Microsoft Skype for Business StyleBook
The Skype for Business 2015 application relies on several external components to function. The Skype for Business network consists of various systems, such as servers and their operating systems, databases, authentication and authorizing systems, networking systems and infrastructure,and telephone PBX systems. Skype for Business Server 2015 is available in two versions, Standard Edition and Advanced Edition. The primary difference is in support for high-availability features that are only included in the Advanced Edition. To implement high availability, multiple Front-End servers must be deployed to a pool and SQL servers must be mirrored.
An Advanced Edition deployment enables the creation of multiple servers with different roles.
The primary components in Skype for Business 2015 application are:
- Front-End servers
- Edge Servers
- Director servers
- Database (SQL) servers
Front-end servers:
In the Skype for Business application, the Front-End server is the core server in your network. It provides the links and services for user authentication, registration, presence, address book, A/V conferencing, application sharing, instant messaging, and web conferencing. If you are deploying Skype for Business 2015 Enterprise edition, the topology typically consists of at least two Front-End servers load balanced in a Front-End pool with a database server that hosts the SQL Server instance holding the Skype for Business database.
Edge servers:
Deploying Edge Servers for Skype for Business is necessary if external users who are not logged into your
organization’s internal network need to be able to interact with internal users. These external users can be authenticated and anonymous remote users, federated partners, or other mobile clients.
There are four types of roles in Skype for Business Edge Server:
- Access Edge, which handles SIP Traffic and authenticates external connections, allows remote connection and allows federation Connection
- Web Conferencing, which handles Data Conferencing Packets, and allows external users to access Skype for Business
- A/V Conferencing, which handles A/V Conferencing Packets, and extends audio and video, app sharing and file transfer to external users
- XMPP Proxy, which handles XMPP packets, and allows XMPP based servers or clients to connect to Skype for Business.
Director servers:
The main function of the Director server in Skype for Business 2015 is to authenticate endpoints and “direct” the users to the pool that contains their account. In Skype for Business 2015, though the Director is a completely dedicated and specific role on a standalone server, it is an optional server. This facilitates security by making it easier to deploy or remove the configurations.
Directors are most useful where multiple pools exist because they provide a single point of contact for authenticating endpoints. Also, for remote users, a Director serves as an extra hop between the Edge pool and Front-End pool, adding an extra layer of protection against attacks.
The following figure diagrammatically represents the deployment of Skype servers in the network:
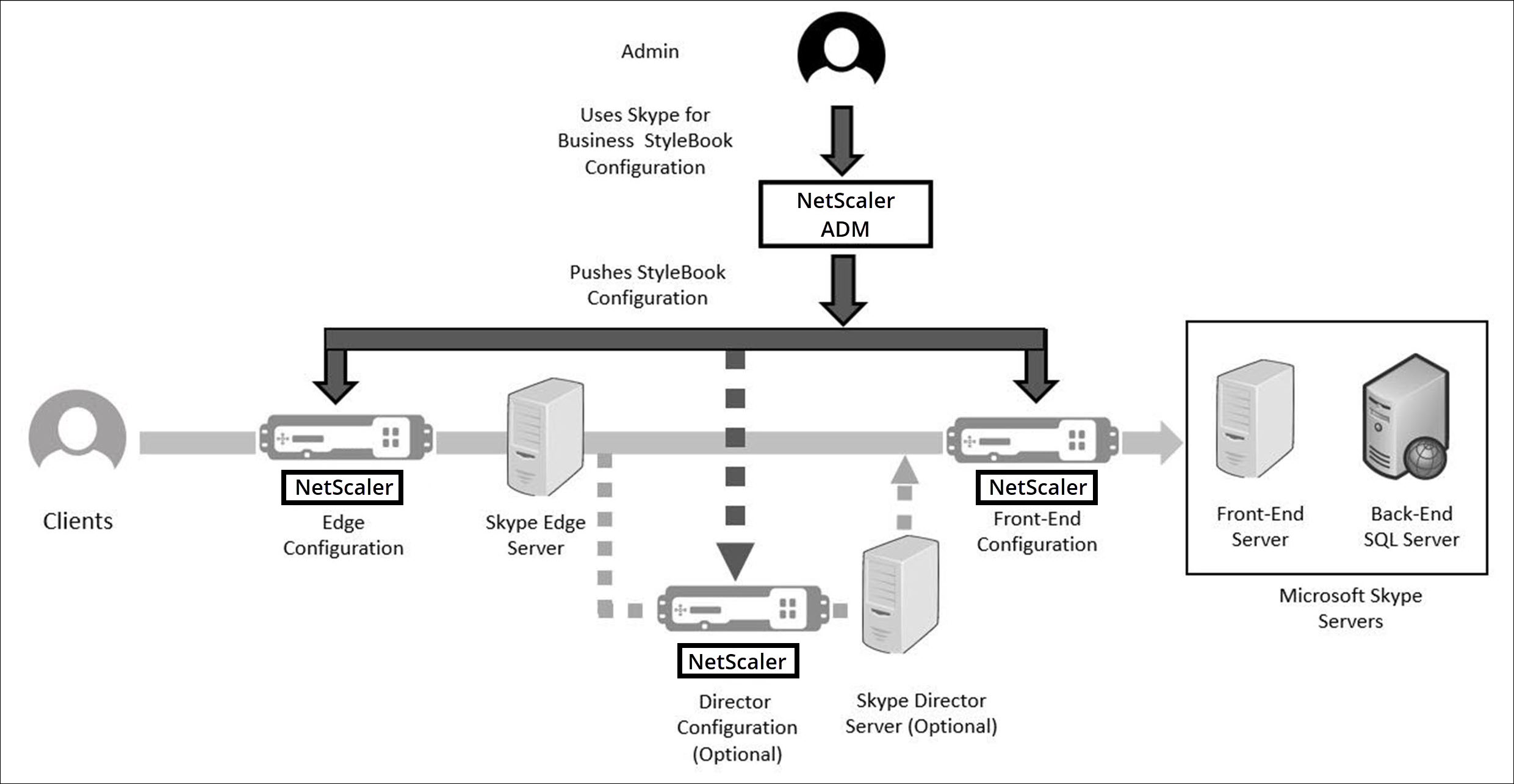
Configuring NetScaler instances in an enterprise
The following table lists the IP addresses used in the sample configuration included in the instructions below:
| Skype for Business Servers | Virtual IP Address | Server IP Addresses | NetScaler Instance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Servers | External VIP - 192.20.20.20 | 192.20.20.21; 192.20.20.22 | 10.102.29.141 |
| Internal VIP - 10.10.10.20 | 10.10.10.21; 10.10.10.22 | ||
| Front-end Servers | 10.10.10.10 | 10.10.10.11; 10.10.10.12 | 10.102.29.60 |
| Director Server | 10.10.10.30 | 10.10.10.31; 10.10.10.32 | 10.102.29.93 |
To configure front-end servers:
- In NetScaler Console, navigate to Applications > Configuration, and click Create New. The Choose StyleBook page displays all the StyleBooks available for your use in NetScaler Console. Scroll down and select Microsoft Skype for Business 2015 StyleBook. The StyleBook opens as a user interface page on which you can enter the values for all the parameters defined in this StyleBook.
- In the Edge Server section, enter the following virtual IP (VIP) addresses and IP addresses of all the Edge Servers in the network.
- External VIP address and IP addresses for the Edge Servers that will be used for Access Edge, web conferencing Edge, and A/V Edge.
- Internal VIP address and IP addresses for the Edge Servers that will be connected to the internal network.
- Two external and two internal Edge Servers in your network.
- In the Front-End Server section, enter the IP address of the virtual Front-End server (VIP) that is to be created for the Skype for Business Front-End servers. Also, enter the IP addresses of all the Skype for Business Front-End servers in the network.
- In the Director Server section, enter the virtual IP address (VIP) for the Director servers that is to be created for the Skype for Business application. Also, enter the IP addresses for all the Skype for Business Director servers in the network. Create at least two Director servers for high-availability.
- The Advanced Settings section lists all the default ports configured on the NetScaler instances for the three Skype servers.
The following table provides you a list of all default ports and protocols:
| Label | Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP Port | 80 | HTTP | Used for communication from Front-End Servers to the web farm FQDNs when HTTPS is not used. |
| HTTPS Port | 443 | HTTPS | Used for communication from Front-End Servers to the web farm FQDNs. |
| Auto Discover Internal Port | 4443 | HTTPS | HTTPS (from Reverse Proxy) and HTTPS Front-End inter-pool communications for Auto Discover sign-in. |
| RPC Port | 135 | DCOM and remote procedure call (RPC) | Used for DCOM based operations such as moving users, user replicator synchronization, and address book synchronization. |
| SIP Port | 5061 | TCP (TLS) | Used by Front-End servers for all internal SIP communications. |
| SIP Focus Port | 444 | HTTPS, TCP | Used for HTTPS communication between the Focus (the component that manages the Skype conference state) and the individual servers. |
| SIP Group Port | 5071 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the response group application. |
| SIP AppSharing Port | 5065 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP listening requests for application sharing. |
| SIP Attendant Port | 5072 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the attendant (that is, for dial-in conferencing). |
SIP Conf Announcement Port |
5073 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the Skype for Business server conferencing announcement service (that is, for dial-in conferencing). |
| SIP CallPark Port | 5075 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the CallPark application. |
| SIP Call Admission Port | 448 | TCP | Used for call admission control by the Skype for Business server bandwidth policy service. |
| SIP Call Admission TURN Port | 5080 | TCP | Used for call admission control by the bandwidth policy service for Audio/Video Edge TURN traffic. |
| SIP Audio Test Port | 5076 | TCP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the audio test service. |
| HTTPS External Port | 443 | HTTPS | Used for external ports for SIP/ TLS communication for remote user access, accessing internal Web conferences, and STUN/TCP inbound and outbound media communications for accessing internal media and A/V sessions. |
| HTTPS Internal Port | 443 | HTTPS | Used for internal ports for SIP/ TLS communication for remote user access, accessing internal Web conferences, and STUN/TCP inbound and outbound media communications for accessing internal media and A/V sessions. |
| SIP External Remote Access Port | 5061 | TCP | Used for external ports for SIP/MTLS communication for remote user access or federation. |
| SIP Internal Remote Access Port | 5061 | TCP | Used for internal ports for SIP/MTLS communication for remote user access or federation. |
| SIP External STUN UDP Port | 3478 | UDP | Used for external ports for STUN/ UDP inbound and outbound media communications. |
| SIP Internal STUN UDP Port | 3478 | UDP | Used for internal ports for STUN/UDP inbound and outbound media communications. |
| SIP Internal IM Port | 5062 | Used for internal ports for SIP/MTLS authentication of IM communications flowing outbound through the internal firewall. | |
| HTTP Port | 80 | TCP | Used for initial communication from Directors to the web farm FQDNs. |
| HTTPS Port | 443 | HTTPS | Used for communication from Directors to the web farm FQDNs. |
| Auto Discover Internal Port | 4443 | HTTPS | Used for HTTPS (from Reverse Proxy) and HTTPS Director inter-pool communications for Auto Discover sign-in. |
| SIP Internal Port | 5061 | TCP | Used for internal communications between servers and for client connections. |
-
In the Target Instances section, select the three different NetScaler instance on which to deploy the three Skype for Business servers.
Note
You can also click the refresh icon to add recently discovered NetScaler instances in NetScaler Console to the available list of instances in this window.
-
Click Create to create the configuration on the selected NetScaler instances.
Tip
Citrix recommends that you select Dry Run to check the configuration objects that must be created on the target instance before you run the actual configuration on the instance.
When the configuration is successfully created, the StyleBook creates 25 load balancing virtual servers. That is, for each port, one load balancing virtual server is defined along with one service group, and the service group is bound to the load balancing virtual server. The configuration also adds the Front-End servers as service group members and binds them to the service group. The number of service group members created is equal to the number of Front-End servers created.
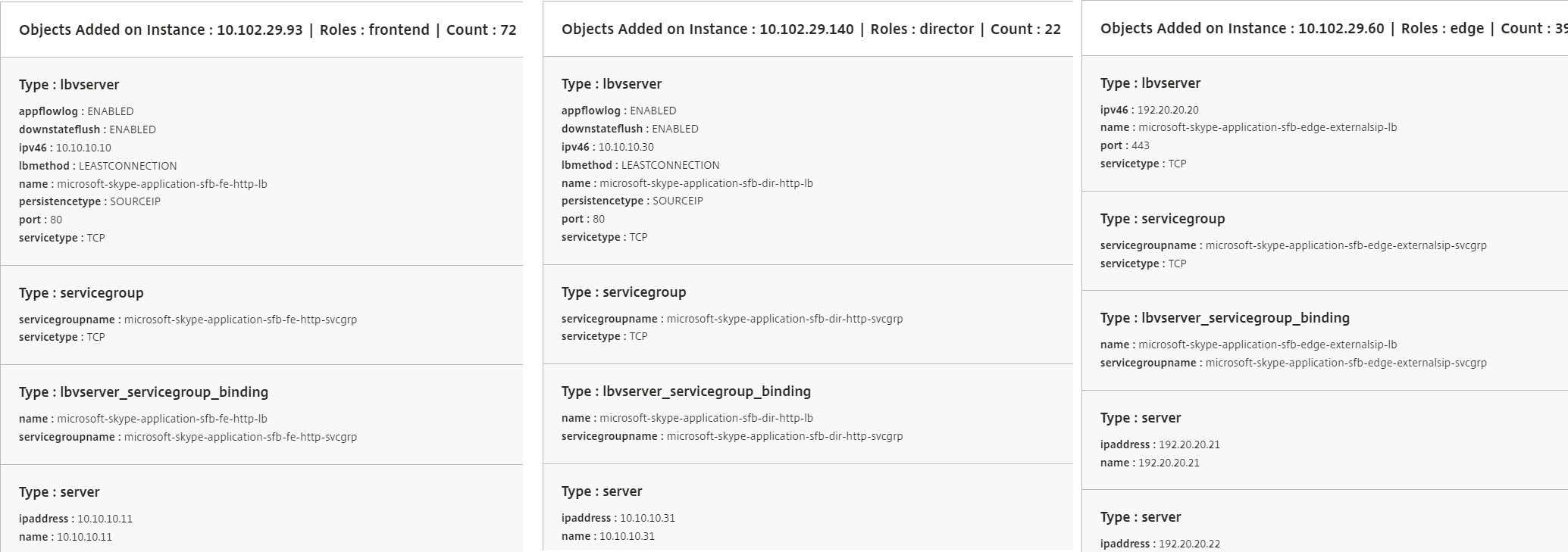
The following figure shows the objects created in each server: