PPPoE Sessions
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) connects multiple computer users on an Ethernet LAN to a remote site through common customer premises appliances, for example; Citrix SD-WAN. PPPoE allows users to share a common Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable modem, or wireless connection to the Internet. PPPoE combines the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), commonly used in dialup connections, with the Ethernet protocol, which supports multiple users in a LAN. The PPP protocol information is encapsulated within an Ethernet frame.
Citrix SD-WAN appliances use PPPoE to provide support Internet service provider (ISP) to have ongoing and continuous DSL and cable modem connections unlike dialup connections. PPPoE provides each user-remote site session to learn each other’s network addresses through an initial exchange called “discovery”. After a session is established between an individual user and the remote site, for example, an ISP provider, the session can be monitored. Corporations use shared Internet access over DSL lines using Ethernet and PPPoE.
Citrix SD-WAN act as a PPPoE client. It authenticates with PPPoE server and obtains dynamic IP address, or uses static IP address to establish PPPoE connections.
The following is required to establish successful PPPoE sessions:
- Configure virtual network interface (VNI).
- Unique credentials for creating PPPoE session.
- Configure WAN link. Each VNI can have only one WAN link configured.
- Configure Virtual IP address. Each session obtains a unique IP address, dynamic, or static based on the provided configuration.
- Deploy appliance in bridge mode to use PPPoE with static IP address and configure the interface as “trusted.”
- Static IP is preferred to have a configuration to force the server proposed IP; if different from the configured static IP, otherwise an error can occur.
- Deploy appliance as an Edge device to use PPPoE with dynamic IP and configure the interface as “untrusted.”
- Authentication protocols supported are, PAP, CHAP, EAP-MD5, EAP-SRP.
- Maximum number of multiple sessions depends on the number of VNIs configured.
-
Create multiple VNIs to support Multiple PPPoE sessions per interface group.
Note:
Multiple VNIs are allowed to create with same 802.1Q VLAN tag.
Limitations for PPPoE configuration:
- 802.1q VLAN tagging is not supported.
- EAP-TLS authentication is not supported.
- Address/Control compression.
- Deflate Compression.
- Protocol field compression negotiation.
- Compression Control Protocol.
- BSD Compress Compression.
- IPv6 and IPX protocols.
- PPP Multi Link.
- Van Jacobson style TCP/IP header compression.
- Connection-ID compression option in Van Jacobson style TCP/IP header compression.
- PPPoE is not supported on LTE interfaces
From Citrix SD-WAN 11.3.1 release, an extra 8 bytes PPPoE header is considered for adjusting TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS). The extra 8 bytes PPPoE header adjusts the MSS in the synchronize packets based on the MTU.
To facilitate PPPoE configuration, DHCP Client option is replaced with a new option called the Client Mode in the SD-WAN web management interface under Sites configuration.
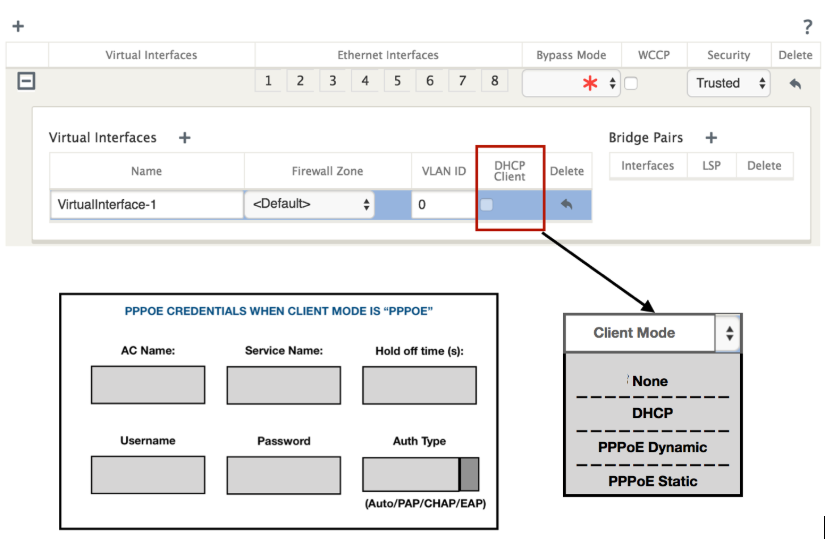
The following table describes the Client Mode PPPoE configuration options available on an MCN and branch SD-WAN appliance, respectively.
MCN
- None
- PPPoE Static
Branch
- None
- PPPoE Static
- PPPoE Dynamic
- DHCP
Configure MCN appliance
-
In the SD-WAN MCN appliance GUI, navigate to configuration > Virtual WAN > Configuration Editor. Add site under the Basic tab. For more information, refer to the branch node configuration at, configure MCN.
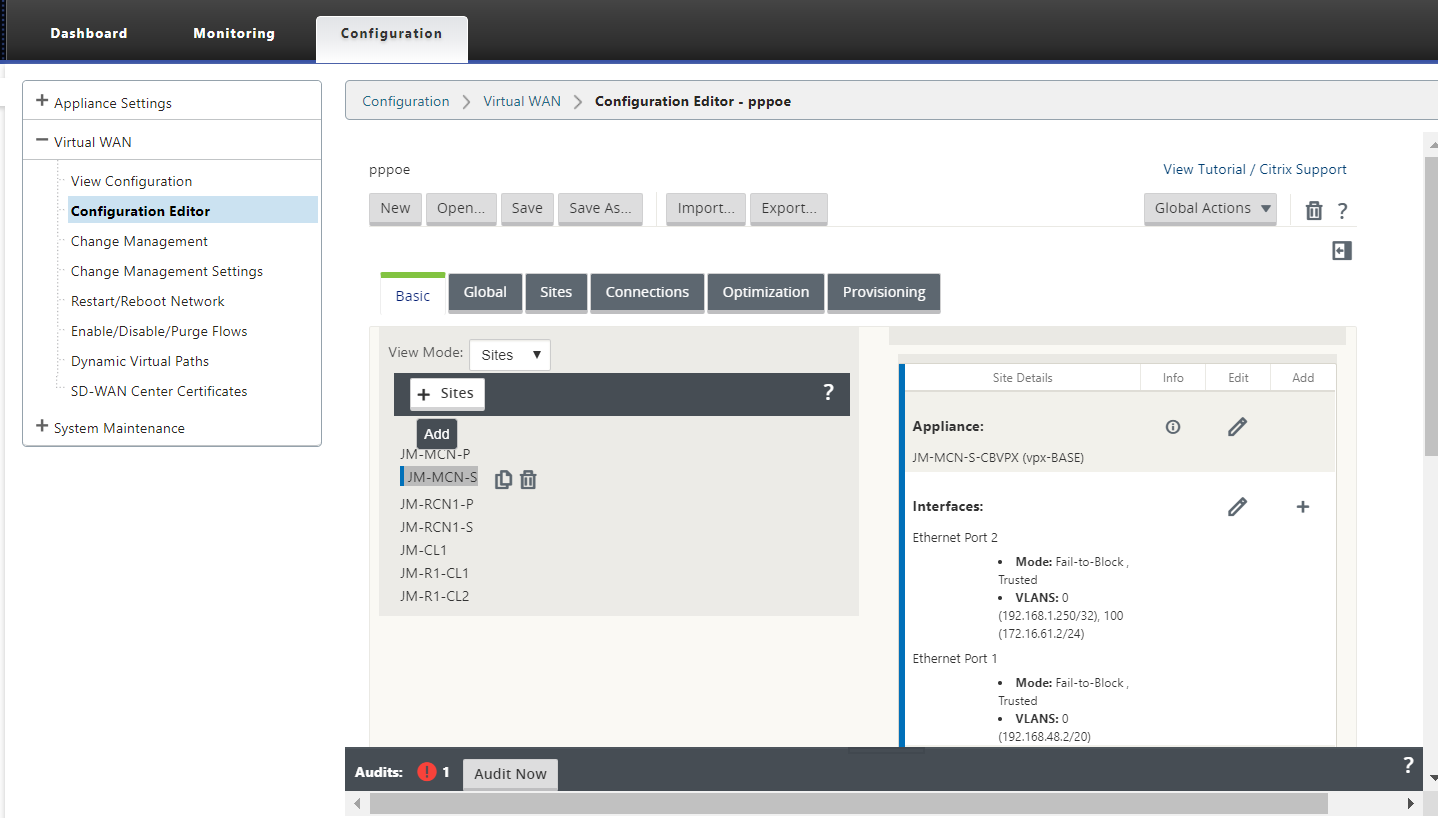
-
After the new site is created, open the Sites tab. Select the newly created site from the View Site drop-down list.
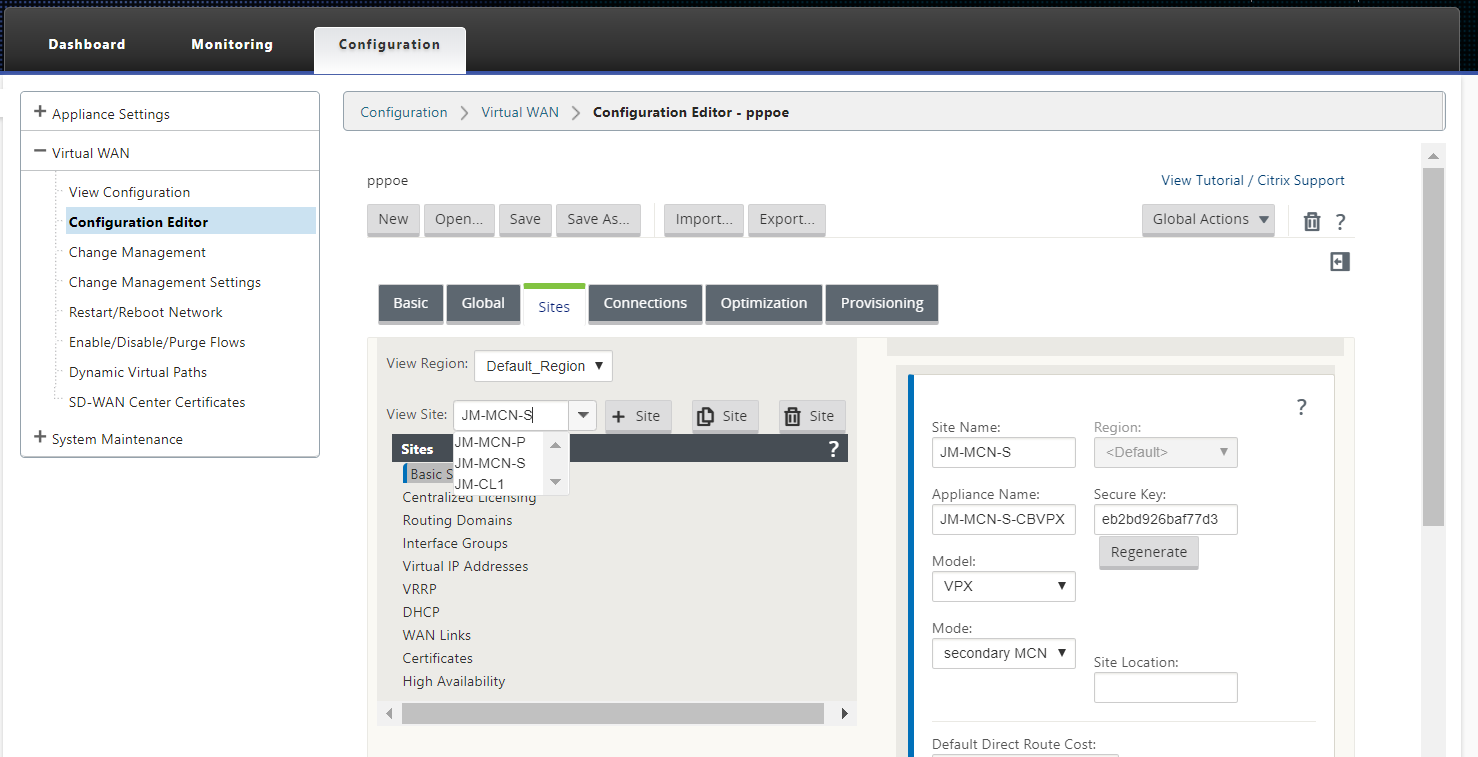
-
Select Interface Groups for the MCN site. Do the following:
- Add Virtual Interfaces.
- Configure Ethernet Interfaces.
- Configure Bypass Mode.
- Choose WCCP, if necessary.
- Choose Security – Trusted/Untrusted.
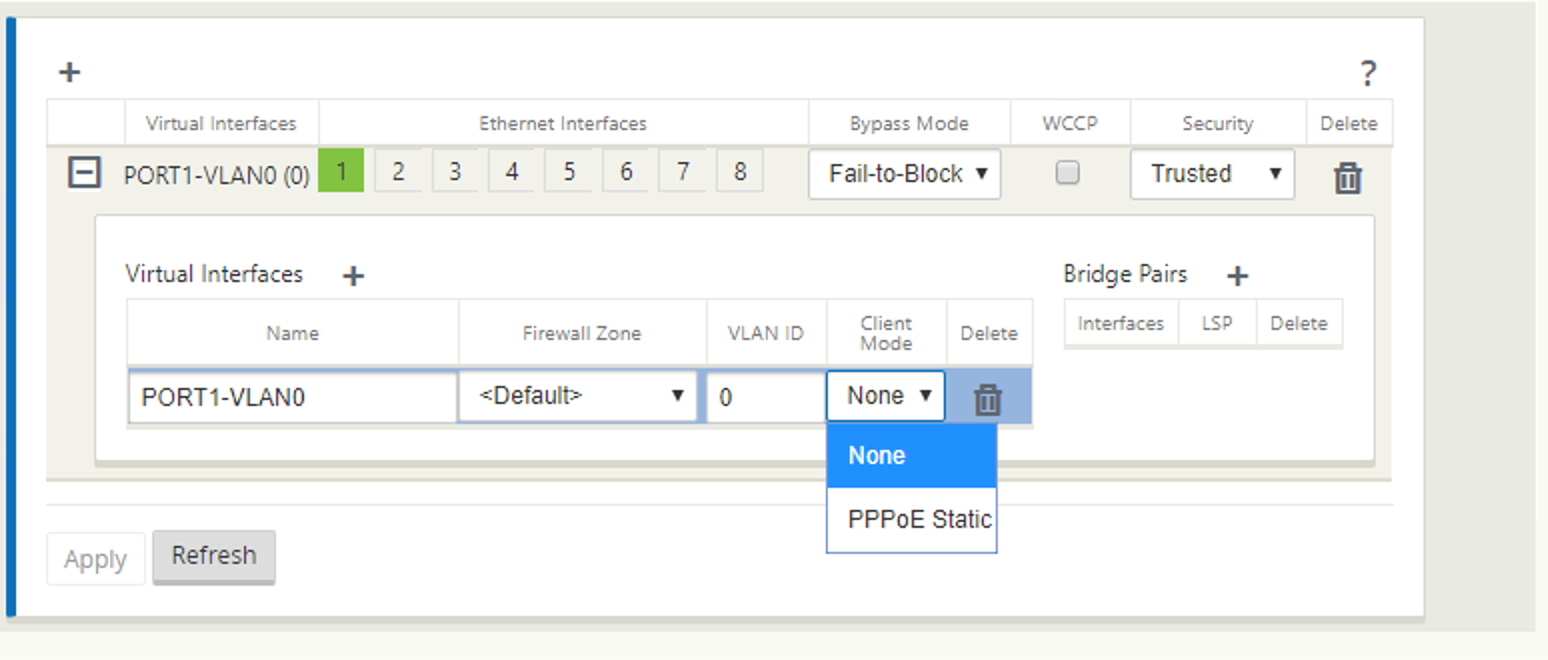
For virtual interface:
- Configure Name, Firewall Zone, VALN ID, and Client Mode.
- A VNI configured with multiple interfaces can have only one interface used for PPPoE connectivity.
- If a VNI configured with multiple interfaces and a PPPoE connectivity is changed to a different interface, then the monitor page can be used to stop the existing session and start a new session, then a new session can be established over the new interface.
-
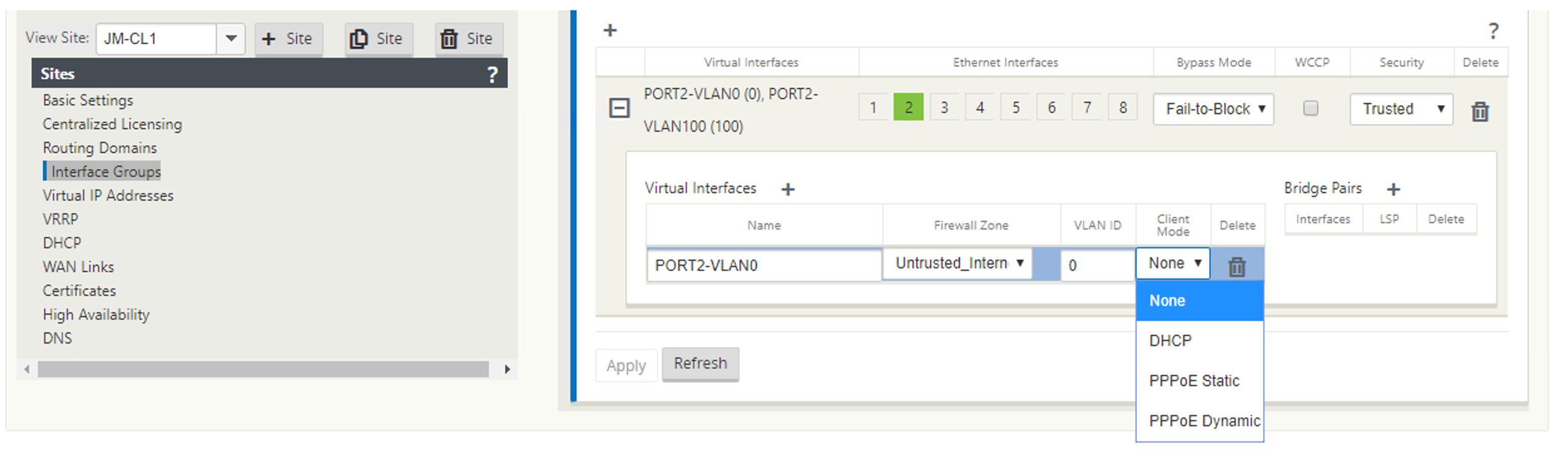
Select PPPoE Static or None based on your network configuration requirement for the Client Mode option on the MCN appliance. The following more options are displayed.
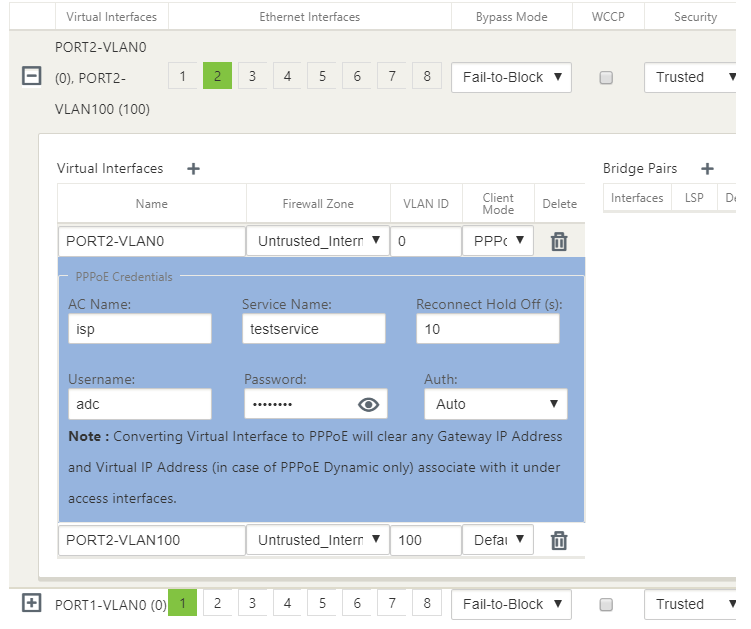
Configure the following PPPoE parameters and click Apply.
- Access Concentrator (AC) Name field.
- Service Name.
- Hold-off reconnect time (default is to reconnect immediately, ‘0’)
- Authentication type - (AUTO/PAP/CHAP/EAP).
- When Auth option is set to Auto, the SD-WAN appliance honors the supported authentication protocol request received from the server.
- When Auth option is set to PAP/CHAP/EAP, then only specific authentication protocols are honored. If PAP is in the configuration and server sends an authentication request with CHAP, the connection request is rejected. If server does not negotiate with PAP, an authentication failure occurs.
- CHAP includes – CHAP, Microsoft CHAP, and Microsoft CHAPv2.
- EAP supports EAP-MD5.
-
User name and password.
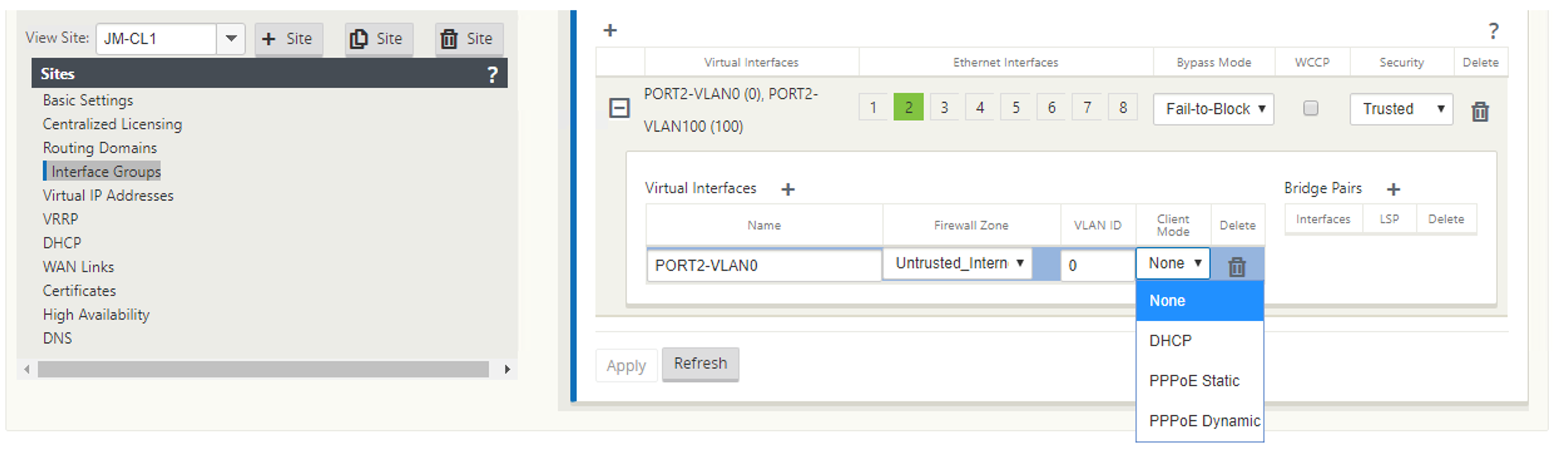
The following figure displays the PPPoE client mode options for a branch SD-WAN appliance. If PPPoE Dynamic is selected, the VNI is required to be “Untrusted.”
Configure WAN links
-
In the SD-WAN GUI, navigate to Sites > WAN Links. Only one WAN link creation is allowed per PPPoE static or dynamic VNI. The WAN link configuration varies depending on the VNI selection of the Client Mode.
-
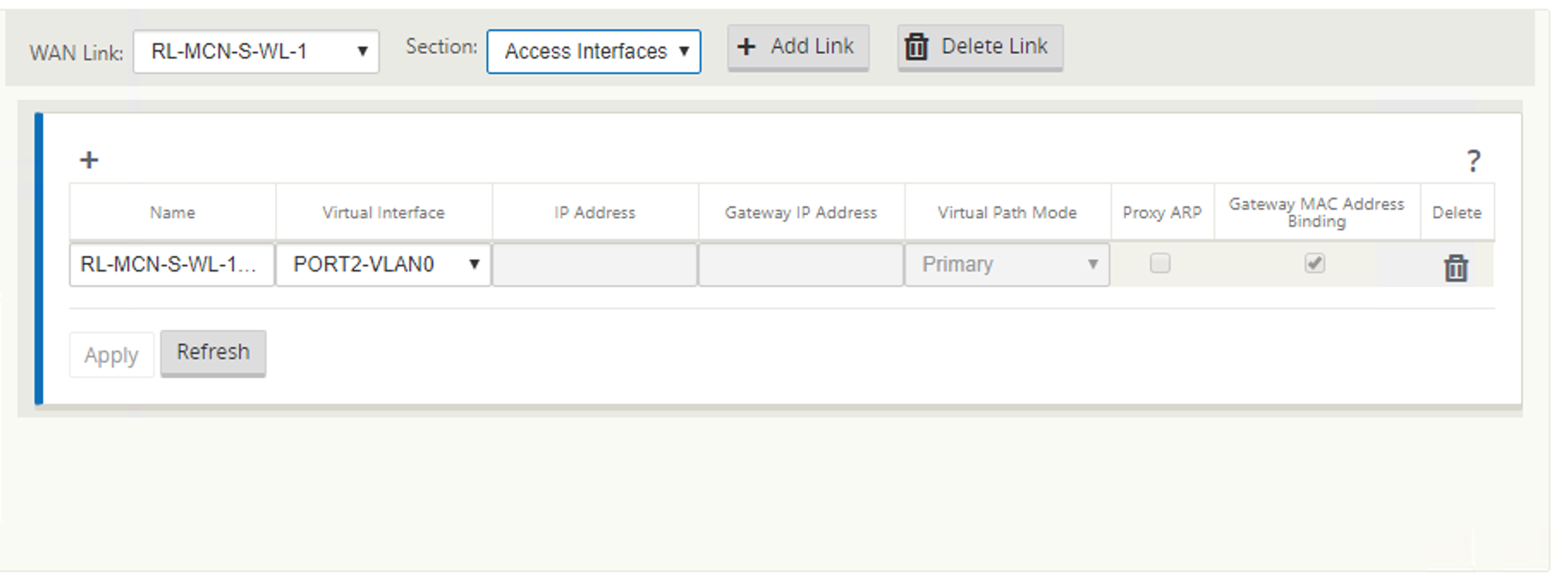
If the VNI is configured with PPPoE dynamic client mode:
- IP address and Gateway IP address fields become inactive.
- Virtual path mode is set to “Primary.”
- Proxy ARP cannot be configured.
By default, Gateway MAC Address Binding is selected.
-
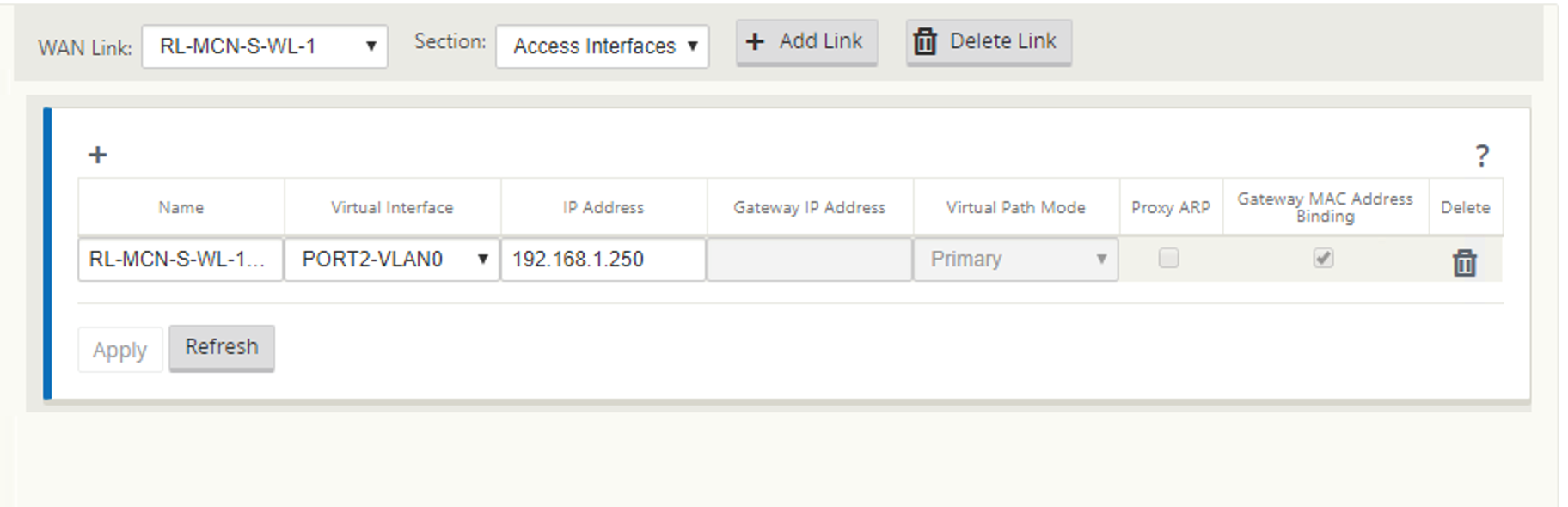
If the VNI is configured with PPPoE static client mode, configure the IP address.
Note:
If the server does not honor the configured static IP address and offers a different IP address, an error occurs. The PPPoE session tries to re-establish connection periodically, until the server accepts the configured IP address.
Monitor PPPoE sessions
You can monitor PPPoE sessions by navigating to the Monitoring > PPPoE page in the SD-WAN GUI.
The PPPoE page provides status information of the configured VNIs with the PPPoE static or dynamic client mode. It allows you to manually start or stop the sessions for troubleshooting purposes.
- If the VNI is up and ready, the IP and Gateway IP columns shows the current values in the session. It indicates that these are recently received values.
- If the VNI is stopped or is in failed state, the values are last received values.
- Hovering mouse over Gateway IP column shows the MAC address of the PPPoE Access Concentrator from where the Session and IP is received.
-
Hovering mouse over the “state” value shows a message, which is more useful for a “Failed” state.
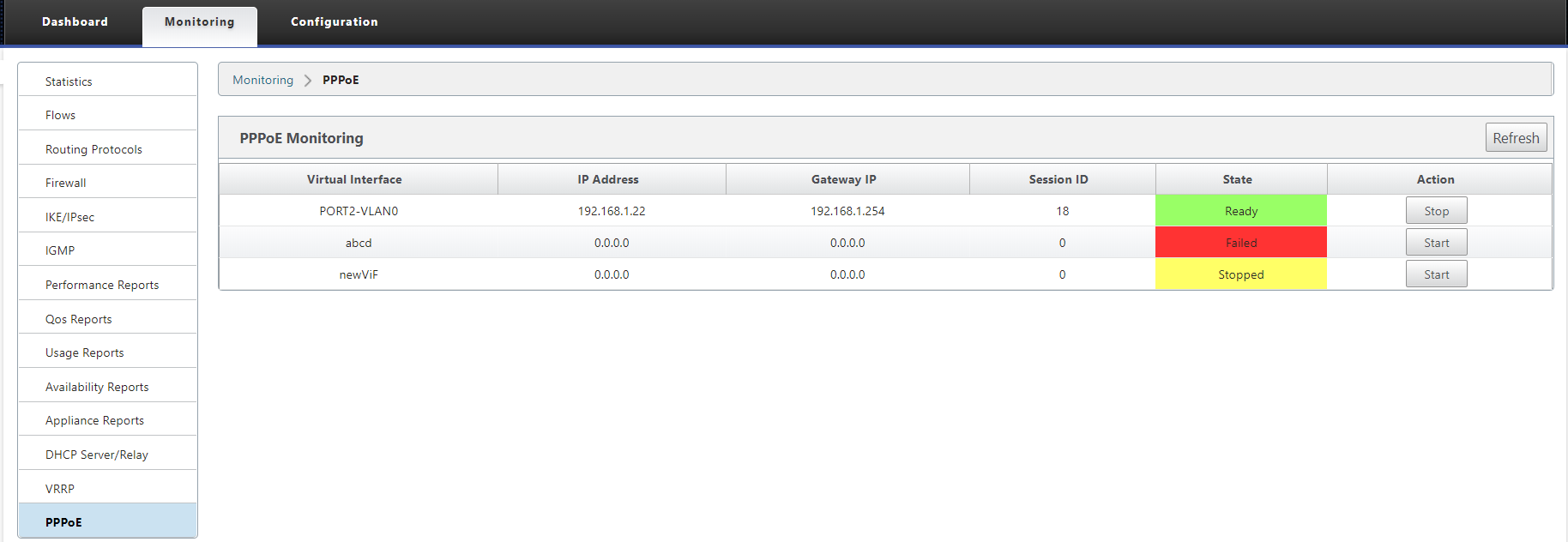
The State column displays the status of the PPPoE session using three color codes; green, red, yellow, and values. The following table describes the states and descriptions. You can hover over the states to obtain descriptions.
| PPPoE session type | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Configured | Yellow | A VNI is configured with PPPoE. This is an initial state. |
| Dialing | Yellow | After a VNI is configured, the PPPoE session state moves to dialing state by starting the PPPoE discovery. Packet information is captured. |
| Session | Yellow | VNI is moved from Discovery state to Session state. waiting to receive IP, if dynamic or waiting for acknowledgment from server for the advertised IP, if static. |
| Ready | green | IP packets are received and VNI and associated WAN link is ready for use. |
| Failed | red | PPP/PPPoE session is terminated. The reason for the failure can be due to Invalid Configuration or fatal error. The session attempts to reconnect after 30 seconds. |
| Stopped | yellow | PPP/PPPoE session is manually stopped. |
| Terminating | yellow | An intermediate state terminating due to a reason. This state automatically starts after certain duration (5 seconds for normal error or 30 secs for a fatal error). |
| Disabled | yellow | The SD-WAN service is disabled. |
Troubleshooting PPPoE session failures
On the Monitoring page, when there is a problem in establishing a PPPoE session:
- Hovering mouse over the Failed status shows the reason for the recent failure.
- To establish a fresh session or for troubleshooting an active PPPoE session, use the monitoring->PPPoE page and restart the session.
- If a PPPoE session is stopped manually, it cannot be started until either it is manually started and a configuration change is activated, or service is restarted.
A PPPoE session might fail due to the following reasons:
-
When SD-WAN fails to authenticate itself to the peer due to incorrect username/password in the configuration.
-
PPP negotiation fails - negotiation does not reach the point where at least one network protocol is running.
-
System memory or system resource issue.
-
Invalid/bad configuration (wrong AC name or service name).
-
Failed to open serial port due to operating system error.
-
No response received for the echo packets (link is bad or server is not responding).
-
There were several continuous unsuccessful dialing sessions with in a minute.
After 10 consecutive failures, the reason for the failure is observed.
- If the failure is normal, it restarts immediately.
- If the failure is an error then restart reverts for 10 seconds.
- If the failure is fatal the restart reverts for 30 seconds before restarting.
LCP Echo request packets are generated from SD-WAN for every 60 seconds and failure to receive 5 echo responses is considered as link failure and it re-establishes the session.
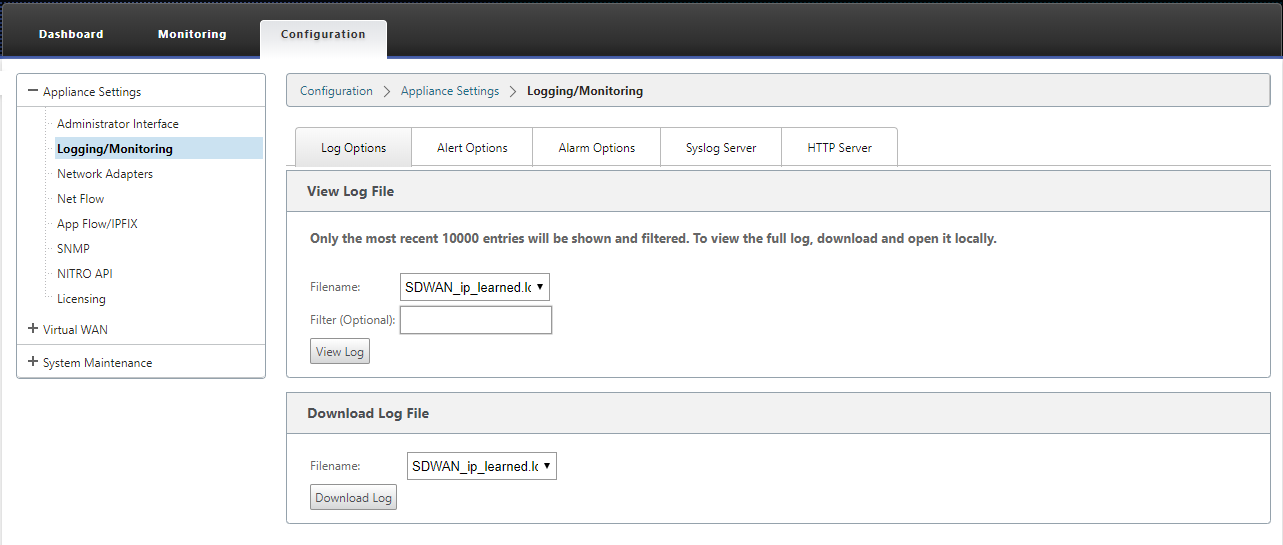
PPPoE log file
The SDWAN_ip_learned.log file contains logs related to PPPoE.
To view or download the SDWAN_ip_learned.log file from the SD-WAN GUI, navigate to Appliance Settings > Logging/Monitoring > Log Options. View or download the SDWAN_ip_learned.log file.