Enhancements for Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer support in the NetScaler Ingress Controller
Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer support in the NetScaler Ingress Controller is enhanced with the following features:
- BGP route health injection (RHI) support
- Advertise or recall load balancer IP addresses (VIPs) based on the availability of service’s pods in a set of nodes (zones) defined by node’s labels
Support for automatic configuration of BGP RHI on NetScaler
Route health injection (RHI) allows the NetScaler to advertise the availability of a VIP as a host route throughout the network using BGP. However, you had to manually perform the configuration on NetScaler to support RHI. Using NetScaler Ingress Controllers deployed in a Kubernetes environment, you can automate the configuration on NetScalers to advertise VIPs.
When a service of type LoadBalancer is created, the NetScaler Ingress Controller configures a VIP on the NetScaler for the service. If BGP RHI support is enabled for the NetScaler Ingress Controller, it automatically configures NetScaler to advertise the VIP to the BGP network. Using the service.citrix.com/vipparams annotation, you can enable IP parameters for the VIP. For example, see the service.YAML file in the step 5 of Configuring BGP RHI on NetScalers using the NetScaler Ingress Controller. For information on the supported IP parameters, see nsip configuration.
Advertise and recall VIPs based on the availability of pods
In the topology as shown in the following diagram, nodes in a Kubernetes cluster are physically distributed across three different racks. They are logically grouped into three zones. Each zone has a NetScaler MPX as the Tier-1 ADC and a NetScaler Ingress Controller on the same in the Kubernetes cluster. NetScaler Ingress Controllers in all zones listen to the same Kubernetes API server. So, whenever a service of type LoadBalancer is created, all NetScalers in the cluster advertises the same IP address to the BGP fabric. Even, if there is no workload on a zone, the NetScaler in that zone still advertises the IP address.
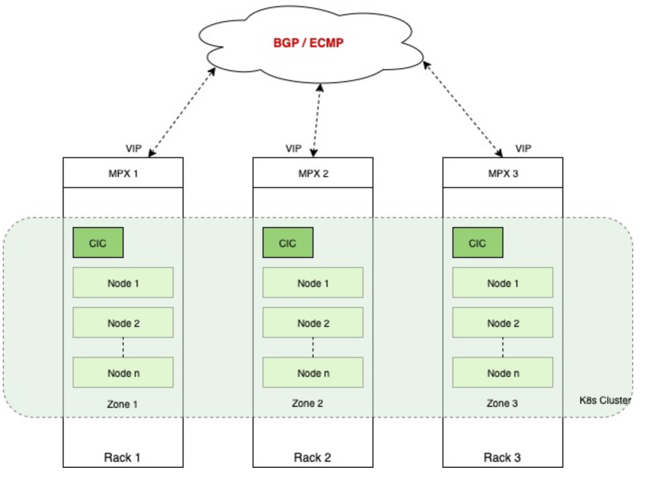
NetScaler provides a solution to advertise or recall the VIP based on the availability of pods in a zone. You need to label the nodes on each zone so that the NetScaler Ingress Controller can identify nodes belonging to the same zone. The NetScaler Ingress Controller on each zone performs a check to see if there are pods on nodes in the zone. If there are pods on nodes in the zone, it advertises the VIP. Otherwise, it revokes the advertisement of VIP from the NetScaler on the zone.
Configuring BGP RHI on NetScalers using the NetScaler Ingress Controller
This topic provides information on how to configure BGP RHI on NetScalers using the NetScaler Ingress Controller based on a sample topology. In this topology, nodes in a Kubernetes cluster are deployed across two zones. Each zone has a NetScaler VPX or MPX as the Tier-1 ADC and a NetScaler Ingress Controller for configuring ADC in the Kubernetes cluster. The ADCs are peered using BGP with the upstream router.
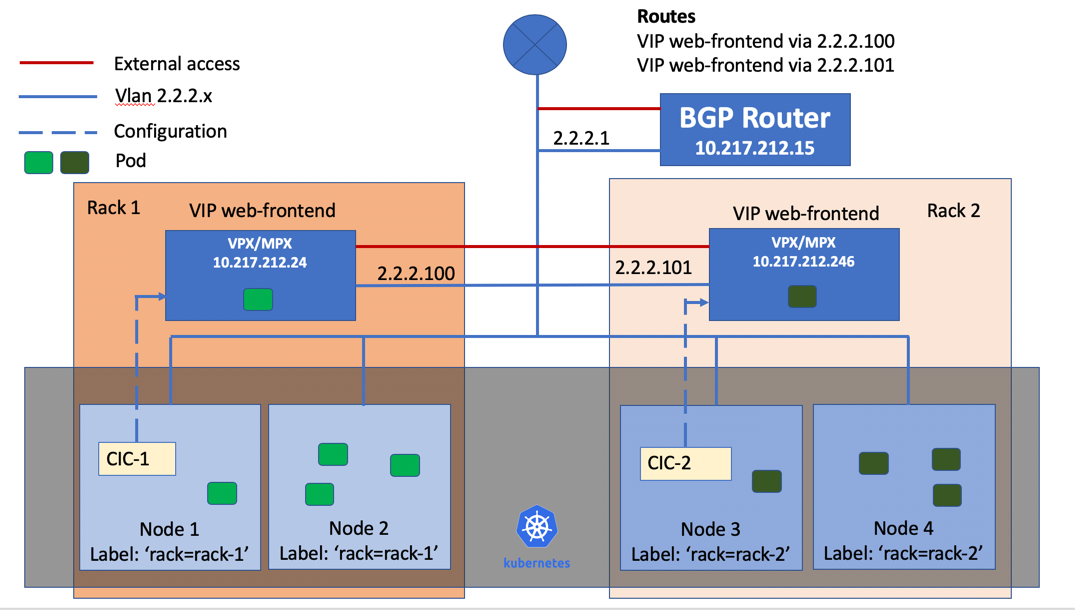
Prerequisites
- Configure NetScaler MPX or VPX as a BGP peer with the upstream routers.
Perform the following steps to configure BGP RHI support based on the sample topology.
-
Label nodes in each zone using the following command:
For zone 1:
kubectl label nodes node1 rack=rack-1 kubectl label nodes node2 rack=rack-1For zone 2:
kubectl label nodes node3 rack=rack-2 kubectl label nodes node4 rack=rack-2 -
Configure the following environmental variables in the NetScaler Ingress Controller configuration YAML files as follows:
For zone 1:
- name: "NODE_LABELS" value: "rack-1" - name: "BGP_ADVERTISEMENT" value: "True"For zone 2:
- name: "NODE_LABELS" value: "rack-2" - name: "BGP_ADVERTISEMENT" value: "True"A sample
cic.yamlfile for deploying the NetScaler Ingress Controller on zone 1 is provided as follows:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: cic-k8s-ingress-controller-1 labels: app: cic-k8s-ingress-controller-1 spec: serviceAccountName: cic-k8s-role containers: - name: cic-k8s-ingress-controller image: "quay.io/citrix/citrix-k8s-ingress-controller:1.36.5" env: # Set NetScaler NSIP/SNIP, SNIP in case of HA (mgmt has to be enabled) - name: "NS_IP" value: "10.217.212.24" # Set username for Nitro - name: "NS_USER" valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: nslogin key: username # Set user password for Nitro - name: "NS_PASSWORD" valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: nslogin key: password - name: "EULA" value: "yes" - name: "NODE_LABELS" value: "rack=rack-1" - name: "BGP_ADVERTISEMENT" value: "True" args: - --ipam citrix-ipam-controller imagePullPolicy: Always -
Deploy the NetScaler Ingress Controller using the following command.
Note:
You need to deploy the NetScaler Ingress Controller on both racks (per zone).
Kubectl create -f cic.yaml -
Deploy a sample application using the
web-frontend-lb.yamlfile.Kubectl create -f web-frontend-lb.yaml
The content of the
web-frontend-lb.yamlis as follows:apiVersion: v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: web-frontend spec: selector: matchLabels: app: web-frontend replicas: 4 template: metadata: labels: app: web-frontend spec: containers: - name: web-frontend image: 10.217.6.101:5000/web-test:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 imagePullPolicy: Always -
Create a service of type
LoadBalancerfor exposing the application.Kubectl create -f web-frontend-lb-service.yamlThe content of the
web-frontend-lb-service.yamlis as follows:apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: web-frontend annotations: service.citrix.com/class: 'cic-vpx' service.citrix.com/frontend-ip: 1.1.1.1 service.citrix.com/vipparams: '{"vserverrhilevel": "ONE_VSERVER", "hostroute": "ENABLED", "metric": 10}' labels: app: web-frontend spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP name: http selector: app: web-frontend -
Verify the service group creation on NetScalers using the following command.
show servicegroup <service-group-name>Following is a sample output for the command.
# show servicegroup k8s-web-frontend_default_80_svc_k8s-web-frontend_default_80_svc k8s-web-frontend_default_80_svc_k8s-web-frontend_default_80_svc - TCP State: ENABLED Effective State: UP Monitor Threshold : 0 Max Conn: 0 Max Req: 0 Max Bandwidth: 0 kbits Use Source IP: NO Client Keepalive(CKA): NO TCP Buffering(TCPB): NO HTTP Compression(CMP): NO Idle timeout: Client: 9000 sec Server: 9000 sec Client IP: DISABLED Cacheable: NO SC: OFF SP: OFF Down state flush: ENABLED Monitor Connection Close : NONE Appflow® logging: ENABLED ContentInspection profile name: ??? Process Local: DISABLED Traffic Domain: 0 1) 10.217.212.23:30126 State: UP Server Name: 10.217.212.23 Server ID: None Weight: 1 Last state change was at Wed Jan 22 23:35:11 2020 Time since last state change: 5 days, 00:45:09.760 Monitor Name: tcp-default State: UP Passive: 0 Probes: 86941 Failed [Total: 0 Current: 0] Last response: Success - TCP syn+ack received. Response Time: 0 millisec 2) 10.217.212.22:30126 State: UP Server Name: 10.217.212.22 Server ID: None Weight: 1 Last state change was at Wed Jan 22 23:35:11 2020 Time since last state change: 5 days, 00:45:09.790 Monitor Name: tcp-default State: UP Passive: 0 Probes: 86941 Failed [Total: 0 Current: 0] Last response: Success - TCP syn+ack received. -
Verify the VIP advertisement on the BGP router using the following command.
>VTYSH # show ip route bgp B 172.29.46.78/32 [200/0] via 2.2.2.100, vlan20, 1d00h35m [200/0] via 2.2.2.101, vlan20, 1d00h35m Gateway of last resort is not set