Troubleshooting NetScaler node controller issues
This topic explains how to troubleshoot issues that you might encounter while using the node controller. You can collect logs to determine the causes and apply workarounds for some of the common issues related to the configuration of the node controller.
To validate node controller and the basic node configurations, refer to the image on the deployment page.
Router pods not starting
If kube-nsnc-router pods are not starting then it might be due to certain cluster restrictions that prevent privileged pods to be deployed by non-admin users/privileges.
As a workaround, perform one of the following:
- Use
kube-systemnamespace to deploy node controller. - Assign
cluster-adminrole to node controllerclusterrolebinding.
Note:
If you choose option 1, then you cannot create multiple instances of node controller in a single cluster as only one
kube-systemnamespace available per cluster.
Service status DOWN
To debug the issues when the service is in the “down” state, perform the following steps:
-
Verify the logs of the node controller pod by using the following command:
kubectl logs <nsnc-pod> -n <namespace> <!--NeedCopy-->Check for any ‘permission’ errors in the logs. node controller creates
kube-nsnc-routerpods, which requireNET_ADMINprivilege to perform the configurations on nodes. Therefore, the node controller service account must have theNET_ADMINprivilege and the ability to create host modekube-nsnc-routerpods. -
Verify the logs of the
kube-nsnc-routerpod by using the following command:kubectl logs <kube-nsnc-pod> -n <namespace> <!--NeedCopy-->Check for any errors in the node configuration. The following is a sample router pod log:
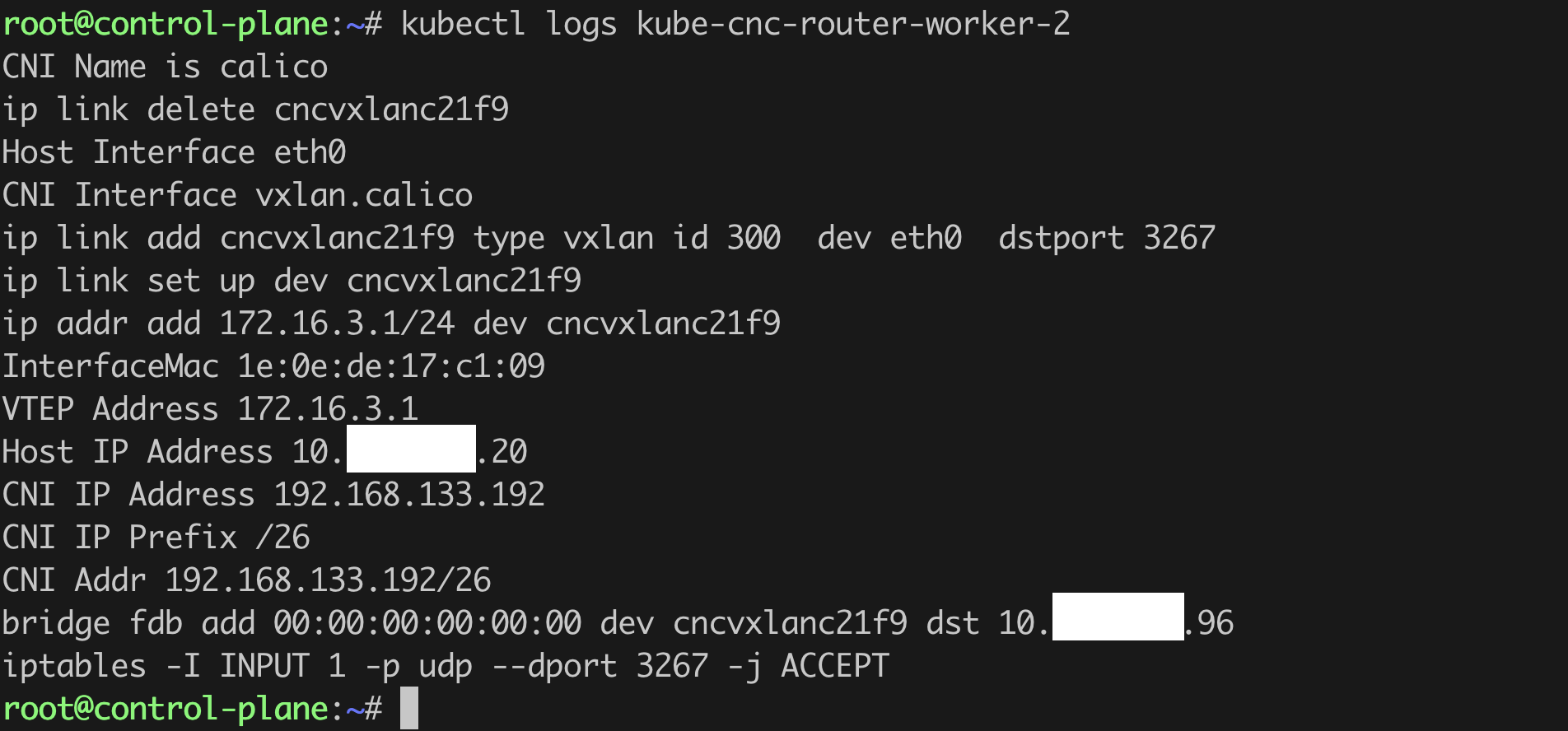
-
Verify the
kube-nsnc-routerConfigMap output by using the following command:kubectl get configmaps -n <namespace> kube-nsnc-router -o yaml <!--NeedCopy-->Check for an empty field in the “data” section of the ConfigMap. The following is a sample two-node data section:
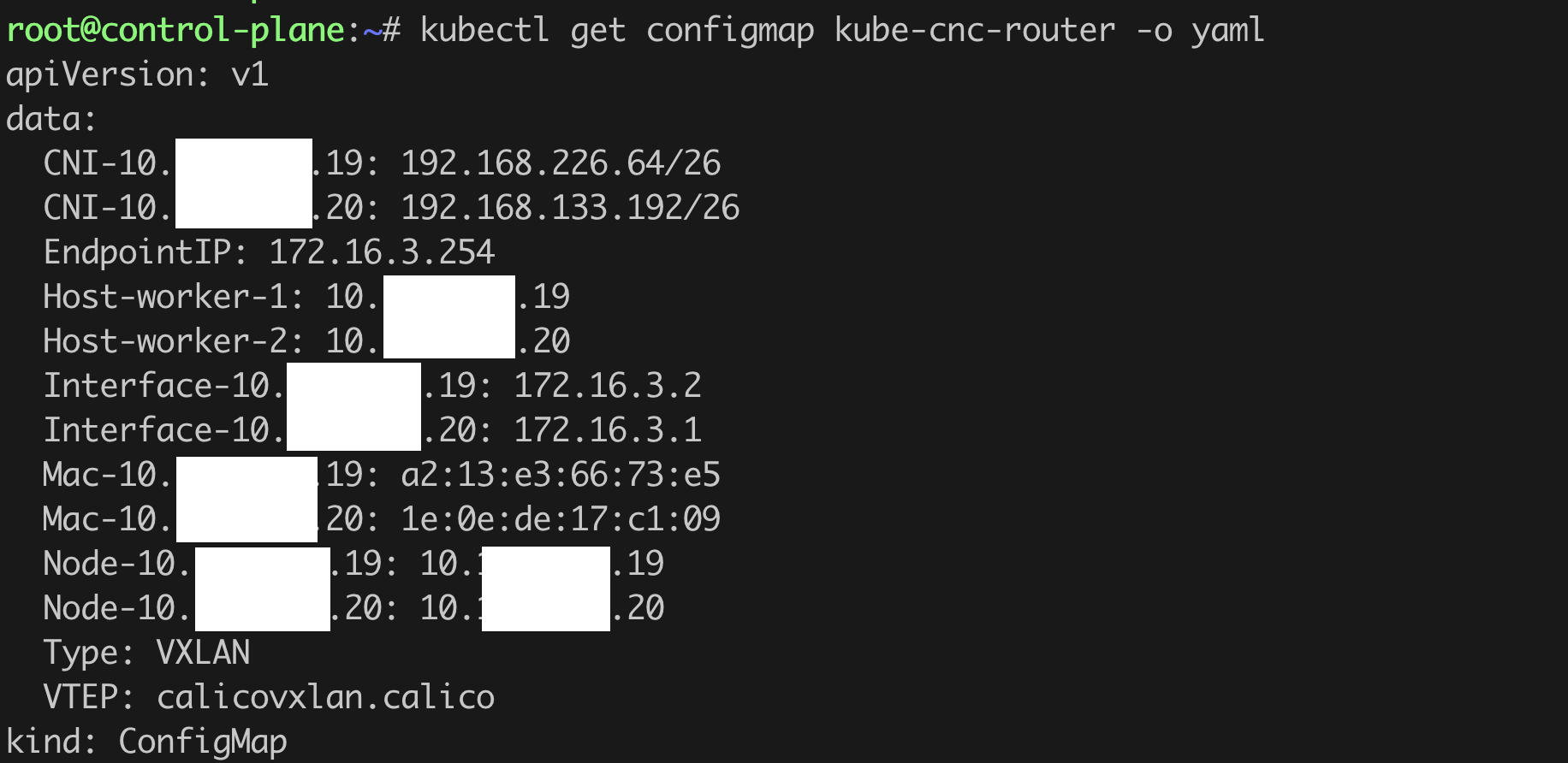
-
Verify the node configuration and ensure that:
-
node controller interface
nsncvxlan<md5_of_namespace>is created.- The assigned VTEP IP address is the same as the corresponding router gateway entry in NetScaler.
- The status of the interface is functioning.
-
iptablerule port is created.- The port is the same that of VXLAN created on NetScaler.
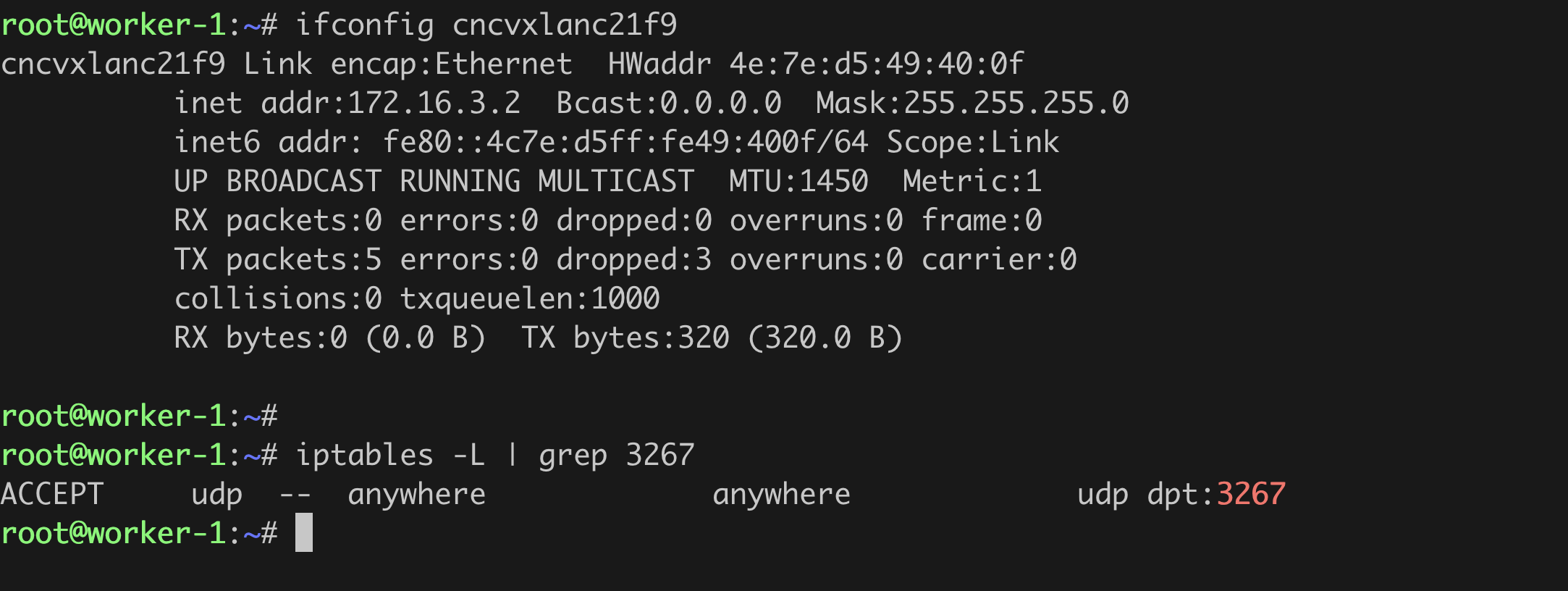
-
Service status is up and operational, but the ping from NetScaler is not working
This issue might occur due to the presence of a PBR entry, which directs the packets from NetScaler with SRCIP as NSIP to the default gateway. This issue does not impact any functionality.
You can use the VTEP of NetScaler as source IP address using the -S option of ping command in the NetScaler command line interface. For example:
ping <serviceIP> -S <vtepIP>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
If it is necessary to ping with NSIP itself then you must remove the PBR entry or add a PBR entry for the endpoint with high priority.
cURL to the pod endpoint or VIP is not working
Though, services are in up state, if you cannot cURL to the pod endpoint, means that the stateful TCP session to the endpoint is failing. One reason might be that the ns mode ‘MBF’ is set to enable. This issue depends upon deployments and might occur only on certain versions of NetScaler.
To resolve this issue, you must disable MBF ns mode or bind a netprofile with the netprofile disabled to the service group.
Note:
If disabling the MBF resolves the issue, then you must continue to set MBF to disabled.
Customer support
For general support, when you raise issues with the customer support, provide the following details, which help for faster debugging. cURL or ping from NetScaler to the endpoint and get the details for the following:
For the node, provide the details for the following commands:
-
tcpdumpcapture on node controller interface on nodes.tcpdump -i nsncvxlan<hash_of_namesapce> -w nsncvxlan.pcap <!--NeedCopy--> -
tcpdumpcapture on node Mgmt interface, for example, “eth0”.tcpdump -i eth0 -w mgmt.pcap <!--NeedCopy--> -
tcpdumpcapture on CNI interface, for example, “vxlan.calico”.tcpdump -i vxlan.calico -w cni.pcap <!--NeedCopy--> -
output of
ifconfig -aon the node. -
output of
iptables -Lon the node.
For NetScaler, provide the details for the following show commands:
show ipshow vxlan <vxlan_id>show routeshow arpshow bridgetableshow ns pbrsshow ns bridgetableshow ns mode-
Try to capture
nstraceby using ping/cURL:start nstrace -size 0 -mode rx new_rx txb tx -capsslkeys enABLED <!--NeedCopy-->stop nstrace <!--NeedCopy-->