JSON command injection protection check
The JSON command injection check examines the incoming JSON traffic for unauthorized commands that break the system security or modify the system. When examining the traffic, if any malicious commands are detected, the appliance blocks the request or performs the configured action.
In a command injection attack, the attacker aims to run unauthorized commands on the NetScaler operating system or the back-end server. To achieve this, the attacker injects operating system commands using a vulnerable application. The back-end application is vulnerable to injection attacks if the appliance simply forwards a request without any security check. Therefore, it is highly important to configure a security check, so the NetScaler appliance can protect your web application by blocking unsafe data.
How command injection protection works
- For an incoming JSON request, WAF examines the traffic for keywords or special characters. If the JSON request has no patterns that match any of the denied keywords or special characters, the request is allowed. Otherwise, the request is blocked, dropped, or redirected based on the configured action.
- If you prefer to exempt a keyword or a special character from the list, you can create a relaxation rule to bypass the security check under specific conditions.
- You can enable logging to generate log messages. You can monitor the logs to determine whether responses to legitimate requests are getting blocked. A large increase in the number of log messages can indicate attempts to launch an attack.
- You can also enable the statistics feature to gather statistical data about violations and logs. An unexpected surge in the stats counter might indicate that your application is under attack. If legitimate requests are getting blocked, you might have to revisit the configuration to see if you must configure the new relaxation rule or modify the existing one.
Keywords and special characters denied for command injection check
To detect and block JSON command injection attacks, the appliance has a set of patterns (keywords and special characters) defined in the default signature file. Following is a list of keywords blocked during command injection detection.
<commandinjection>
<keyword type="LITERAL" builtin="ON">7z</keyword>
<keyword type="LITERAL" builtin="ON">7za</keyword>
<keyword type="LITERAL" builtin="ON">7zr</keyword>
…
</commandinjection>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Special characters defined in the signature file are:
| ; & $ > < ' \ ! >> #
Note:
You can find the list of keywords and patterns in the /netscaler/default_signatures.xml file.
Configuring JSON command injection check by using the CLI
You can use either the set appfw profile command or add an appfw profile command to configure the JSON command injection settings. You can enable the block, log, and stats actions. You must also set the command injection type such as key words and string characters that you want to detect in the payloads.
At the command prompt, type:
set appfw profile <profile-name> –cmdInjectionAction <action-name> -CMDInjectionType <CMDInjectionType>]
Note:
By default, the command injection action is set as Block, Log, and Stats. Also, the default command injection type is set as
CmdSplCharANDKeyWord. After an upgrade, the existing Web app Firewall profiles have the action set as None..
Example:
set appfw profile profile1 -JSONCMDInjectionAction block -JSONCMDInjectionType CmdSplChar
Where, the available JSON command injection actions are:
None - Disable command injection protection. Log - Log command injection violations for the security check. Block - blocks traffic that violates the command injection security check. Stats - Generates statistics for command injection security violations.
Where, the available JSON command injection types are:
Cmd SplChar - Checks special characters
CmdKeyWord - Checks command injection Keywords
CmdSplCharANDKeyWord - This is the default action. The action checks special characters and command injection. Keywords and blocks only if both are present.
CmdSplCharORKeyWord - Checks special characters and command injection Keywords and blocks if either of them is found.
Configuring relaxation rules for JSON command injection protection check
If your application requires you to bypass the JSON command injection inspection for a specific ELEMENT or ATTRIBUTE in the payload, you can configure a relaxation rule.
The JSON command Injection inspection relaxation rules have the following syntax.
bind appfw profile <profile name> –JSONCMDURL <expression> -comment <string> -isAutoDeployed ( AUTODEPLOYED | NOTAUTODEPLOYED ) -state ( ENABLED | DISABLED )
Example for relaxation rule for Regex in header
bind appfw profile abc_json -jsoncmDURL http://1.1.1.1/hello.html
Whereas, the following relaxes requests from all URLs hosted on 1.1.1.1:
bind appfw profile abc_json -jsoncmDURL http://1.1.1.1/*”
To remove the relaxation, use ‘unbind’.
unbind appfw profile abc_json -jsoncmDURL “ http://1.1.1.1/*”
Configure JSON command injection check by using the GUI
Complete the following steps to configure the JSON command injection check.
- Navigate to Security > NetScaler Web App Firewall and Profiles.
- On the Profiles page, select a profile and click Edit.
- On the NetScaler Web App Firewall Profile page, go to Advanced Settings section and click Security Checks.
- In Security Checks section, select JSON Command Injection and click Action settings.
-
In the JSON Command Injection Settings page, set the following parameters
- Actions. Select one or more actions to perform for JSON command injection security check.
- Check Request Containing. Select a command injection pattern to check if the incoming request has the pattern.
- Click OK.
Viewing command injection traffic and violation statistics
The NetScaler Web App Firewall Statistics page shows security traffic and security violation details in a tabular or graphical format.
To view security statistics by using the command interface.
At the command prompt, type:
stat appfw profile profile1
| Appfw profile Traffic Statistics | Rate (/s) | Total |
|---|---|---|
| Requests | 0 | 0 |
| Request Bytes | 0 | 0 |
| Responses | 0 | 0 |
| Response Bytes | 0 | 0 |
| Aborts | 0 | 0 |
| Redirects | 0 | 0 |
| Long Term Ave Response Time (ms) | – | 0 |
| Recent Ave Response Time (ms) | – | 0 |
| HTML/XML/JSON Violation Statistics | Rate (/s) | Total |
|---|---|---|
| Start URL | 0 | 0 |
| Deny URL | 0 | 0 |
| Referer header | 0 | 0 |
| Buffer overflow | 0 | 0 |
| Cookie consistency | 0 | 0 |
| Cookie hijacking | 0 | 0 |
| CSRF form tag | 0 | 0 |
| HTML Cross-site scripting | 0 | 0 |
| HTML SQL injection | 0 | 0 |
| Field format | 0 | 0 |
| Field consistency | 0 | 0 |
| Credit card | 0 | 0 |
| Safe object | 0 | 0 |
| Signature Violations | 0 | 0 |
| Content Type | 0 | 0 |
| JSON Denial of Service | 0 | 0 |
| JSON SQL injection | 0 | 0 |
| JSON Cross-Site Scripting | 0 | 0 |
| File Upload Types | 0 | 0 |
| Infer Content Type XML Payload | 0 | 0 |
| HTML CMD Injection | 0 | 0 |
| XML Format | 0 | 0 |
| XML Denial of Service (XDoS) | 0 | 0 |
| XML Message Validation | 0 | 0 |
| Web Services Interoperability | 0 | 0 |
| XML SQL Injection | 0 | 0 |
| XML Cross-Site Scripting | 0 | 0 |
| XML Attachment | 0 | 0 |
| SOAP Fault Violations | 0 | 0 |
| XML Generic Violations | 0 | 0 |
| Total Violations | 0 | 0 |
| HTML/XML/JSON Log Statistics | Rate (/s) | Total |
|---|---|---|
| Start URL logs | 0 | 0 |
| Deny URL logs | 0 | 0 |
| Referer header logs | 0 | 0 |
| Buffer overflow logs | 0 | 0 |
| Cookie consistency logs | 0 | 0 |
| Cookie hijacking logs | 0 | 0 |
| CSRF from tag logs | 0 | 0 |
| HTML cross-site scripting logs | 0 | 0 |
| HTML cross-site scripting transform logs | 0 | 0 |
| HTML SQL Injection logs | 0 | 0 |
| HTML SQL transform logs | 0 | 0 |
| Field format logs | 0 | 0 |
| Field consistency logs | 0 | 0 |
| Credit cards | 0 | 0 |
| Credit card transform logs | 0 | 0 |
| Safe object logs | 0 | 0 |
| Signature logs | 0 | 0 |
| Content Type logs | 0 | 0 |
| JSON Denial of Service logs | 0 | 0 |
| JSON SQL injection logs | 0 | 0 |
| JSON Cross-Site Scripting logs | 0 | 0 |
| File upload types logs | 0 | 0 |
| Infer Content Type XML Payload L | 0 | 0 |
| JSON CMD Injection | 0 | 0 |
| HTML Command Injection logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML Format logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML Denial of Service(XDoS) logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML Message Validation logs | 0 | 0 |
| WSI logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML SQL Injection logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML cross-site scripting logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML Attachment logs | 0 | 0 |
| SOAP Fault logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML Generic logs | 0 | 0 |
| Total log messages | 0 | 0 |
| Server Error Response Statistics Rate (/s) | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP Client Errors (4xx Resp) | 0 | 0 |
| HTTP Server Errors (5xx Resp) | 0 | 0 |
| HTML/XML/JSON Log Statistics | Rate (/s) | Total |
|---|---|---|
| JSON Command Injection logs | 0 | 0 |
| XML format logs | 0 | 0 |
Viewing JSON command injection statistics by using the NetScaler GUI
Complete the following steps to view the command injection statistics:
- Navigate to Security > NetScaler Web App Firewall > Profiles.
- In the details pane, select a Web App Firewall profile and click Statistics.
- The NetScaler Web App Firewall Statistics page displays the JSON command injection traffic and violation details.
- You can select Tabular View or switch to Graphical View to display the data in a tabular or graphical format.
JSON command injection traffic statistics
JSON command injection violation statistics
Configure fine grain relaxation for JSON command injection
The Web App Firewall gives you an option to relax a specific JSON key or value from the JSON based command injection check. You can completely bypass the inspection for one or more fields by configuring the fine grain relaxation rules.
Previously, the only way to configure relaxations for JSON protection checks is to specify the entire URL and that would bypass the verification of the entire URL.
The JSON based command injection security protection provides relaxation for the following:
- Key names
- Key values
JSON based command injection protection enables you to configure relaxations that allow specific patterns and block the rest. For example, the Web App Firewall currently has a default set of more than 100 SQL keywords. Because hackers can use these keywords in command injection attacks, the Web App Firewall flags all as potential threats. If you want to relax one or more keywords that are considered safe for the specific location, you can configure a relaxation rule that can bypass the security check and block the rest. The commands used in relaxations have optional parameters for Value Type and Value Expression. You can specify whether the value expression is a regular expression or a literal string. The value type can be left blank, or you have an option to select Keyword or Special String.
Note:
Regular expressions are powerful. Especially if you are not thoroughly familiar with PCRE-format regular expressions, double-check any regular expressions you write. Make sure that they define exactly the URL that you want to add as an exception, and nothing else. Careless use of wildcards, and especially of the dot-asterisk (.*) metacharacter or wildcard combination, can have results that you do not want, such as blocking access to web content that you did not intend to block or allowing an attack that the JSON SQL Injection check would otherwise have blocked.
Points to Consider
- Value expression is an optional argument. A field name might not have any value expression.
- A key name can be bound to multiple value expressions.
- Value expressions must be assigned a value type. The value type can be: 1) Keyword, 2) SpecialString.
- You can have multiple relaxation rules per key name/URL combination.
Configure JSON fine grain relaxation for command injection attacks using command interface
To configure JSON file grain relaxation rule, you must bind the fine grain relaxation entities to the Web App Firewall profile.
At the command prompt, type:
bind appfw profile <profile name> -jsoncmdURL <URL> -key <key name> -valueType <keyword/SpecialString> <value Expression>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
bind appfw profile appprofile1 -jsoncmdurl www.example.com -key blg_cnt -isRegex NOTREGEX -valueType Keyword “cat” -isvalueRegex NOTREGEX
To configure fine grain relaxation rule for JSON-based command injection attacks by using the GUI
- Navigate to Application Firewall > Profiles, select a profile, and click Edit.
- In the Advanced Settings pane, click Relaxation Rules.
- In the Relaxation Rules section, select a JSON Command Injection record and click Edit.
- In the JSON Command Injection Relaxation Rule slider, click Add.
-
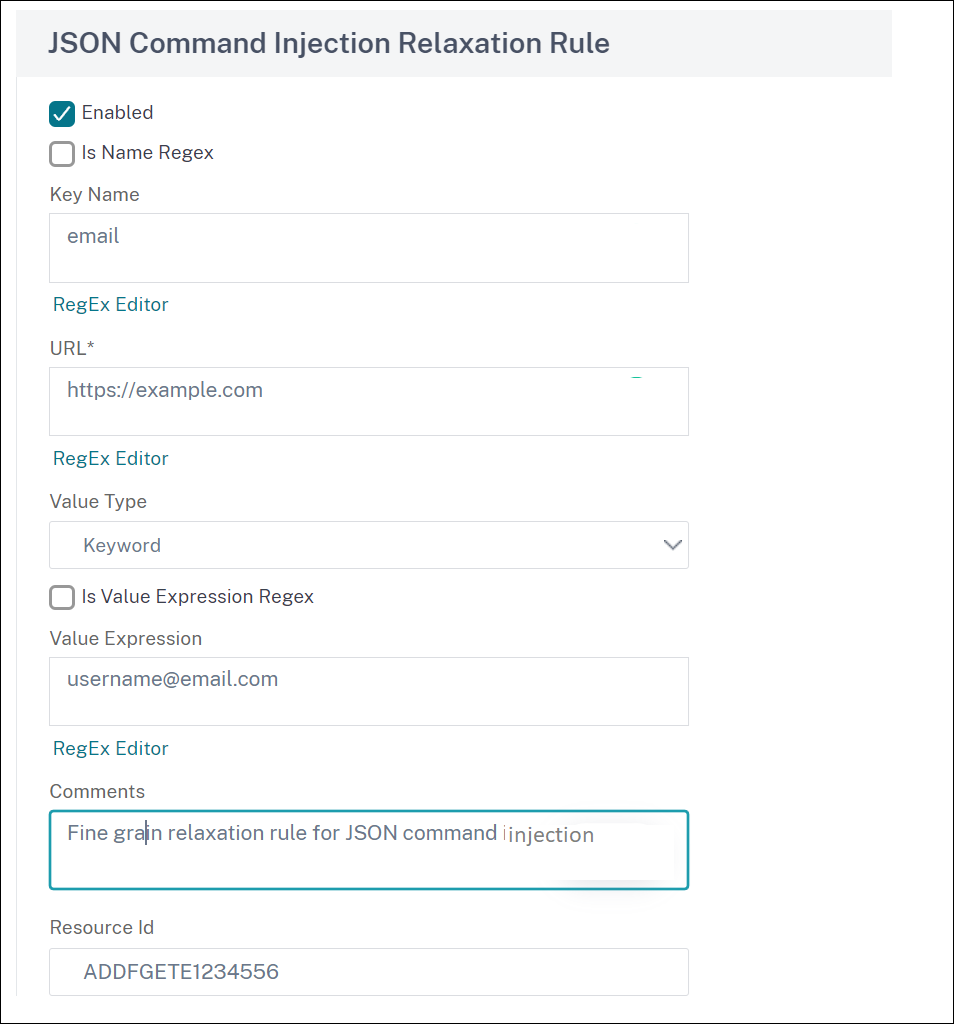
In the JSON Command Injection Relaxation Rule page, set the following parameters.
- Enabled
- Is Name Regex
- Key Name
- URL
- Value Type
- Comments
- Resource ID
- Click Create.
In this article
- How command injection protection works
- Keywords and special characters denied for command injection check
- Configuring JSON command injection check by using the CLI
- Configuring relaxation rules for JSON command injection protection check
- Configure JSON command injection check by using the GUI
- Viewing command injection traffic and violation statistics
- Viewing JSON command injection statistics by using the NetScaler GUI
- Configure fine grain relaxation for JSON command injection
- Points to Consider