Convert a NetScaler MPX 15000 appliance to a NetScaler SDX 15000 appliance
You can convert a NetScaler MPX appliance to an NetScaler SDX appliance by upgrading the software through a new solid-state drive (SSD). NetScaler supplies a field conversion kit to migrate a NetScaler MPX appliance to an SDX appliance.
The conversion requires all eight SSDs.
Note
Citrix recommends that you configure the lights out management (LOM) port of the appliance before starting the conversion process. For more information on the LOM port of the ADC appliance, see Lights out management port of the NetScaler SDX appliance.
To convert an MPX appliance to an SDX appliance, you must access the appliance through a console cable attached to a computer or terminal. Before connecting the console cable, configure the computer or terminal to support the following configuration:
- VT100 terminal emulation
- 9600 baud
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- Parity and flow control set to NONE
Connect one end of the console cable to the RS232 serial port on the appliance, and the other end to the computer or terminal.
Note
To use a cable with an RJ-45 converter, insert the optional converter into the console port and attach the cable to it.
Citrix® recommends you to connect a VGA monitor to the appliance to monitor the conversion process, because the LOM connection is lost during the conversion process.
With the cable attached, verify that the MPX appliance’s components are functioning correctly. You are then ready to begin the conversion. The conversion process modifies the BIOS, installs a Citrix Hypervisor and a Service Virtual Machine image, and copies the NetScaler VPX image to the Solid State Drive.
The conversion process also sets up a redundant array of independent disks (RAID) controller for local storage and NetScaler VPX storage. SSD slots #1 and #2 are used for local storage and SSD slots #3 and #4 are used for NetScaler VPX storage.
After the conversion process, modify the appliance’s configuration and apply a new license. You can then provision the VPX instances through the Management Service on what is now an NetScaler SDX appliance.
Verify proper operation of the MPX appliance’s components
- Access the console port and enter the administrator credentials.
-
Run the following command from the command line interface of the appliance to display the serial number:
show hardware. You might need the serial number to log on to the appliance after the conversion.Example
> show hardware Platform: NSMPX-15000-50G 16*CPU+128GB+4*MLX(50)+8*F1X+2*E1K+2*2-CHIP COL 520400 Manufactured on: 9/13/2017 CPU: 2100MHZ Host Id: 1862303878 Serial no: 4VCX9CUFN6 Encoded serial no: 4VCX9CUFN6 Netscaler UUID: d9de2de3-dc89-11e7-ab53-00e0ed5de5aa BMC Revision: 5.56 Done <!--NeedCopy-->The serial number might be helpful when you want to contact Citrix technical support.
-
Run the following command to display the status of the active interfaces:
show interfaceExample
> show interface 1) Interface 0/1 (Gig Ethernet 10/100/1000 MBits) #4 flags=0xc020 <ENABLED, UP, UP, autoneg, HAMON, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=0c:c4:7a:e5:3c:50, uptime 1h08m02s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 Actual: media UTP, speed 1000, duplex FULL, fctl OFF, throughput 1000 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(19446) Bytes(1797757) Errs(0) Drops(19096) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(368) Bytes(75619) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 2) Interface 0/2 (Gig Ethernet 10/100/1000 MBits) #5 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=0c:c4:7a:e5:3c:51, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 3) Interface 10/1 (10G Ethernet) #6 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HAMON, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=200, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:76, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 4) Interface 10/2 (10G Ethernet) #7 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=200, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:77, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 5) Interface 10/3 (10G Ethernet) #8 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:78, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 6) Interface 10/4 (10G Ethernet) #9 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:79, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 7) Interface 10/5 (10G Ethernet) #0 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:aa, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 8) Interface 10/6 (10G Ethernet) #1 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:ab, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 9) Interface 10/7 (10G Ethernet) #2 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:ac, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 10) Interface 10/8 (10G Ethernet) #3 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=00:e0:ed:5d:e5:ad, downtime 1h08m15s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Rx Ring: Configured size=2048, Actual size=512, Type: Elastic 11) Interface 50/1 (50G Ethernet) #13 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=24:8a:07:a3:1f:84, downtime 1h08m22s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 12) Interface 50/2 (50G Ethernet) #12 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=24:8a:07:a3:1f:6c, downtime 1h08m22s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 13) Interface 50/3 (50G Ethernet) #11 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=24:8a:07:a3:1f:98, downtime 1h08m22s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 14) Interface 50/4 (50G Ethernet) #10 flags=0x4000 <ENABLED, DOWN, down, autoneg, HEARTBEAT, 802.1q> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=24:8a:07:94:b9:b6, downtime 1h08m22s Requested: media AUTO, speed AUTO, duplex AUTO, fctl OFF, throughput 0 LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(0) Bytes(0) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) NIC: InDisc(0) OutDisc(0) Fctls(0) Stalls(0) Hangs(0) Muted(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. 15) Interface LO/1 (Netscaler Loopback interface) #14 flags=0x20008020 <ENABLED, UP, UP> MTU=1500, native vlan=1, MAC=0c:c4:7a:e5:3c:50, uptime 1h08m18s LLDP Mode: NONE, LR Priority: 1024 RX: Pkts(5073645) Bytes(848299459) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) TX: Pkts(9923625) Bytes(968741778) Errs(0) Drops(0) Stalls(0) Bandwidth thresholds are not set. Done <!--NeedCopy--> -
In the show interface command’s output, verify that all the interfaces are enabled and the status of every interface is shown as UP/UP.
Notes: > >- The interface status is displayed as UP/UP only if the cables are connected to the interfaces. > >- If you do not have an SFP+ transceiver for every port, verify the interfaces in stages. After checking the first set of interfaces, unplug the SFP+ transceivers and plug them in to the next set of ports.
-
Run the following command for each of the interfaces that are not in the UP/UP state:
> enable interface 50/1 Done > enable interface 50/2 Done > enable interface 50/3 Done > enable interface 50/4 Done <!--NeedCopy-->Where x is the new interface number
-
Run the following command to verify that the status of the power supplies is normal:
stat system –detailExample
> stat system -detail NetScaler Executive View System Information: Up since Sat Dec 5 04:17:29 2020 Up since(Local) Sat Dec 5 04:17:29 2020 Memory usage (MB) 4836 InUse Memory (%) 4.08 Number of CPUs 13 System Health Statistics (Standard): CPU 0 Core Voltage (Volts) 1.80 CPU 1 Core Voltage (Volts) 1.80 Main 3.3 V Supply Voltage 3.35 Standby 3.3 V Supply Voltage 3.23 +5.0 V Supply Voltage 5.00 +12.0 V Supply Voltage 12.06 Battery Voltage (Volts) 3.02 Intel CPU Vtt Power(Volts) 0.00 5V Standby Voltage(Volts) 4.95 Voltage Sensor2(Volts) 0.00 CPU Fan 0 Speed (RPM) 3500 CPU Fan 1 Speed (RPM) 3600 System Fan Speed (RPM) 3600 System Fan 1 Speed (RPM) 3600 System Fan 2 Speed (RPM) 3500 CPU 0 Temperature (Celsius) 37 CPU 1 Temperature (Celsius) 47 Internal Temperature (Celsius) 26 Power supply 1 status NORMAL Power supply 2 status NORMAL Power supply 3 status NOT SUPPORTED Power supply 4 status NOT SUPPORTED System Disk Statistics: /flash Size (MB) 23801 /flash Used (MB) 7009 /flash Available (MB) 14887 /flash Used (%) 32 /var Size (MB) 341167 /var Used (MB) 56502 /var Available (MB) 257371 /var Used (%) 18 System Health Statistics(Auxiliary): Voltage 0 (Volts) 1.20 Voltage 1 (Volts) 1.20 Voltage 2 (Volts) 1.20 Voltage 3 (Volts) 1.20 Voltage 4 (Volts) 1.54 Voltage 5 (Volts) 0.00 Voltage 6 (Volts) 0.00 Voltage 7 (Volts) 0.00 Fan 0 Speed (RPM) 3600 Fan 1 Speed (RPM) 0 Fan 2 Speed (RPM) 0 Fan 3 Speed (RPM) 0 Temperature 0 (Celsius) 24 Temperature 1 (Celsius) 30 Temperature 2 (Celsius) 0 Temperature 3 (Celsius) 0 Done <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to generate a tar of system configuration data and statistics:
show techsupportExample
> show techsupport showtechsupport data collector tool - $Revision$! NetScaler version 13.0 The NS IP of this box is 10.217.206.43 This is not HA configuration Copying selected configuration files .... Running shell commands .... Running CLI show commands .... Collecting ns running configuration.... Collecting running gslb configuration.... Running CLI stat commands .... Running vtysh commands .... Copying newnslog files .... Copying core files from /var/core .... Copying core files from /var/crash .... Copying GSLB location database files .... Copying GSLB auto sync log files .... Copying Safenet Gateway log files .... Copying messages, ns.log, dmesg and other log files .... Creating archive .... /var/tmp/support/support.tgz ---- points to ---> /var/tmp/support/collector_P_10.217.206.43_5Dec2020_05_32.tar.gz showtechsupport script took 1 minute(s) and 17 second(s) to execute. Done <!--NeedCopy-->Note
The output of the command is available in the /var/tmp/support/collector_<IP_address>_P_<date>.tar.gz file. Copy this file to another computer for future reference. The output of the command might be helpful when you want to contact Citrix technical support.
-
At the command line interface, switch to the shell prompt. Type:
shellExample
> shell Copyright (c) 1992-2013 The FreeBSD Project. Copyright (c) 1979, 1980, 1983, 1986, 1988, 1989, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994 The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. root@ns# <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to verify the number of Cavium cards available depending upon your appliance:
root@ns# grep "memory" /var/nslog/dmesg.bootExample
root@ns# grep "memory" /var/nslog/dmesg.boot real memory = 139586437120 (133120 MB) avail memory = 132710871040 (126562 MB) root@ns# <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to verify the number of CPU cores depending upon your appliance:
root@ns# grep "cpu" /var/nslog/dmesg.bootExample
root@ns# grep "cpu" /var/nslog/dmesg.boot cpu0 (BSP): APIC ID: 0 cpu1 (AP): APIC ID: 2 cpu2 (AP): APIC ID: 4 cpu3 (AP): APIC ID: 6 cpu4 (AP): APIC ID: 8 cpu5 (AP): APIC ID: 10 cpu6 (AP): APIC ID: 12 cpu7 (AP): APIC ID: 14 cpu8 (AP): APIC ID: 16 cpu9 (AP): APIC ID: 18 cpu10 (AP): APIC ID: 20 cpu11 (AP): APIC ID: 22 cpu12 (AP): APIC ID: 24 cpu13 (AP): APIC ID: 26 cpu14 (AP): APIC ID: 28 cpu15 (AP): APIC ID: 30 cpu0: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu1: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu2: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu3: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu4: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu5: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu6: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu7: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu8: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu9: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu10: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu11: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu12: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu13: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu14: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 cpu15: <ACPI CPU> on acpi0 est0: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu0 p4tcc0: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu0 est1: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu1 p4tcc1: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu1 est2: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu2 p4tcc2: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu2 est3: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu3 p4tcc3: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu3 est4: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu4 p4tcc4: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu4 est5: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu5 p4tcc5: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu5 est6: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu6 p4tcc6: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu6 est7: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu7 p4tcc7: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu7 est8: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu8 p4tcc8: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu8 est9: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu9 p4tcc9: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu9 est10: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu10 p4tcc10: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu10 est11: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu11 p4tcc11: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu11 est12: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu12 p4tcc12: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu12 est13: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu13 p4tcc13: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu13 est14: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu14 p4tcc14: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu14 est15: <Enhanced SpeedStep Frequency Control> on cpu15 p4tcc15: <CPU Frequency Thermal Control> on cpu15 root@ns# <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to verify that the /var drive is mounted as
/dev/ ar0s1a: root@ns# df –hExample
root@ns# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Capacity Mounted on /dev/md0 422M 404M 9.1M 98% / devfs 1.0k 1.0k 0B 100% /dev procfs 4.0k 4.0k 0B 100% /proc /dev/ar0s1a 23G 6.9G 14G 32% /flash /dev/ar0s1e 333G 32G 274G 10% /var root@ns# <!--NeedCopy--> -
Type the following command to run the ns_hw_err.bash script, which checks for latent hardware errors: root@ns
# ns_hw_err.bashExample
root@ns# ns_hw_err.bash NetScaler NS13.0: Build 71.3602.nc, Date: Nov 12 2020, 07:26:41 (64-bit) platform: serial 4VCX9CUFN6 platform: sysid 520400 - NSMPX-15000-50G 16*CPU+128GB+4*MLX(50)+8*F1X+2*E1K+2*2-CHIP COL 8955 HDD MODEL: ar0: 434992MB <Intel MatrixRAID RAID1> status: READY Generating the list of newnslog files to be processed... Generating the events from newnslog files... Checking for HDD errors... Checking for HDD SMART errors... Checking for Flash errors... Checking for Mega Raid Controller errors... Checking for SSL errors... Dec 5 06:00:31 <daemon.err> ns monit[996]: 'safenet_gw' process is not running Checking for BIOS errors... Checking for SMB errors... Checking for MotherBoard errors... Checking for CMOS errors... License year: 2020: OK Checking for SFP/NIC errors... Dec 5 06:02:32 <daemon.err> ns monit[996]: 'safenet_gw' process is not running Checking for Firmware errors... Checking for License errors... Checking for Undetected CPUs... Checking for DIMM flaps... Checking for Memory Channel errors... Checking for LOM errors... Checking the Power Supply Errors... Checking for Hardware Clock errors... Script Done. root@ns# <!--NeedCopy--> -
Important: Physically disconnect all ports except the LOM port, including the management port, from the network.
-
At the shell prompt, switch to the ADC command line. Type: exit
Example
root@ns# exit logout Done <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to shut down the appliance. You are asked if you want to completely stop the ADC. Type:
shutdown -p nowExample
> shutdown -p now Are you sure you want to completely stop NetScaler (Y/N)? [N]:y Done > Dec 5 06:09:11 <auth.notice> ns shutdown: power-down by root: Dec 5 06:09:13 <auth.emerg> ns init: Rebooting via init mechanism Dec 5 06:09:13 <syslog.err> ns syslogd: exiting on signal 15 Dec 5 06:09:13 aslearn[1662]: before pthread_join(), task name: Aslearn_Packet_Loop_Task Dec 5 06:09:15 aslearn[1662]: Exiting function ns_do_logging Dec 5 06:09:15 aslearn[1662]: before pthread_join(), task name: Aslearn_WAL_Cleanup_Task Dec 5 06:09:15 aslearn[1662]: before pthread_join(), task name: Aslearn_HA_Primary_Task Dec 5 06:09:15 aslearn[1662]: 1662 exiting gracefully Dec 5 06:09:18 [1672]: nsnet_tcpipconnect: connect() failed; returned -1 errno=61 qat0: qat_dev0 stopped 12 acceleration engines pci4: Resetting device qat1: qat_dev1 stopped 12 acceleration engines pci6: Resetting device qat2: qat_dev2 stopped 12 acceleration engines pci132: Resetting device qat3: qat_dev3 stopped 12 acceleration engines pci134: Resetting device Dec 5 06:09:33 init: some processes would not die; ps axl advised reboot initiated by init with parent kernel Waiting (max 60 seconds) for system process `vnlru' to stop...done Waiting (max 60 seconds) for system process `bufdaemon' to stop...done Waiting (max 60 seconds) for system process `syncer' to stop... Syncing disks, vnodes remaining...0 0 0 done All buffers synced. Uptime: 1h53m18s ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 usbus0: Controller shutdown uhub0: at usbus0, port 1, addr 1 (disconnected) usbus0: Controller shutdown complete usbus1: Controller shutdown uhub1: at usbus1, port 1, addr 1 (disconnected) ugen1.2: <vendor 0x8087> at usbus1 (disconnected) uhub3: at uhub1, port 1, addr 2 (disconnected) ugen1.3: <FTDI> at usbus1 (disconnected) uftdi0: at uhub3, port 1, addr 3 (disconnected) ugen1.4: <vendor 0x1005> at usbus1 (disconnected) umass0: at uhub3, port 3, addr 4 (disconnected) (da0:umass-sim0:0:0:0): lost device - 0 outstanding, 0 refs (da0:umass-sim0:0:0:0): removing device entry usbus1: Controller shutdown complete usbus2: Controller shutdown uhub2: at usbus2, port 1, addr 1 (disconnected) ugen2.2: <vendor 0x8087> at usbus2 (disconnected) uhub4: at uhub2, port 1, addr 2 (disconnected) ugen2.3: <vendor 0x0557> at usbus2 (disconnected) uhub5: at uhub4, port 7, addr 3 (disconnected) ugen2.4: <vendor 0x0557> at usbus2 (disconnected) ukbd0: at uhub5, port 1, addr 4 (disconnected) ums0: at uhub5, port 1, addr 4 (disconnected) usbus2: Controller shutdown complete ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 ixl_shutdown: lldp start 0 acpi0: Powering system off <!--NeedCopy-->
Upgrade the appliance
To upgrade the appliance, follow these steps:
- Power off the ADC appliance.
-
Locate two solid-state drives (SSDs) on the back of the appliance in slot #1 and slot #2, as shown in the following figure:
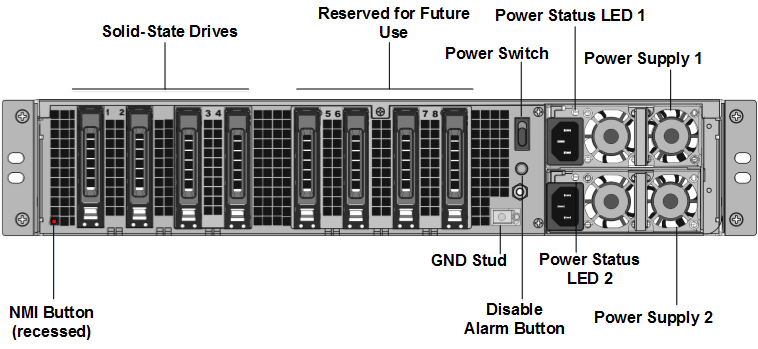
-
Verify that the replacement solid-state drives (SSDs) are the ones required for your ADC model. The conversion requires minimum of four SSDs. The NetScaler label is on the top of one of the SSDs. The SSD is pre-populated with a new version of the BIOS and a recent build of the required NetScaler SDX Management Service. This SSD must be installed in slot # 1.
-
Remove the SSDs by pushing the safety latch of the drive cover down while pulling the drive handle.
-
On the new NetScaler® certified SSD drive, open the drive handle completely to the left. Then insert the new drive into the slot #1 as far as possible.
-
To seat the drive, close the handle flush with the rear side of the appliance so that the drive locks securely into the slot.
Important: The orientation of the SSD is important. When you insert the drive, make sure that the NetScaler product label is at the side.
-
Insert a second NetScaler certified SSD, which matches the capacity of the SSD in slot #1, in slot # 2.
Note: If the license of your appliance is 14040 40G, 14060 40G, 14080 40G, insert more blank NetScaler certified SSDs in slots #3, #4, #5, and #6.
NetScaler SDX Model Included Virtual Instances Platform Maximum SSDs included on base model Extra SSDs for max instances SDX 15020/SDX 15020-50G 5 55 Two 240 GB RAID-supported removable boot solid-state drives (SSDs), (slots 1 and 2). Two 240 GB RAID-supported removable storage repositories (slots 3 and 4 paired) SSDs, and four 480 GB storage repositories (slots 5–6 paired and 7–8 paired) SSDs. NA SDX 15030/SDX 15030-50G 20 55 Two 240 GB RAID-supported removable boot solid-state drives (SSDs), (slots 1 and 2). Two 240 GB RAID-supported removable storage repositories (slots 3 and 4 paired) SSDs, and four 480 GB storage repositories (slots 5–6 paired and 7–8 paired) SSDs. NA Important
Mixing and matching of old and new SSDs is not supported. SSDs in slot #1 and slot #2, which constitute the first RAID pair (local storage), must be of the same size and type. Similarly, SSDs in slot #3 and slot #4, which constitute the second RAID pair (VPX storage), must be of the same size and type. Use only drives that are part of the provided conversion kit.
-
Disconnect all network cables from the data ports and the management ports.
-
Start the ADC appliance. For instructions, see “Switching on the Appliance” in Installing the Hardware.
The conversion process can run for approximately 30 minutes, during which you must not power cycle the appliance. The entire conversion process might not be visible on the console and might appear to be unresponsive.
The conversion process updates the BIOS, installs the Citrix Hypervisor and the Management Service Operating system. It also copies the NetScaler VPX image to the SSD for instance provisioning, and forms the Raid1 pair.
Note: The serial number of the appliance remains the same.
-
Keep the console cable attached during the conversion process. Allow the process to complete, at which point the SDX login: prompt appears.
-
During the conversion process the LOM port connection might be lost as it resets the IP address to the default value of 192.168.1.3. The conversion status output is available on the VGA monitor.
-
The default credentials for the Citrix Hypervisor are changed to root/nsroot after the appliance is converted from an MPX to SDX. If this password does not work, try typing nsroot/the serial number of the appliance. The serial number bar code is available at the back of the appliance, and is also available in the output of the
show hardwarecommand. - To make sure that the conversion is successful, verify that the FVT result indicates success. Run the following command: tail /var/log/fvt/fvt.log
Reconfigure the converted appliance
After the conversion process, the appliance no longer has its previous working configuration. Therefore, you can access the appliance through a web browser only by using the default IP address: 192.168.100.1/16. Configure a computer on network 192.168.0.0 and connect it directly to the appliance’s management port (0/1) with a cross-over Ethernet cable. Alternately, access the NetScaler SDX appliance through a network hub by using a straight through Ethernet cable. Use the default credentials to log on, and then do the following:
- Select the Configuration tab.
- Verify that the System Resource section displays the accurate number of CPU cores, SSL cores, and the total memory for your NetScaler SDX appliance.
- Select the System node and, under Set Up Appliance, click Network Configuration to modify the network information of the Management Service.
- In the Modify Network Configuration dialog box, specify the following details:
- Interface*—The interface through which clients connect to the Management Service. Possible values: 0/1, 0/2. Default: 0/1.
- Citrix Hypervisor™ IP Address*—The IP address of Citrix Hypervisor.
- Management Service IP Address*—The IP address of the Management Service.
- Netmask*—The subnet mask for the subnet in which the SDX appliance is located.
- Gateway*—The default gateway for the network.
- DNS Server—The IP address of the DNS server.
*A mandatory parameter
-
Click OK. Connection to the Management Service is lost as the network information was changed.
-
Connect the NetScaler SDX appliance’s management port 0/1 to a switch to access it through the network. Browse to the IP address used earlier and log on with the default credentials.
-
Apply the new licenses. For instructions, see SDX Licensing Overview.
- Navigate to Configuration > System and, in the System Administration group, click Reboot Appliance. Click Yes to confirm. You are now ready to provision the VPX instances on the NetScaler SDX appliance. For instructions, see Provisioning NetScaler instances.