the VIPs configured. After you configure VIP addresses as part of the metadata, you can configure an LB virtual server using the same IP that is used to create the forwarding rules. Thus, we can use forwarding rules to mitigate the limitations we have w.r.t scale in using public VIP addresses on an NetScaler VPX instance on GCP.
For more information on forwarding rules, see Forwarding rules overview.
For more information on HA, see High Availability.
Points to note
- Google charges some additional cost for each virtual IP forwarding rule. The actual cost depends on the number of entries created. The associated cost can be found from the Google pricing documents.
- Forwarding rules are applicable only for public VIPs. You can use alias IP addresses when the deployment needs private IP addresses as VIPs.
- You can create forwarding rules only for the protocols, which need the LB virtual server. VIPs can be created, updated, or deleted on the fly. You can also add a new load balancing virtual server with the same VIP address but with a different protocol.
Before you start
- NetScaler VPX instance must be deployed on GCP.
-
External IP address must be reserved. For more information, see Reserving a static external IP address.
-
Ensure that your GCP service account has the following IAM permissions:
REQUIRED_IAM_PERMS = [ "compute.addresses.list", "compute.addresses.get", "compute.addresses.use", "compute.forwardingRules.create", "compute.forwardingRules.delete", "compute.forwardingRules.get", "compute.forwardingRules.list", "compute.instances.use", "compute.subnetworks.use", "compute.targetInstances.create" "compute.targetInstances.get" "compute.targetInstances.use", ] <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enable Cloud Resource Manager API for your GCP project.
-
If you use VIP scaling on a standalone VPX instance, ensure that your GCP service account has the following IAM permissions:
REQUIRED_IAM_PERMS = [ "compute.addresses.list", "compute.addresses.get", "compute.addresses.use", "compute.forwardingRules.create", "compute.forwardingRules.delete", "compute.forwardingRules.get", "compute.forwardingRules.list", "compute.instances.use", "compute.subnetworks.use", "compute.targetInstances.create", "compute.targetInstances.list", "compute.targetInstances.use", ] <!--NeedCopy--> -
If you use VIP scaling in a high availability mode, ensure that your GCP service account has the following IAM permissions:
REQUIRED_IAM_PERMS = [ "compute.addresses.get", "compute.addresses.list", "compute.addresses.use", "compute.forwardingRules.create", "compute.forwardingRules.delete", "compute.forwardingRules.get", "compute.forwardingRules.list", "compute.forwardingRules.setTarget", "compute.instances.use", "compute.instances.get", "compute.instances.list", "compute.instances.setMetadata", "compute.subnetworks.use", "compute.targetInstances.create", "compute.targetInstances.list", "compute.targetInstances.use", "compute.zones.list", ] <!--NeedCopy-->Note:
In a high availability mode, if your service account does not have owner or editor roles, you must add the Service Account User role to your service account.
Configure external IP addresses for VIP scaling on NetScaler VPX instance
- In the Google Cloud Console, navigate to the VM Instances page.
- Create a new VM instance or use an existing instance.
- Click the instance name. On the VM instance details page, click Edit.
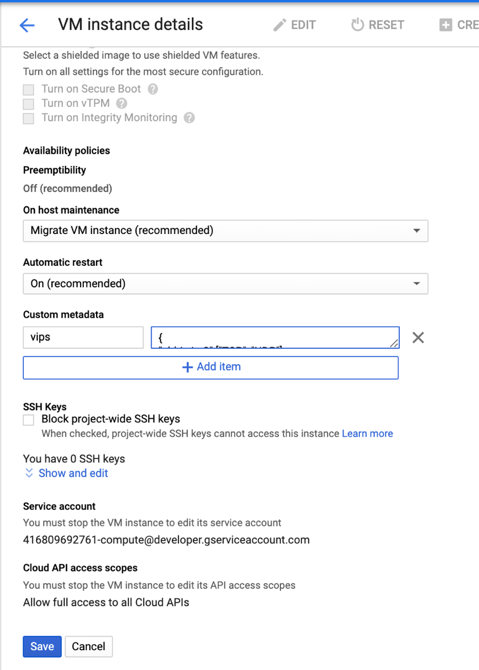
- Update the Custom metadata by entering the following:
- Key = vips
-
Value = Provide a value in the following JSON format:
{ “Name of external reserved IP”: [list of protocols], }
GCP supports the following protocols:
- AH
- ESP
- ICMP
- SCT
- TCP
- UDP
For more information, see Custom metadata.
Example for Custom metadata:
{ “external-ip1-name”:[“TCP”, “UDP”], “external-ip2-name”:[“ICMP”, “AH”] }
In this example, the NetScaler VPX instance internally creates one forwarding rule for each IP, protocol pair. The metadata entries are mapped to the forwarding rules. This example helps you understand how many forwarding rules are created for a metadata entry.
Four forwarding rules are created as follows:
- external-ip1-name and TCP
- external-ip1-name and UDP
- external-ip2-name and ICMP
- external-ip2-name and AH
Note:
In HA mode, you must add custom metadata only on the primary instance. On failover, the custom metadata is synchronized to the new primary.
- Click Save.
Setting up a load balancing virtual server with external IP address on a NetScaler VPX instance
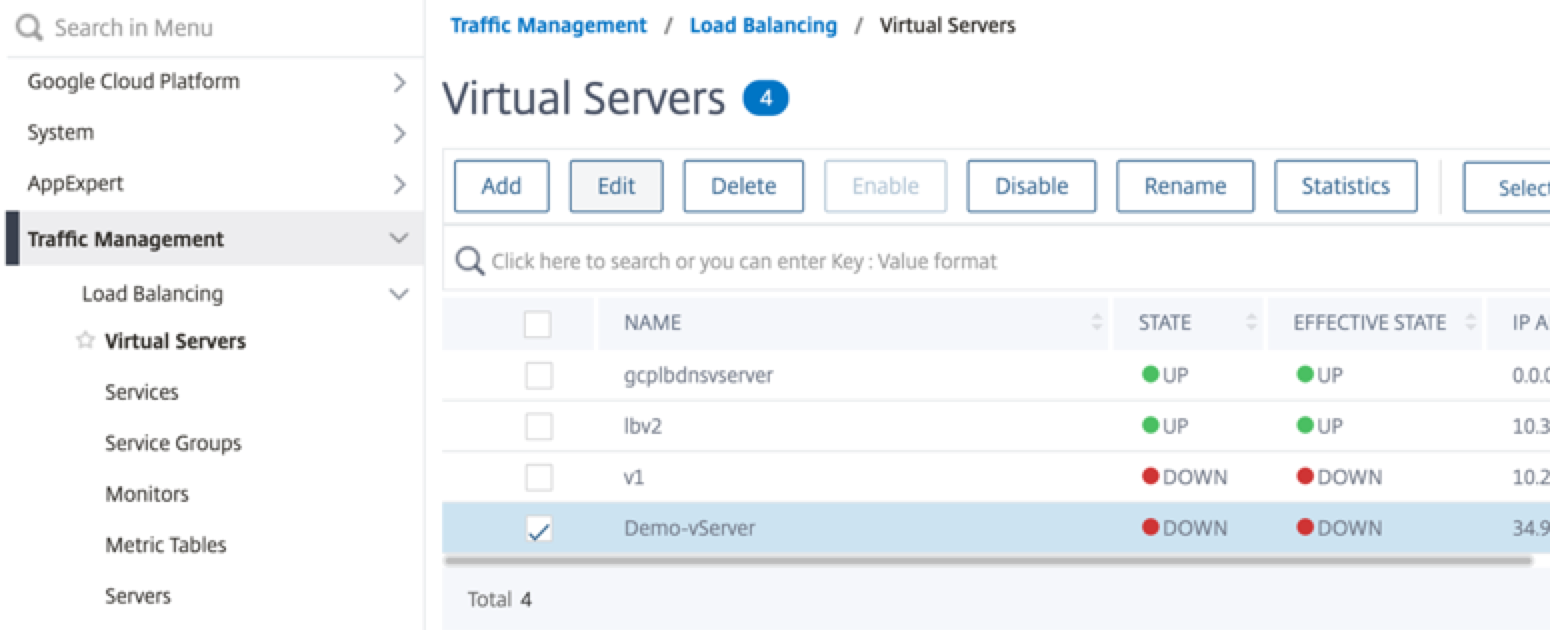
Step 1. Add a load balancing virtual server.
-
Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers > Add.
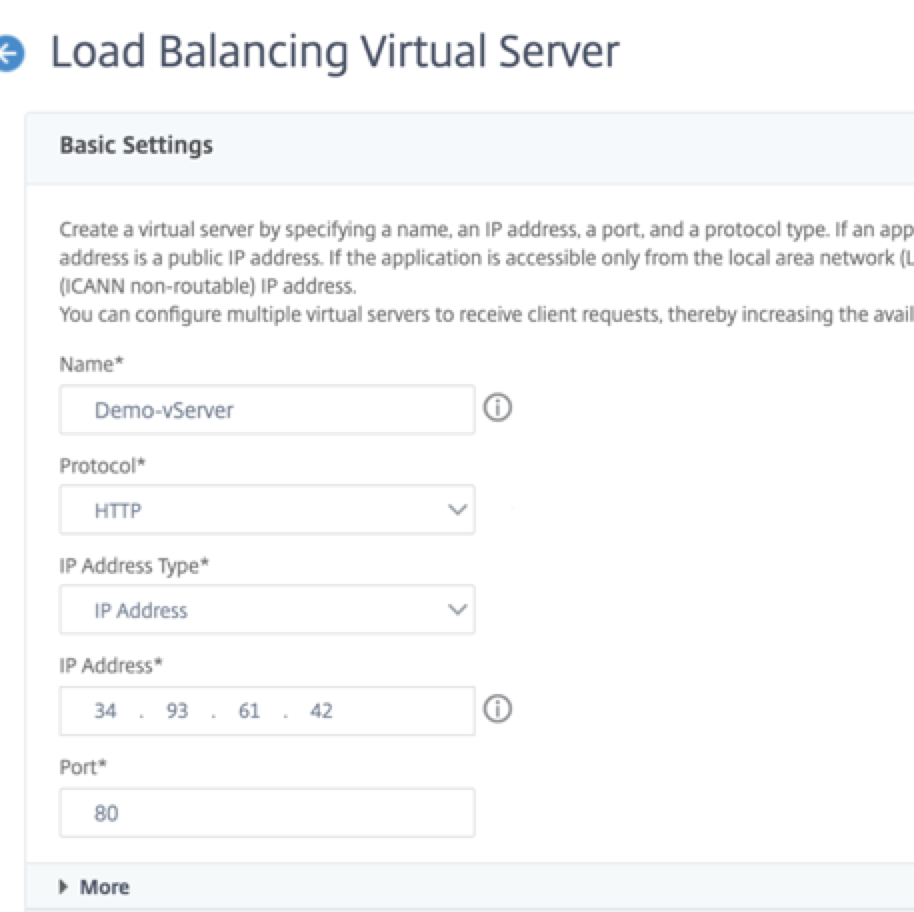
-
Add the required values for Name, Protocol, IP Address Type (IP Address), IP Address (External IP address of the forwarding rule that is added as VIP on ADC) and Port, and click OK.
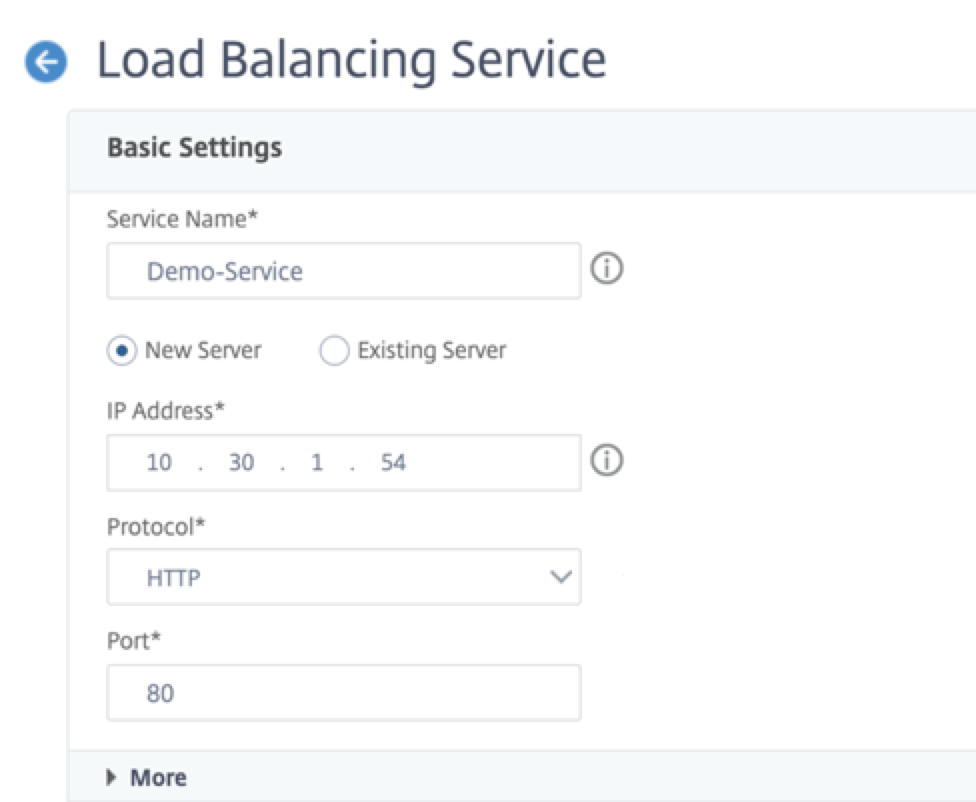
Step 2. Add a service or service group.
- Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Services > Add.
-
Add the required values for Service Name, IP Address, Protocol and Port, and click OK.
Step 3. Bind the service or service group to the load balancing virtual server.
- Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers.
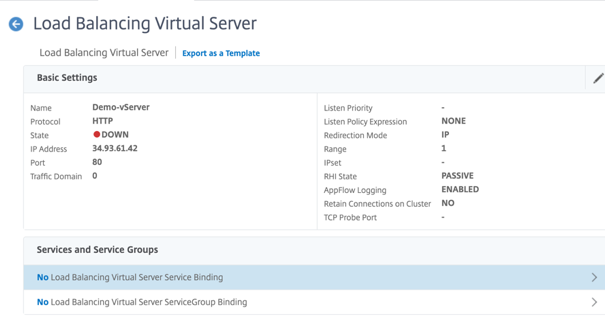
- Select the load balancing virtual server configured in Step 1, and click Edit.
-
In the Service and Service Groups page, click No Load Balancing Virtual Server Service Binding.
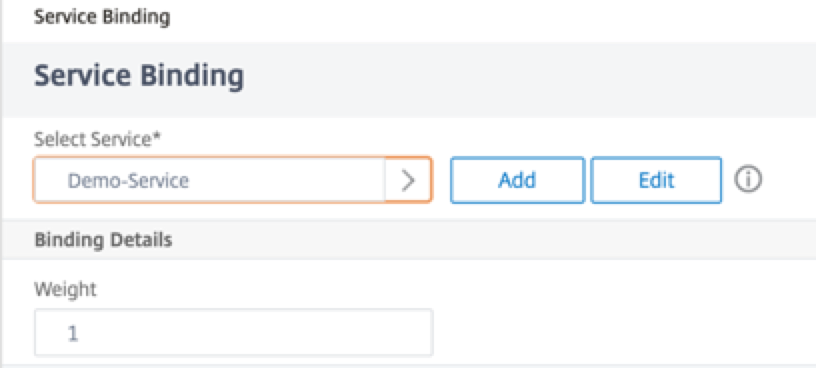
-
Select the service configured in the Step 3, and click Bind.
- Save the configuration.