-
Configuring the VPN User Experience
-
How to Configure Full VPN Setup on a Citrix Gateway Appliance
-
Integrating the Citrix Gateway plug-in with Citrix Receiver™
-
AlwaysOn VPN before Windows logon (Formally AlwaysOn service)
-
-
Installing and Configuring Citrix Gateway in a Double-Hop DMZ
-
Configuring Settings on the Virtual Servers on the Citrix Gateway Proxy
-
Configuring the Appliance to Communicate with the Appliance Proxy
-
Configuring Citrix Gateway to Handle the STA and ICA Traffic
-
Opening the Appropriate Ports on the Firewalls
-
-
Maintaining and Monitoring the System
-
Deploying with Citrix Endpoint Management, Citrix Virtual Apps, and Citrix Virtual Desktops™
-
Accessing Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ Resources with the Web Interface
-
Integrating Citrix Gateway with Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops
-
Configuring Additional Web Interface Settings on Citrix Gateway
-
Configuring Access to Applications and Virtual Desktops in the Web Interface
-
-
Integrate Citrix Gateway with Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops
-
Configuring Settings for Your Citrix Endpoint Management Environment
-
Configuring Load Balancing Servers for Citrix Endpoint Management
-
Configuring Load Balancing Servers for Microsoft Exchange with Email Security Filtering
-
Configuring Citrix Endpoint Management NetScaler® Connector (XNC) ActiveSync Filtering
-
Allowing Access from Mobile Devices with Citrix Mobile Productivity Apps
-
Configuring Domain and Security Token Authentication for Citrix Endpoint Management
-
Configuring Client Certificate or Client Certificate and Domain Authentication
-
-
Citrix Gateway Enabled PCoIP Proxy Support for VMware Horizon View
-
Proxy Auto Configuration for Outbound Proxy support for Citrix Gateway
-
Integrate Citrix Gateway with Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Opening the Appropriate Ports on the Firewalls
You must ensure that the appropriate ports are open on the firewalls to support the different connections that occur among the various components involved in a double-hop DMZ deployment. For more information about the connection process, see Communication Flow in a Double-Hop DMZ Deployment.
The following figure shows common ports that can be used in a double-hop DMZ deployment.
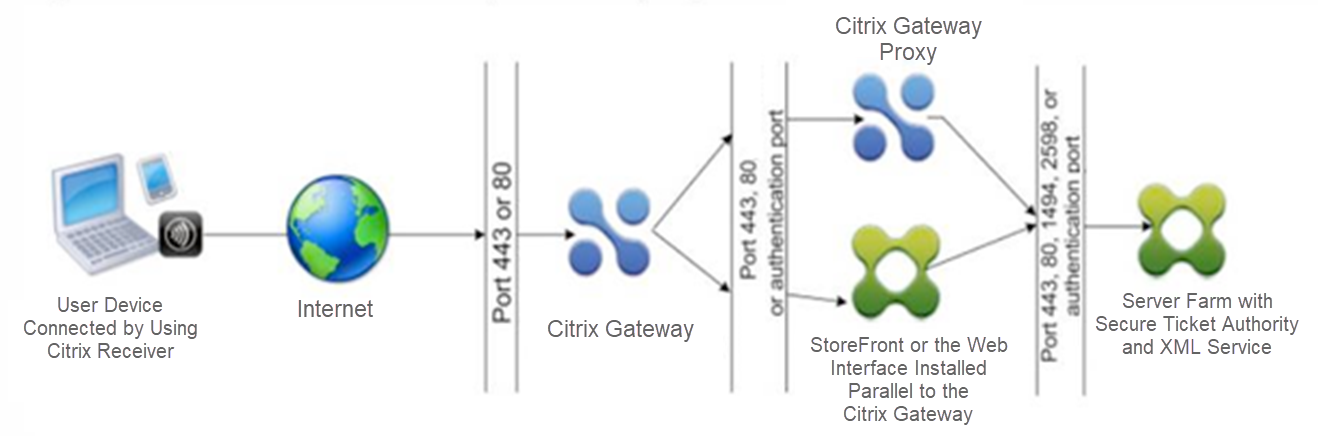
The following table shows the connections that occur through the first firewall and the ports that must be open to support the connections.
| Connections through the first firewall | Ports used |
|---|---|
| The web browser from the Internet connects to Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ. Note: Citrix Gateway includes an option to redirect connections that are made on port 80 to a secure port. If you enable this option on Citrix Gateway, you can open port 80 through the first firewall. When a user makes an unencrypted connection to Citrix Gateway on port 80, Citrix Gateway automatically redirects the connection to a secure port. | Open TCP port 443 through the first firewall. |
| Citrix Receiver from the Internet connects to Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ. | Open TCP port 443 through the first firewall. |
The following table shows the connections that occur through the second firewall and the ports that must be open to support the connections.
| Connections through the second firewall | Ports used |
|---|---|
| Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ connects to the Web Interface in the second DMZ. | Open either TCP port 80 for an unsecure connection or TCP port 443 for a secure connection through the second firewall. |
| Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ connects to Citrix Gateway in the second DMZ. | Open TCP port 443 for a secure SOCKS connection through the second firewall. |
| If you enabled authentication on Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ, this appliance might need to connect to an authentication server in the internal network. | Open the TCP port on which the authentication server listens for connections. Examples include port 1812 for RADIUS and port 389 for LDAP. |
The following table shows the connections that occur through the third firewall and the ports that must be open to support the connections.
| Connections through the third firewall | Ports used |
|---|---|
| StoreFront or the Web Interface in the second DMZ connects to the XML Service hosted on a server in the internal network. | Open either port 80 for an unsecure connection or port 443 for a secure connection through the third firewall. |
| StoreFront or the Web Interface in the second DMZ connects to the Secure Ticket Authority (STA) hosted on a server in the internal network. | Open either port 80 for an unsecure connection or port 443 for a secure connection through the third firewall. |
| Citrix Gateway in the second DMZ connects to the STA residing in the secure network. | Open either port 80 for an unsecure connection or port 443 for a secure connection through the third firewall. |
| Citrix Gateway in the second DMZ makes an ICA connection to a published application or virtual desktop on a server in the internal network. | Open TCP port 1494 to support ICA connections through the third firewall. If you enabled session reliability on Citrix Virtual Apps, open TCP port 2598 instead of 1494. |
| If you enabled authentication on Citrix Gateway in the first DMZ, this appliance may need to connect to an authentication server in the internal network. | Open the TCP port on which the authentication server listens for connections. Examples include port 1812 for RADIUS and port 389 for LDAP. |
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.