Expressions
One of the most powerful features of a StyleBook is the use of expressions. You can use StyleBooks expressions in various scenarios to compute dynamic values. The following example is an expression to concatenate a parameter value with a literal string.
Example:
$parameters.appname + "-mon"
This expression retrieves the parameter named appname, and concatenates it with the string -mon.
Note
StyleBook supports using the reserved keywords when you define parameters and expressions in a StyleBook definition. The reserved keywords are -
and,false,in,not,true, andor.
The following types of expressions are supported:
Arithmetic expressions
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (*)
- Division (/)
- Modulo (%)
Examples:
- Adding two numbers: $parameters.a + $parameters.b
- Multiplying two numbers: $parameters.a * 10
- Finding the remainder after division of one number by another:
15%10 Results in 5
String expressions
- Concatenate two strings (+)
Example:
Concatenate two strings: str(“app-“) + $parameters.appname
List expressions
Merges two lists (+)
Example:
-
Concatenate two lists: $parameters.external-servers + $parameters.internal-servers
-
If
$parameters.ports-1is [80, 81] and$parameters.port-2is [81, 82], the$parameters.ports-1 + $parameters.ports-2displays as a list [80, 81, 81, 82].
Relational expressions
-
== : Tests if two operands are equal and returns true if they are equal, else returns false.
-
!= : Tests if two operands are different and returns true if they are different, else returns false.
-
> : Returns true if the first operand is greater than the second operand, else returns false.
-
>= : Returns true if the first operand is greater than or equal to the second operand, else returns false.
-
< : Returns true if the first operand is lesser than the second operand, else returns false.
-
<= : Returns true if the first operand is lesser than or equal to the second operand, else returns false.
Example:
- Use of Equality operator:
$parameters.name = = "abcd" - Use of Inequality operator:
$parameters.name != "default" -
Examples for other relational operators
10 > 910 >= 100 < 910 <= 910 == 1010 != 1
Logical expressions - boolean
-
and: The logical ‘and’ operator. If both operands are true, the result is true, else it is false.
-
or: The logical ‘or’ operator. If one of the operands is true, the result is true, else it is false.
-
not: The unary operator. If the operand is true, the result is false, and the opposite way.
-
in: Tests whether the first argument is a substring of the second argument
-
in: Tests if an item is part of a list
Note
You can type-cast expressions where strings are converted into numbers (using int() builtin function) and numbers are converted to strings (using str() builtin function). Similarly, you can cast
tcp-portto a number (using theint()builtin function), and an IP address can be cast to a string (using the str() builtin function).Use a delimiter before and after any operator. You can use the following delimiters:
Before an operator:
space,tab,comma,(,),[,]After an operator:
space,tab,(,[For example:
abc + def
100 % 10
10 > 9
$item in $parameters.some-list
Splat expressions
A splat expression [*] provides a simpler way to retrieve a certain attribute from a complex list for all the iterations. You can now include splat expressions in a StyleBook definition.
Syntax:
list[*].attribute
<!--NeedCopy-->
This expression iterates over all the items of the list specified to its left and returns the attribute value specified to its right.
When you want to retrieve an IP address or host name of each virtual server from the list, you can use the following splat expressions:
Example 1:
$parameters.server-members[*].hostname
<!--NeedCopy-->
This expression returns a list of host names from all the server-members.
Example 2:
$parameters.server-members[*].sub-domains[*].name
<!--NeedCopy-->
This expression returns a list of all names under the subdomains of each server-members.
These expressions always return the right-most element type’s list.
Verbatim string expressions
You can use verbatim strings when special characters in a string have to take their literal form. These strings can contain escape characters, backslash, quotes, parentheses, whitespaces, brackets, and so on. In verbatim strings, the special characters’ usual interpretation is skipped. All the characters in the string are preserved in their literal form.
In StyleBooks, you can include NetScaler Policy Expressions in their literal form using verbatim strings. The Policy Expressions typically contain special characters. Without verbatim strings, you have to escape special characters by breaking strings into substrings.
To create a verbatim string, encapsulate a string between special characters as follows:
~{string}~
<!--NeedCopy-->
You can use verbatim strings in the StyleBook expressions.
Note
Do not use the sequence of characters
}~in an input string because this sequence indicates the end of a verbatim string.
Example:
~{HTTP.REQ.COOKIE.VALUE("jsessionid") ALT HTTP.REQ.URL.BEFORE_STR("=").AFTER_STR(";jsessionid=") ALT HTTP.REQ.URL.AFTER_STR(";jsessionid=")}~
<!--NeedCopy-->
For more informtion, see Allow special characters with their literal form in StyleBooks.
Target expressions
In a StyleBook definition, you can use the $current-target expression to refer the current target NetScaler instance. To specifically refer an IP address of the target NetScaler instance, use this expression as follows:
$current-target.ip
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
components:
-
name: lb-comp
type: ns::lbvserver
properties:
name: $current-target.ip + "-lbvserver"
<!--NeedCopy-->
In this example, the name of the lbvserver uses the IP address of the target NetScaler instance.
Expression Type Validation
StyleBook engine now allows for stronger type checking during compile time, that is, the expressions used while writing the StyleBook are validated during the import of a StyleBook itself rather than while creating the configuration pack.
All references to parameters, substitutions, components, properties of components, outputs of components, user-defined variables (repeat-item, repeat-index, arguments to substitution functions) and so on are all validated for their existence and types.
Example of Type Checks:
In the following example, the expected type of port property of lbvserver StyleBook is tcp-port. In NetScaler Console, the type validations happen at compile-time (import-time). The compiler finds that string and tcp-port are not compatible types and therefore, the StyleBook compiler displays an error and fails to import or migrate a StyleBook.
components:
-
name: lbvserver-comp
type: ns::lbvserver
properties:
name: mylb
ipv46: 10.102.190.15
port: str("80")
servicetype: HTTP
<!--NeedCopy-->
To successfully compile this StyleBook, declare the following as a number in the compiler:
port: 80
Example of Flagging Invalid Expressions:
When you import a StyleBook to NetScaler Console, the compiler identifies the invalid expressions and flag it. As a result, the StyleBook fails to import to NetScaler Console.
In the following example, the expression assigned to the name property in the lb-sg-binding-comp component is: $components.lbvserver-comp.properties.lbvservername. However, there is no property called lbvservername in component lbvserver-comp.
Components:
-
name: lbvserver-comp
type: ns::lbvserver
properties:
name: mylb
ipv46: 10.102.190.15
port: 80
servicetype: HTTP
-
name: sg-comp
type: ns::servicegroup
properties:
servicegroupname: mysg
servicetype: HTTP
-
name: lb-sg-binding-comp
type: ns::lbvserver_servicegroup_binding
condition: $parameters.create-binding
properties:
name: $components.lbvserver-comp.properties.lbvservername
servicegroupname: $components.sg-comp.properties.servicegroupname
<!--NeedCopy-->
Implicit typecasting of datatypes
When you use StyleBook expressions for different datatypes, the StyleBook engine now implicitly typecasts the output to an appropriate datatype. The implicit typecasting of datatypes supports binary operations and value assignments.
Examples for binary operations:
- Adding (+) two variables of type
stringandnumber, sets the output datatype tostring.
$parameters.appname + '_' + $parameters.app_instance_num
- Adding (+) two variables of type
stringandipaddress, sets the output datatype tostring.
$parameters.appname + '_' + $parameters.instance_ip
- Adding (+) two variables of type
ipaddressandnumber, sets the output datatype toipaddress.
$parameters.instance_ip + $parameters.number
- Subtracting (-) two variables of type
ipaddressandnumber, sets the output datatype toipaddress.
$parameters.instance_ip - $parameters.number
- Multiplying (*) two variables of type
stringandnumber, sets the output datatype tostring.
$parameters.dummy_str * $parameters.count
Examples for value assignments:
- If a variable is defined as the
stringdatatype, the assigned value is converted to the defined datatype.
name: $parameters.port * 3
- If a variable is defined as the
portnumberdatatype, the assigned value converted to theportnumberdatatype with exceptions.
port: $index + $parameters.lower_limit
Indexing Lists
Items of a list can be accessed now by indexing them directly:
| Expression | Description |
$components.test-lbs[0] |
Refers to the first item in thetest-lbs component |
$components.test-lbs[0].properties.p1 |
Refers to property p1 of the first item in the test-lbs component |
$components.lbcomps[0].outputs.servicegroups[1].properties.servicegroupname |
Refers to the property servicegroupname of the second item in the servicegroups component, which is an output from the first item of the lbcomps component |
Policy expressions in StyleBooks
The StyleBooks GUI allows you to build NetScaler® policy expressions by selecting items from lists, helping you to create expressions faster and more accurately.
Policy expressions in StyleBooks allow you to create flexible and customizable configurations. You can specify conditions based on various parameters, attributes, or variables. Policy expressions are commonly used to implement NetScaler policy configurations.
Enable policy Expression Editor in StyleBooks GUI
To make the EPA or expression editor available for a parameter, specify the is_policy_expression GUI attribute in the parameter definition. When enabled (set to true) this setting allows you the invoke the Expressions Editor when entering a value for this parameter.
parameters:
-
name: expression
type: string
label: Expression
required: true
gui:
is_policy_expression: true
<!--NeedCopy-->
Create and build policy expressions
-
Navigate to Applications > Configurations > StyleBooks. The StyleBooks page displays all the StyleBooks that are available in your NetScaler Console.
-
Select a StyleBook that includes policy expressions in its parameters.
-
Click Create Configuration. In the Create Configuration page, enter values for all the parameters defined in this StyleBook.
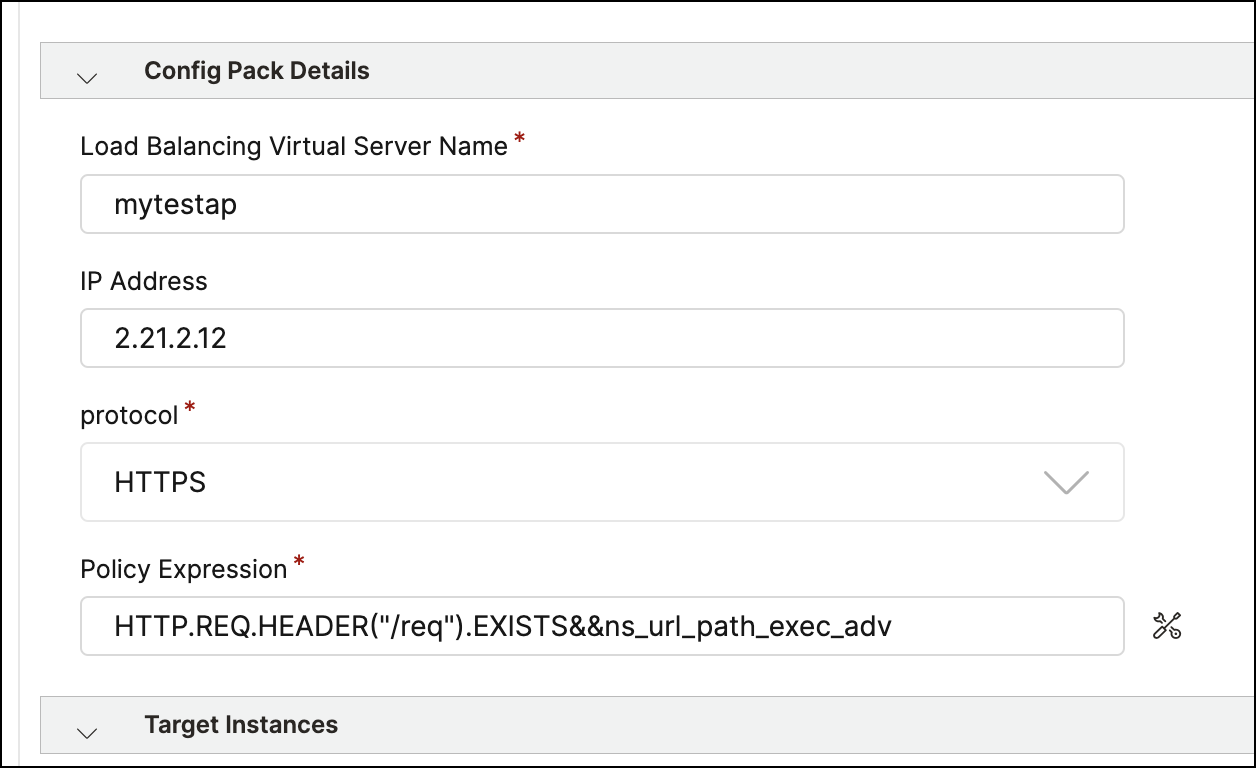
-
Click the icon next to the Expressions field. The Create an expression page appears.
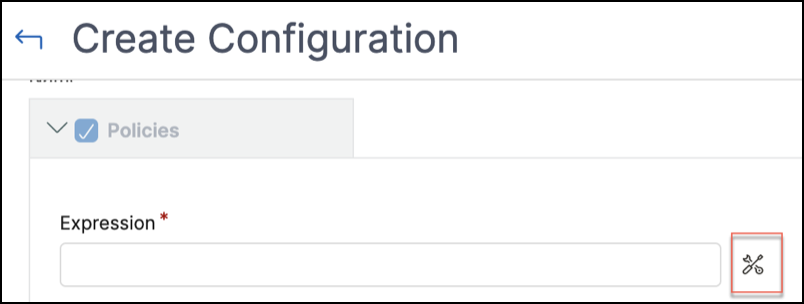
-
In Create an expression, use the intuitive drop-downs to construct your policy expression. Click Submit.
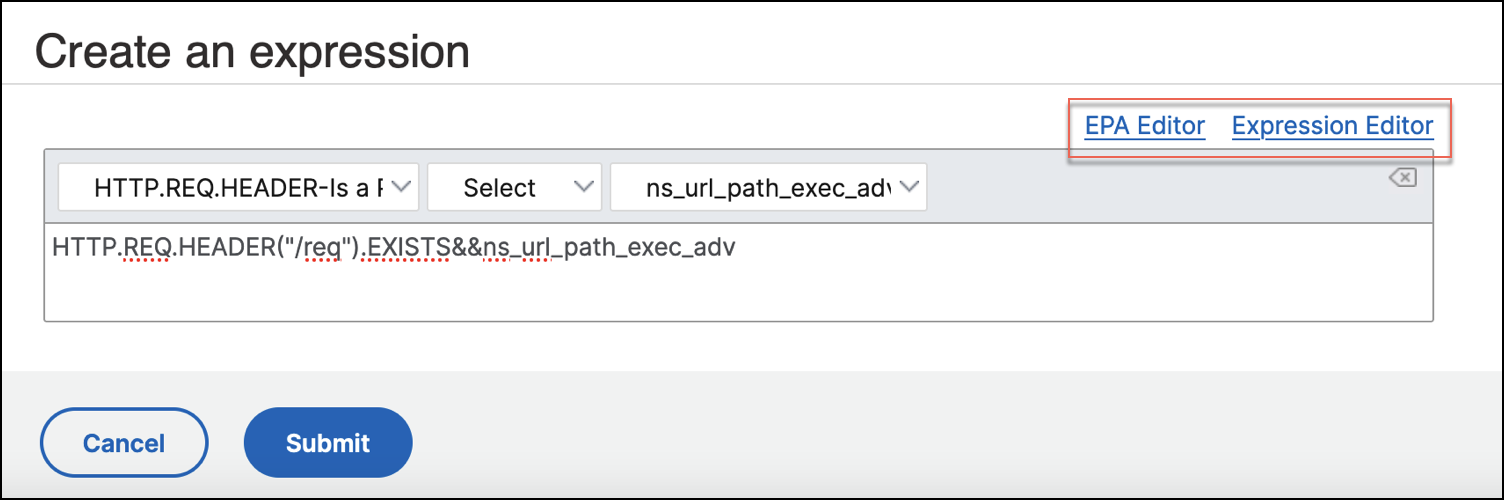
If you want to create a custom policy expression, click on EPA Editor or Expression Editor to build your expressions. Review your expressions in Preview Expressions and then click Submit.
-
Select the target NetScaler instance on which the configuration should be deployed and click Submit.