Static NAT
Static NAT is a one-to-one mapping of a private IP address or subnet inside the SD-WAN network to a public IP address or subnet outside the SD-WAN network. Configure Static NAT by manually entering the inside IP address and the outside IP address to which it has to translate. You can configure Static NAT for the Local, Virtual Paths, Internet, Intranet, and Inter-routing domain services.
Inbound and Outbound NAT
The direction for a connection can either be inside to outside or outside to inside. When a NAT rule is created, it is applied to both the directions depending on the direction match type.
- Inbound: The source address is translated for packets received on the service. The destination address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. For example, Internet service to LAN service – For packets received (Internet to LAN), the source IP address is translated. For packets transmitted (LAN to Internet), the destination IP address is translated.
- Outbound: The destination address is translated for packets received on the service. The source address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. For example, LAN service to Internet service – for packets transmitted (LAN to Internet) the source IP address is translated. For packets received (Internet to LAN) the destination IP address is translated.
Zone Derivation
The source and destination firewall zones for the inbound or outbound traffic should not be the same. If both the source and destination firewall zones are the same, NAT is not performed on the traffic.
For outbound NAT, the outside zone is automatically derived from the service. Every service on SD-WAN is associated to a zone by default. For example, Internet service on a trusted internet link is associated with the trusted internet zone. Similarly, for an inbound NAT, the inside zone is derived from the service.
For a Virtual path service NAT zone derivation does not happen automatically, you have to manually enter the inside and outside zone. NAT is performed on traffic belonging to these zones only. Zones cannot be derived for virtual paths because there might be multiple zones within the Virtual path subnets.
Static NAT Policies for IPv6 Internet service
Citrix SD-WAN supports static NAT policies for IPv6 Internet service from release 11.4.0 onwards. A static NAT policy for IPv6 Internet service specifies the mapping of an inside network prefix to an outside network prefix. The number of static NAT policies required depends on the number of inside networks and the number of outside networks (WAN links). If there are M number of inside networks and N number of WAN links, then the number of static NAT policies required is M x N.
From Citrix SD-WAN release 11.4.0 onwards, while creating a static NAT policy, you can either enter the outside IP address manually or enable Autolearn via PD. When Autolearn via PD is enabled, the Citrix SD-WAN appliance receives delegated prefixes from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation. Before Citrix SD-WAN release 11.4.0, the outside IP address was derived from the service automatically and there was no option to enter the outside IP address manually. If you are upgrading an appliance to 11.4.0 or a later release and have static NAT policies configured for IPv6 Internet service, then you must manually update the policies.
Configuration example
In the following topology, the Citrix SD-WAN™ appliance is configured with 2 inside networks and 2 WAN links:
- Inside network 1 resides in the CORPORATE routing domain with network prefix FD01:0203:6561::/64
- Inside network 2 resides in the Wi-Fi routing domain with network prefix FD01:0203:1265::/64
- Through WAN Link 1, the SD-WAN appliance receives from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, 2 delegated prefixes 2001:0D88:1261::/64 and 2001:0D88:1265::/64. These 2 delegated prefixes are used as the outside network prefixes when the traffic from the inside networks transits WAN link 1.
- Through WAN Link 2, the SD-WAN appliance receives from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, 2 delegated prefixes 2001:DB8:8585::/64 and 2001:DB8:8599::/64. These 2 delegated prefixes are used as the outside network prefixes when the traffic from the inside networks transits WAN link 2.
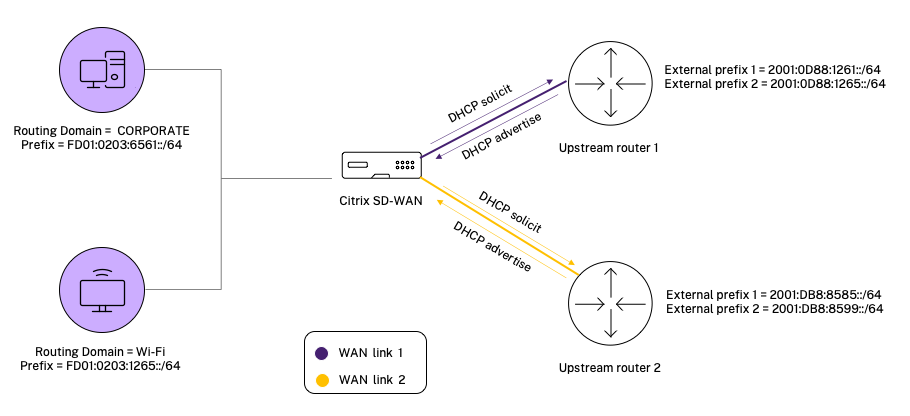
In this scenario, there are M=2 inside networks and N=2 WAN links. Therefore, the number of static NAT policies required for proper deployment of IPv6 Internet service is 2 x 2 = 4. These 4 static NAT policies specify the address translation for:
- Inside network 1 through WAN link 1
- Inside network 1 through WAN link 2
- Inside network 2 through WAN link 1
- Inside network 2 through WAN link 2
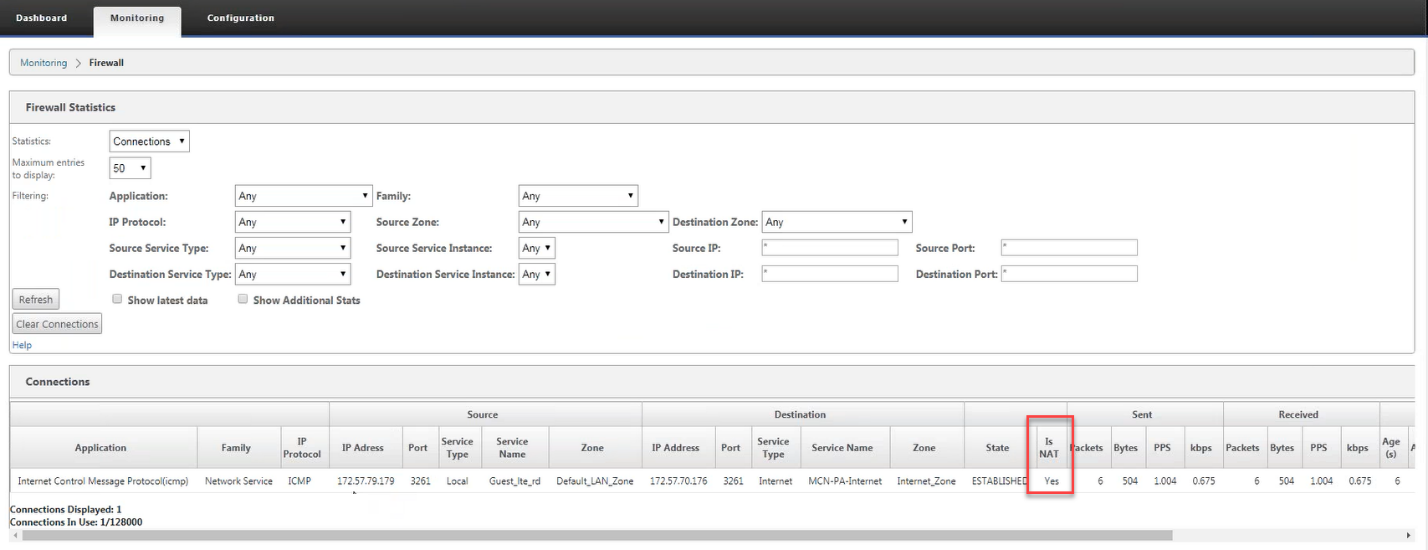
Monitoring
To monitor NAT, navigate to Monitoring > Firewall Statistics > Connections. For a connection you can see if NAT is done or not.
To check if Auto-learn via PD is configured for any NAT rule, navigate to Configuration > Virtual WAN > View Configuration and choose Firewall from the View drop-down list. Auto-learn via PD and PD prefix ID columns display the details.
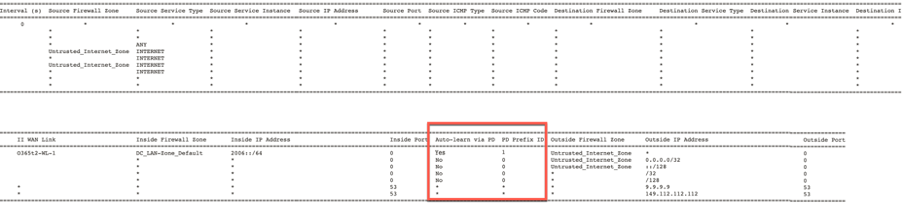
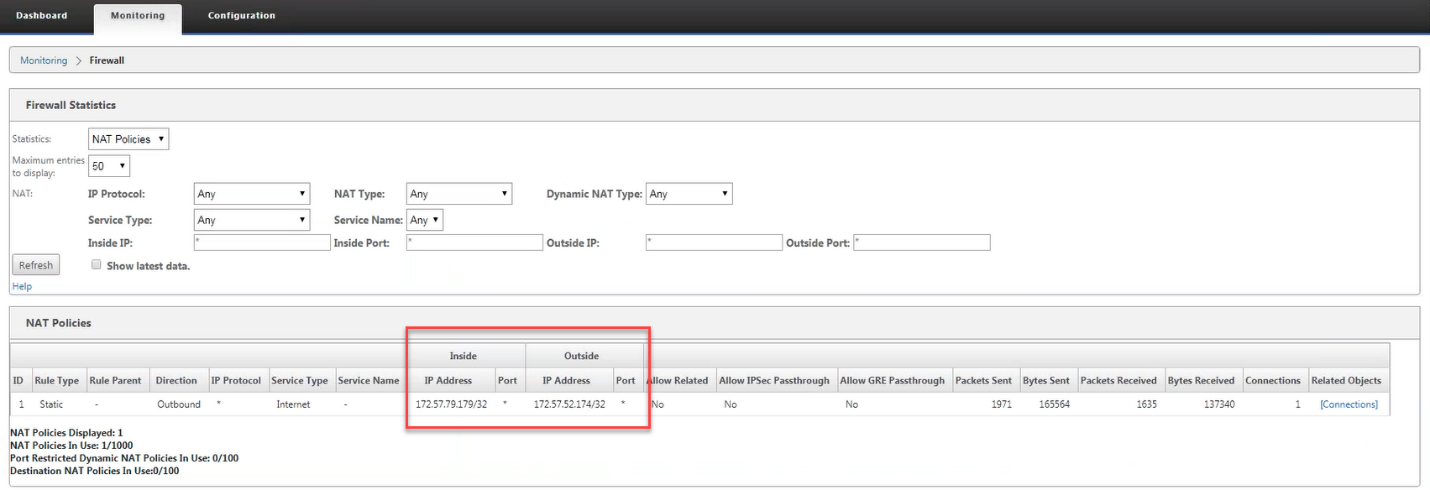
To further see the inside IP address to outside IP address mapping, click Post-Route NAT under Related Objects or navigate to Monitoring > Firewall Statistics > NAT policies.
The following screenshot shows the mapping of inside address to outside address in an IPv4 static NAT policy.
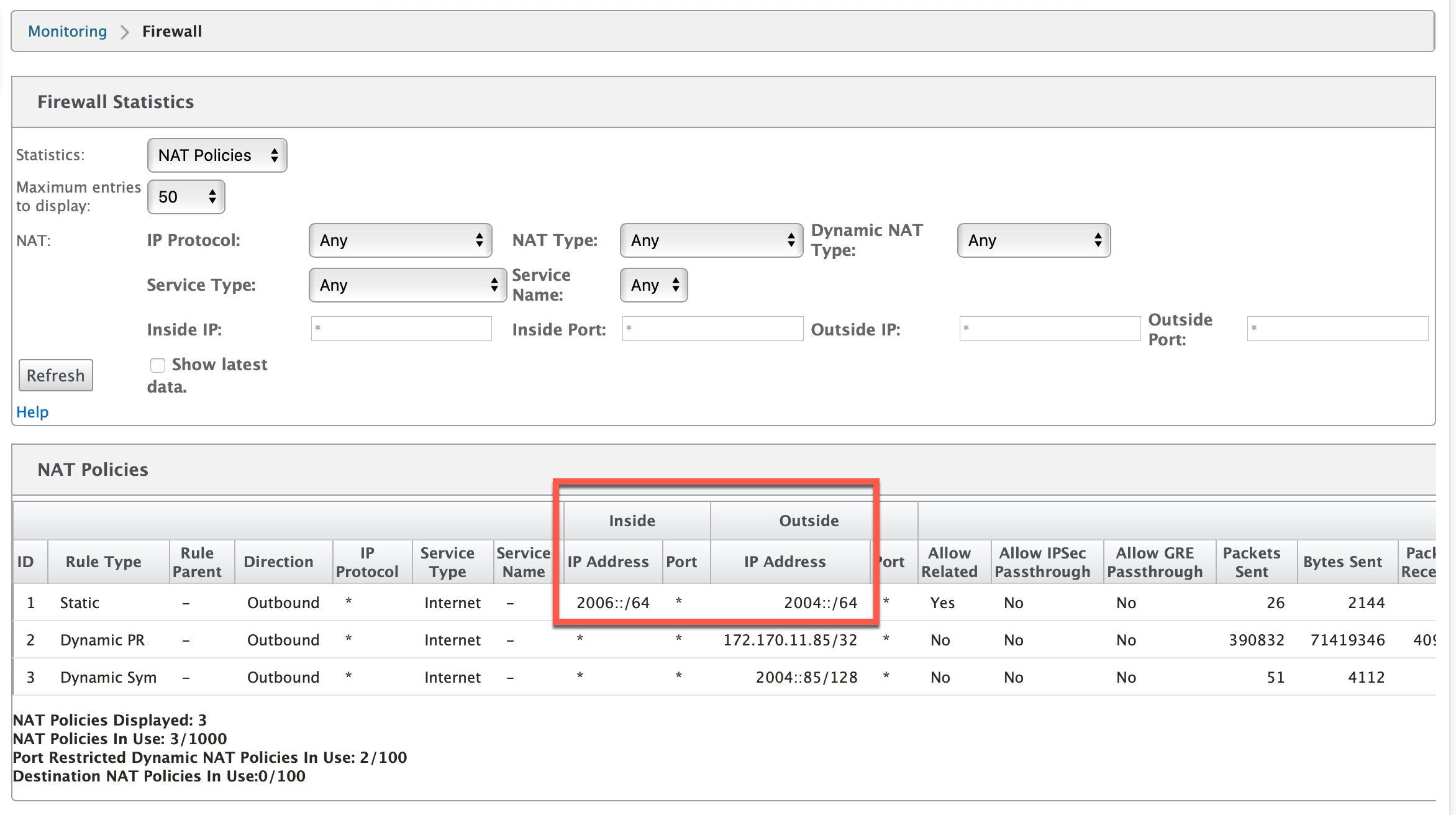
The following screenshot shows the mapping of inside address to outside address in an IPv6 static NAT policy.
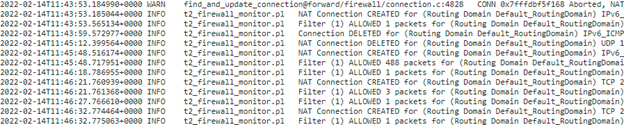
Logs
You can view logs related to NAT in firewall logs. To view logs for NAT, create a firewall policy that matches your NAT policy and ensure that logging is enabled on the firewall filter. NAT logs display the following information:
- Date and time
- Routing domain
- IP protocol
- Source port
- Source IP address
- Translated IP address
- Translated port
- Destination IP address
- Destination port
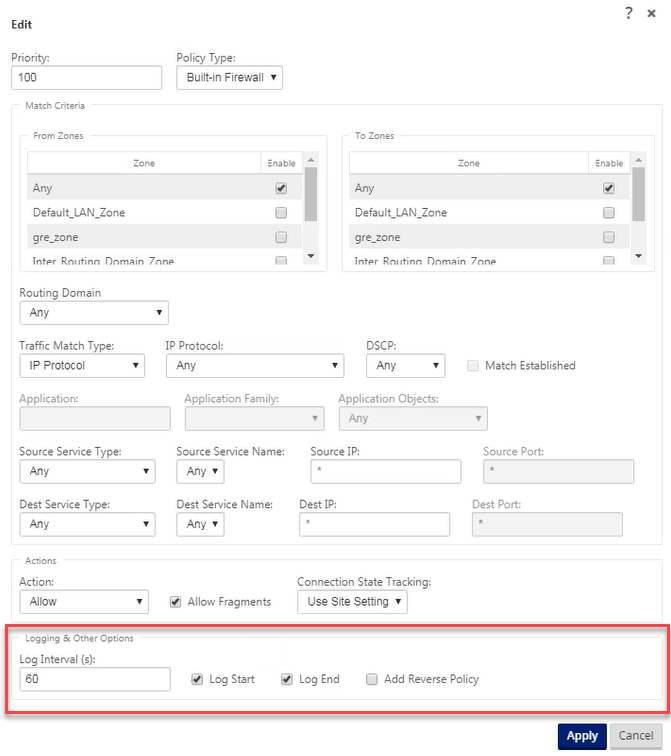
To generate NAT logs, navigate to Logging/Monitoring > Log Options, select SDWAN_firewall.log, and click View Log.
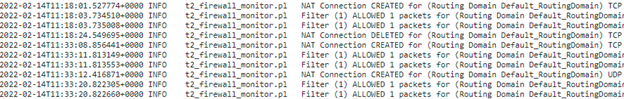
The NAT connection details are displayed in the log file.