-
Configuration guide for Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ workloads
-
Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator™ on-premises configuration on Citrix SD-WAN appliance
-
-
-
Configure firewall segmentation
-
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Configure firewall segmentation
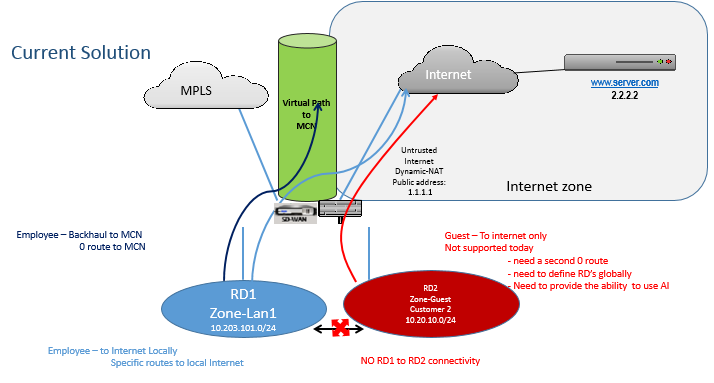
Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) firewall segmentation provides multiple routing domains accesses to the internet through a common interface, with each domain’s traffic isolated from that of the others. For example, employees and guests can access the internet through the same interface, without any access to each other’s traffic.
- Local guest-user Internet access
- Employee-user Internet access for defined applications
- Employee-users may continue hairpin all other traffic to the MCN
- Allow the user to add specific routes for specific routing domains.
- When enabled, this feature applies to all routing domains.
You can also create multiple access interfaces to accommodate separate public facing IP addresses. Either option provides the required security necessary for each user group.
Note
For more information, see how to configure VRFs.
To configure internet services for all Routing Domains:
-
Create Internet Service for a Site. Navigate to Connections > View Region > View Site > [Site Name] > Internet Service > Section > WAN Links and, under WAN Links, select the Use check box.
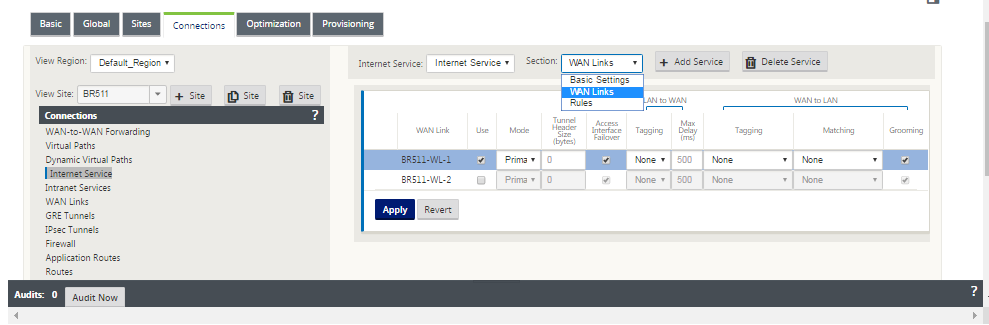
Note
You should see that 0.0.0.0/0 routes added, one per routing domain, under Connections > View Region > View Site > [Site Name] > Routes.
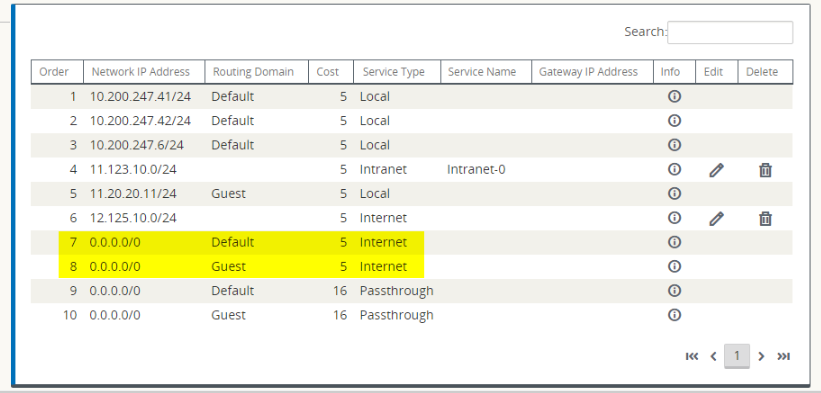
It is no longer required to have all routing domains enabled at the MCN.
-
If you disable routing domains at the MCN, the following message appears if the domains are in use at a branch site:
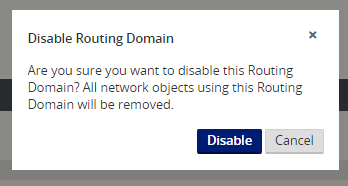
-
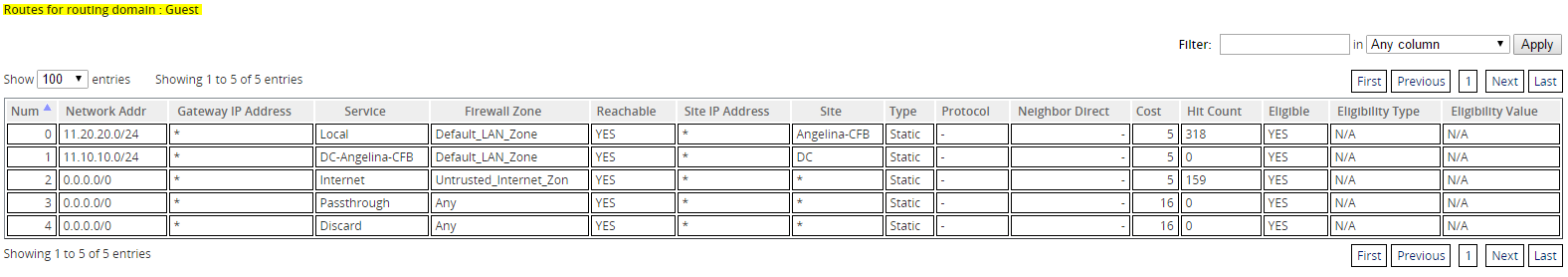
You can confirm that each routing domain is using the internet service by checking the Routing Domain column in the Flows table of the web management interface under Monitor > Flows.
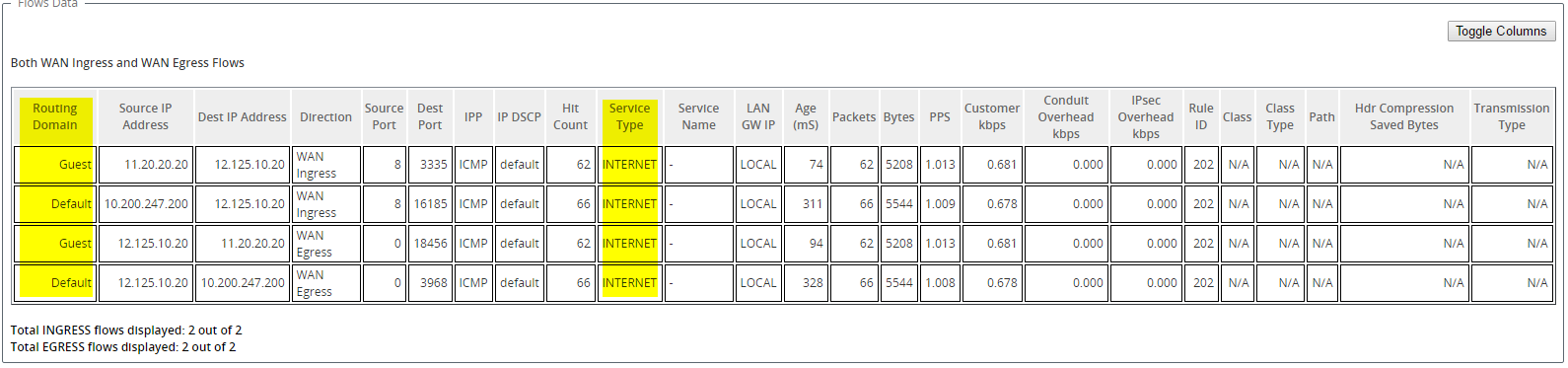
-
You can also check the routing table for each routing domain under Monitor > Statistics > Routes.
Use Cases
In previous Citrix SD-WAN™ releases, virtual routing and forwarding had the following issues, which have been resolved.
- Customers have multiple routing domains at a branch site without the requirement to include all domains at the data center (MCN). They need the ability to isolate different customers’ traffic in a secure manner
- Customers must be able to have a single accessible firewalled Public IP address for multiple routing domains to access the internet at a site (extend beyond VRF lite).
- Customers need an Internet route for each routing domain supporting different services.
- Multiple routing domains at a branch site.
- Internet Access for different routing domains.
Multiple routing domains at a branch site
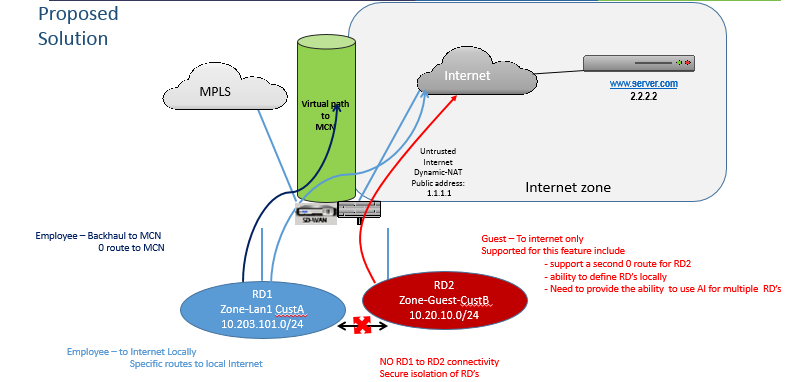
With the Virtual Forwarding and Routing Firewall segmentation enhancements, you can:
- Provide an infrastructure, at the branch site, that supports secure connectivity for at least two user groups, such as employees and guests. The infrastructure can support up to 16 routing domains.
- Isolate each routing domain’s traffic from the traffic of any other routing domain.
-
Provide internet access for each routing domain,
-
A common Access Interface is required and acceptable
-
An Access Interface for each group with separate Public facing IP addresses
-
- Traffic for the employee can be routed directly out to the local internet (specific applications)
- Traffic for the employee can be routed or backhauled to the MCN for extensive filtering (0 route)
- Traffic for the routing domain can be routed directly out to the local internet (0 route)
- Supports specific routes per routing domain, if necessary
- Routing domains are VLAN based
- Removes the requirement for the RD to have to reside at the MCN
- Routing Domain can now be configured at a branch site only
- Allows you to assign multiple RD to an access interface (once enabled)
- Each RD is assigned a 0.0.0.0 route
- Allows specific routes to be added for an RD
- Allows traffic from different RD to exit to the internet using the same access interface
- Allows you to configure a different access interface for each RD
- Must be unique subnets (RD are assigned to a VLAN)
- Each RD can use the same FW default Zone
- The traffic is isolated through the Routing Domain
- Outbound flows have the RD as a component of the flow header. Allows SD-WAN to map return flows to correct Routing domain.
Prerequisites to configure multiple routing domains:
- Internet access is configured and assigned to a WAN Link.
- Firewall configured for NAT and correct policies applied.
- Second routing domain added globally.
- Each routing domain added to a site.
- At Sites > Site Name > WAN Links > WL2 [name] > Access Interface, ensure that the check box is available and internet service has been defined correctly. If you cannot select the check box, the internet service is not defined or assigned to a WAN link for the site.
Deployment scenarios
Limitations
-
The internet service must be added to the WAN link before you can enable Internet access for all Routing Domains. (Until you do, the check box for enabling this option is grayed out).
After enabling internet access for all routing domains, auto add a dynamic-NAT rule.
- Up to 16 Routing Domains per site.
- Access Interface (AI): Single AI per subnet.
- Multiple AIs require a separate VLAN for each AI.
-
If you have two routing domains at a site and have a single WAN Link, both domains use the same public IP address.
- If Internet access for all routing domains is enabled, all sites can route to Internet. (If one routing domain does not require internet access, you can use the firewall to block its traffic.)
-
No support for the same subnet in multiple routing domains.
-
There is no audit functionality
- The WAN links are shared for Internet access.
- No QOS per routing domain; first come first serve.
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.