Dynamic Routing
The following two dynamic routing protocols are supported by Citrix SD-WAN™:
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Prior to Citrix SD-WAN 11.3.1 release, the dynamic routing capabilities were available only for a single router ID. You can configure a unique router ID either globally for the entire protocol (one for OSPF and BGP) or provide no router ID. If a router ID is not provided, the lowest IP of the Virtual Network Instances (VNIs) participating in dynamic routing is auto-selected as the default router ID.
From Citrix SD-WAN 11.3.1 release onwards, you can not only configure a router ID for the entire protocol but also configure a router ID for each routing domain. With this enhancement, you can enable stable dynamic routing across multiple instances with different router ID’s converging in a stable manner.
If you configure a router ID for a specific routing domain, the specific router ID overrides the protocol level routing domain.
OSPF
OSPF is a routing protocol developed for Internet Protocol (IP) networks by the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It includes the early version of OSI’s Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) routing protocol.
OSPF protocol is open, which means that its specification is in the public domain (RFC 1247). OSPF is based on the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm called Dijkstra. It is a link-state routing protocol that calls for sending Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) to all other routers within the same hierarchical area. Information on attached interfaces, metrics used, and other variables are included in OSPF LSAs. OSPF routers accumulate link-state information, which is used by the SPF algorithm to calculate the shortest path to each node.
Note
Citrix SD-WAN appliances do not participate as Designated Router (DR) and BDR (Backup Designated Router) on each multi-access network since the default DR priority is set to “0.”
Citrix SD-WAN appliance does not support summarization as an Area Border Router (ABR).
BGP
BGP is an inter-autonomous system routing protocol. An autonomous network or group of networks is managed under a common administration and with common routing policies. BGP is used to exchange routing information for the Internet and is the protocol used between ISPs. Customer networks deploy Interior gateway protocols such as RIP or OSPF for the exchange of routing information within their networks. Customers connect to ISPs, and ISPs use BGP to exchange customer and ISP routes. When BGP is used between Autonomous Systems (AS), the protocol is called External BGP (EBGP). If a service provider is using BGP to exchange routes within an AS, then the protocol is called Interior BGP (IBGP).
BGP is a robust and scalable routing protocol deployed on the Internet. To achieve scalability, BGP uses many route parameters called attributes to define routing policies and maintain a stable routing environment. BGP neighbors exchange full routing information when the TCP connection between neighbors is first established. When changes to the routing table are detected, the BGP routers send to their neighbors only those routes that have changed. BGP routers do not send periodic routing updates, and advertise only the optimal path to a destination network. You can configure Citrix SD-WAN appliances to learn routes and advertise routes using BGP.
Exterior BGP (eBGP)
Citrix SD-WAN appliances connect to a switch on the LAN side and a Router on the WAN side. As SD-WAN technology starts becoming more integral to Enterprise network deployments, SD-WAN appliances replace the Routers. SD-WAN implements eBGP dynamic routing protocol to function as a dedicated routing device.
SD-WAN appliance establishes a neighborship with peer routers using eBGP towards WAN side and is able to learn, advertise routes from and to peers. You can select importing and exporting eBGP learned routes on peer devices. Also, SD-WAN static, virtual path learned routes can be configured to advertise to eBGP peers.
For more information, see the following use cases:
- SD-WAN site Communicating with non-SD-WAN site over eBGP
- Communication Between SD-WAN sites Using Virtual Path and eBGP
- Implementing OSPF in one-arm topology
- OSPF Type5 to Type1 deployment in MPLS Network
- SD-WAN and non-SD-WAN (third-party) appliance OSPF deployment
- Implementing OSPF using SD-WAN network with high-availability setup
AS path length
BGP protocol uses the AS path length attribute to determine the best route. The AS path length indicates the number of autonomous systems traversed in a route. Citrix SD-WAN uses the BGP AS path length attribute to filter and import routes.
Non-SD-WAN appliances can choose to route traffic to Primary DC or Secondary DC SD-WAN appliances by importing routes based on their AS path length. You can also dynamically steer traffic from a router to Secondary DC by simply increasing the AS path length of the Primary DC appliance on the router, making it unpreferable. Eliminating the need to change the route cost and perform a configuration update.
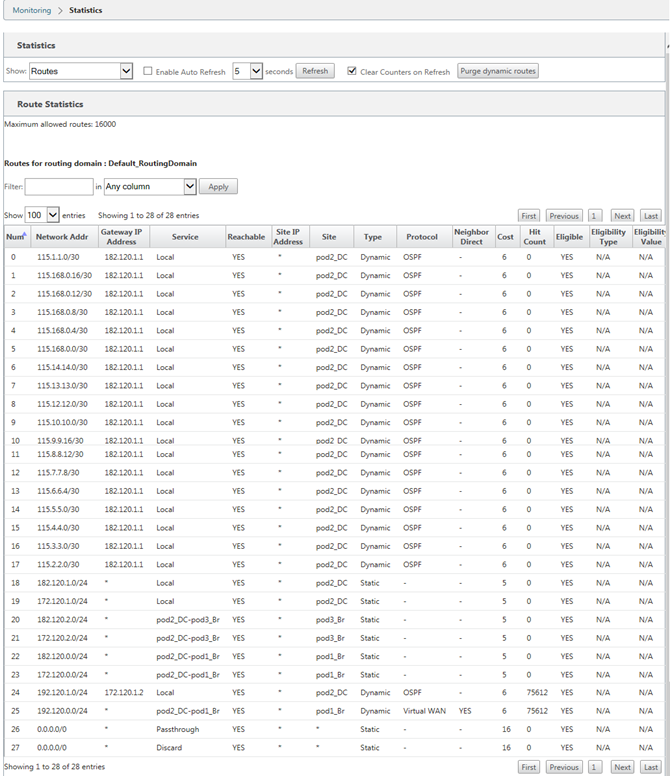
Monitor route statistics
Navigate to Monitor > Statistics. Select Routes from the Show drop-down menu.
All functions for applicable Routes are supported in Citrix SD-WAN network regardless of whether a Route is Dynamic or Static.