-
-
Access Control Lists
-
Implement strict separation of Management and Data planes in NetScaler
-
Configure to source NetScaler FreeBSD data traffic from a SNIP address
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Access Control Lists
Access Control Lists (ACLs) filter IP traffic and secure your network from unauthorized access. An ACL is a set of conditions that the NetScaler evaluates to determine whether to allow access. For example, the Finance department probably does not want to allow its resources to be accessed by other departments, such as HR and Documentation, and those departments want to restrict access to their data.
When the NetScaler receives a data packet, it compares the information in the data packet with the conditions specified in the ACL and allows or denies access. The administrator of the organization can configure ACLs to function in the following processing modes:
- ALLOW—Process the packet.
- BRIDGE—Bridge the packet to the destination without processing it. The packet is directly sent by Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding.
- DENY—Drop the packet.
ACL rules are the first level of defense on the NetScaler.
NetScaler supports the following types of ACLs:
- Simple ACLs filter packets based on their source IP address and, optionally, their protocol, destination port, or traffic domain. Any packet that has the characteristics specified in the ACL is dropped.
- Extended ACLs filter data packets based on various parameters, such as source IP address, source port, action, and protocol. An extended ACL defines the conditions that a packet must satisfy for the NetScaler to process the packet, bridge the packet, or drop the packet.
Nomenclature
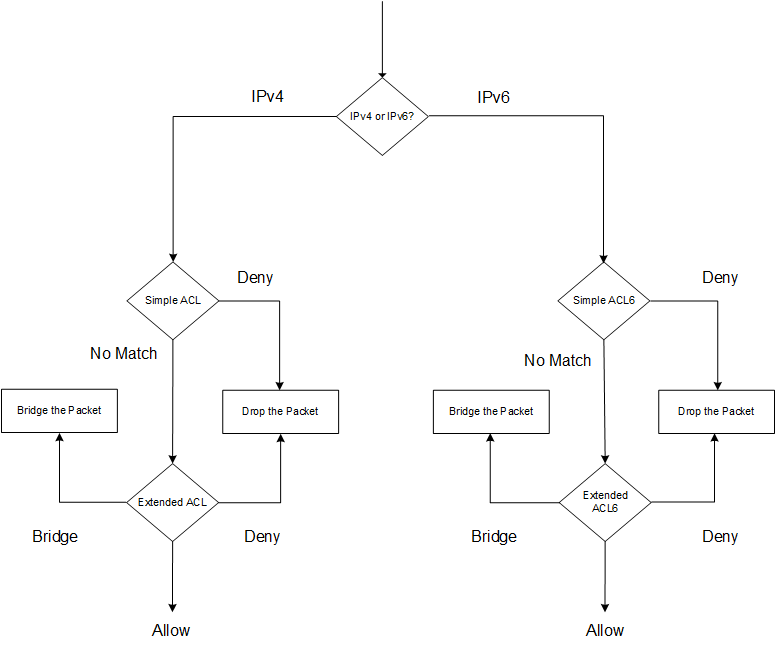
In the NetScaler user interfaces, the terms simple ACL and extended ACL refer to ACLs that process IPv4 packets. An ACL that processes IPv6 packets is called a simple ACL6 and or extended ACL6. When discussing both types, this documentation sometimes refers to both of them as simple ACLs or extended ACLs.
ACL Precedence
If both simple and extended ACLs are configured, incoming packets are compared to the simple ACLs first.
The NetScaler first determines whether the incoming packet is an IPv4 or an IPv6 packet, and then compares the packet’s characteristics to either simple ACLs or simple ACL6s. If a match is found, the packet is dropped. If no match is found, the packet is compared to extended ACLs or extended ACL6s. If that comparison results in a match, the packet is handled as specified in the ACL. The packet can be bridged, dropped, or allowed. If no match is found, the packet is allowed.
Figure 1. Simple and Extended ACLs Flow Sequence
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.