-
-
Domain name system
-
-
-
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Domain name system
Domain Name System (DNS) translates human readable domain names to machine-readable IP addresses, and vice versa. The following DNS features are introduced in SD-WAN release 10 version 2:
- DNS Proxy
- DNS Transparent Forwarding
DNS proxy
DNS proxy intercepts the DNS requests destined to SD-WAN IP address and forwards it to the selective DNS services. You can configure a proxy with multiple forwarders that helps steering DNS requests based on application domain names. DNS forwarding works for the requests that are received through UDP connections.
To configure SD-WAN as a DNS Proxy:
-
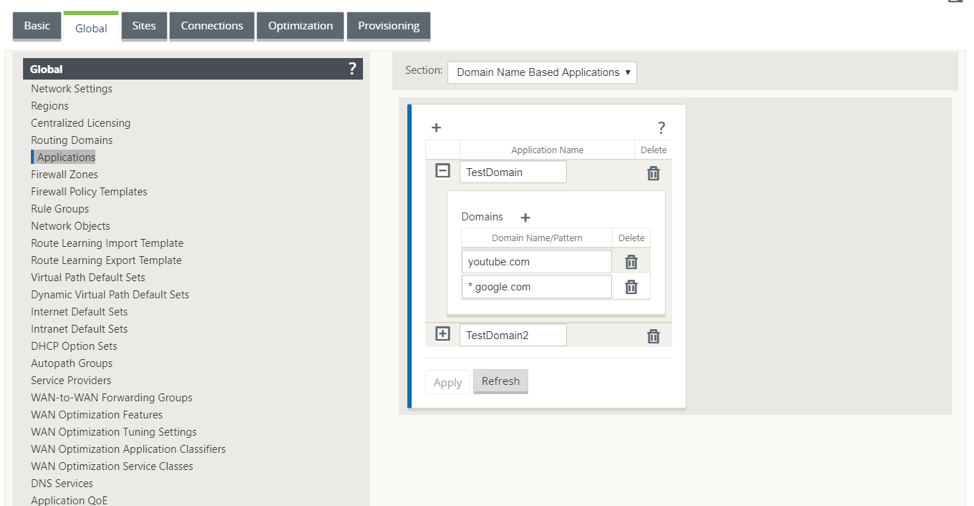
Define the domain name based applications. In the Configuration Editor, navigate to Global > Applications > Domain Name Based Applications.
Enter the application name and the required domain names or patterns. You can group several domain names as an application. You can either enter the full domain name or use wild cards at the beginning. For example - *.google.com
-
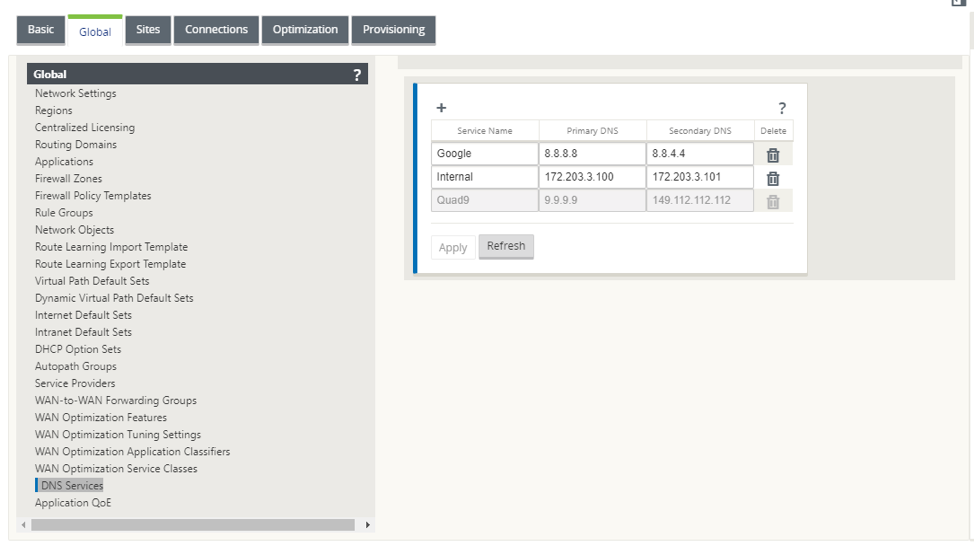
Define the required DNS Services. Navigate to Global > DNS Service. Enter the Service Name and a pair of Primary and Secondary DNS server IP addresses.
You can create internal, ISP, google or any other open source DNS service.
Note:
If you have configured Office 365 breakout policy, a Quad9 DNS service is auto created. For more information, see Office 365 Optimization.
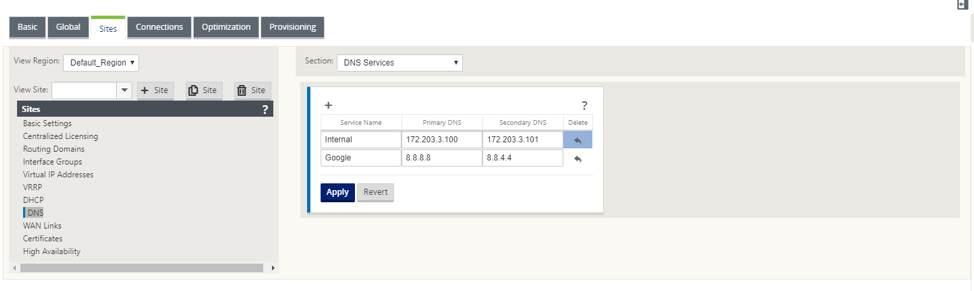
Alternatively, you can also define the DNS services at individual site level. . The site-level DNS service configuration overrides the global configuration. To configure site-specific DNS service, navigate to Sites > DNS > DNS Services. Enter the Service Name and a pair of Primary and Secondary DNS server IP addresses.
-
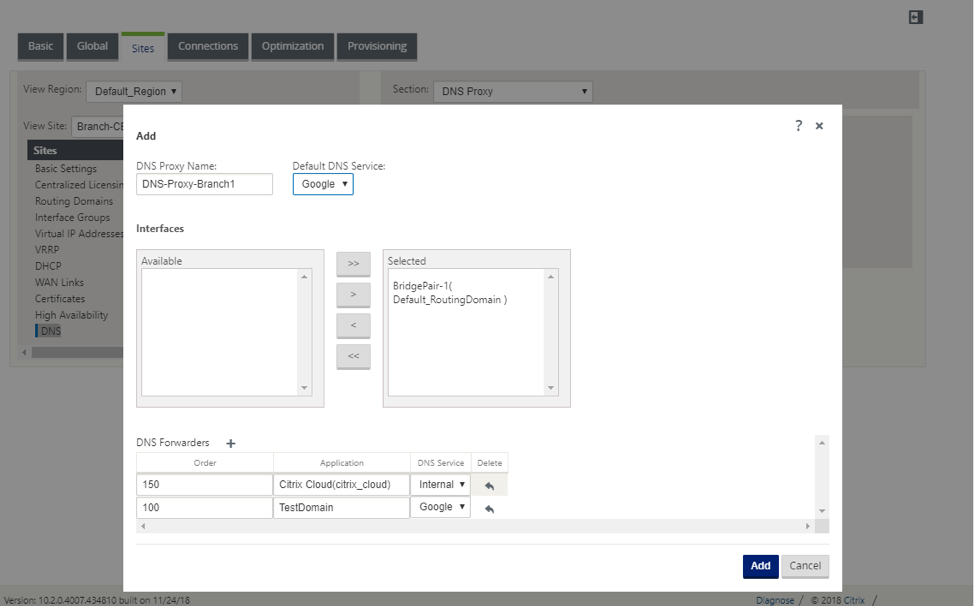
Configure DNS proxy for the site. Navigate to Sites > DNS > DNS Proxy. Click +. Enter values for the following parameters:
- DNS Proxy Name: Name of the DNS Proxy.
- Default DNS Service: The default DNS Service to which the DNS requests will be forwarded to, if none of the applications match in DNS forwarder look-up.
- Interfaces: The interfaces on which the DNS requests will be intercepted. Only trusted interfaces are allowed.
-
DNS Forwarders: List of DNS forwarders.
- Order: The priority of the forwarder.
- Application: Applications for which DNS requests have to be forwarded to the selected DNS service.
- DNS Service: The DNS service that the DNS request will be forwarded to for the specified application.
DNS transparent forwarder
SD-WAN can be configured as a transparent DNS forwarder. In this mode, SD-WAN can intercept DNS requests that are not destined to it’s IP address and forward them to the specified DNS service. Only the DNS requests coming from local service on trusted interface(s) are intercepted. If the DNS requests match any applications in the DNS forwarder list, then it is forwarded to the configured DNS service. DNS forwarding is supported only for requests coming over UDP connections.
To configure SD-WAN as a DNS transparent forwarder:
- Navigate to Sites > DNS > DNS Transparent Forwarders. Click +.
-
Enter values for the following parameters:
- Order: The priority of the forwarder.
- Application: Applications for which DNS requests have to be forwarded to the selected DNS service.
- DNS Service: The DNS service that the DNS request will be forwarded to for the specified application.
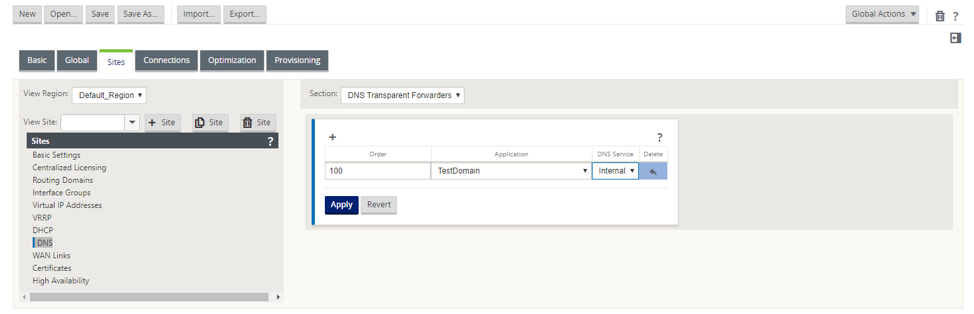
Similarly, continue to add other DNS transparent forwarders as required.
- Click Apply.
Monitoring
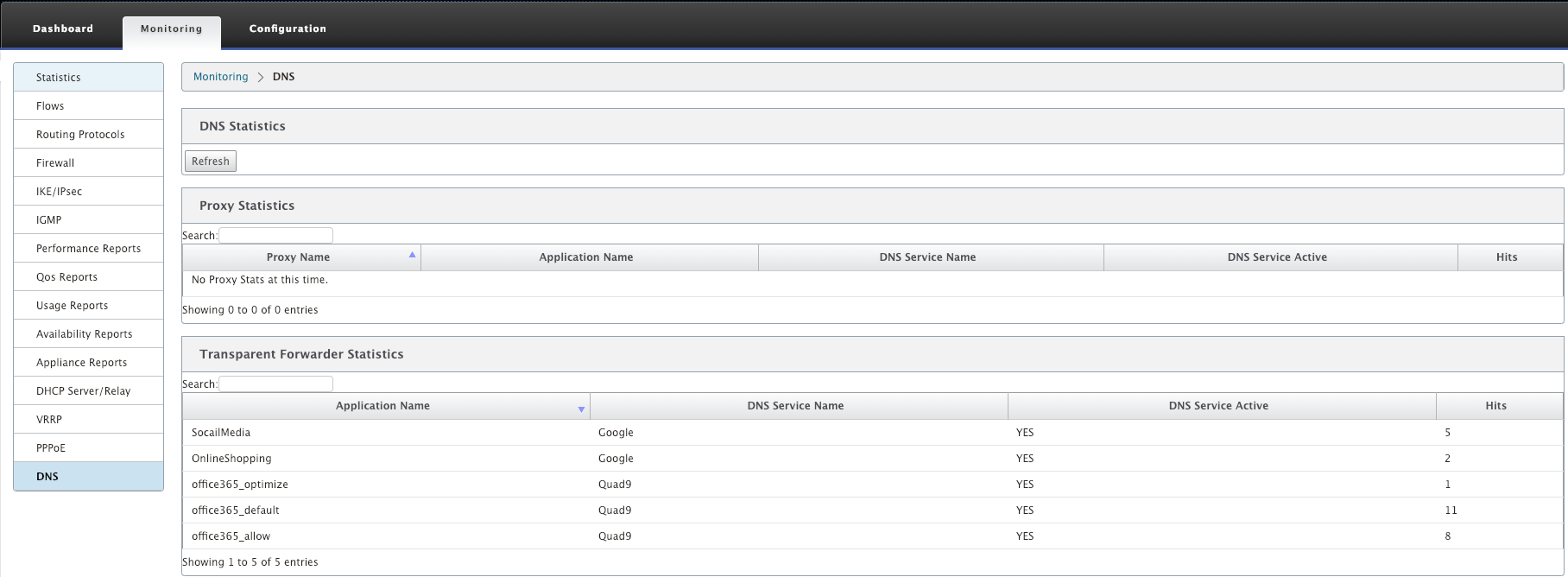
To view Proxy statistics and Transparent forwarder statistics, navigate to Monitoring > DNS. You can view the application name, DNS service name, DNS service status, and the number of hits to the DNS service.
Proxy Statistics
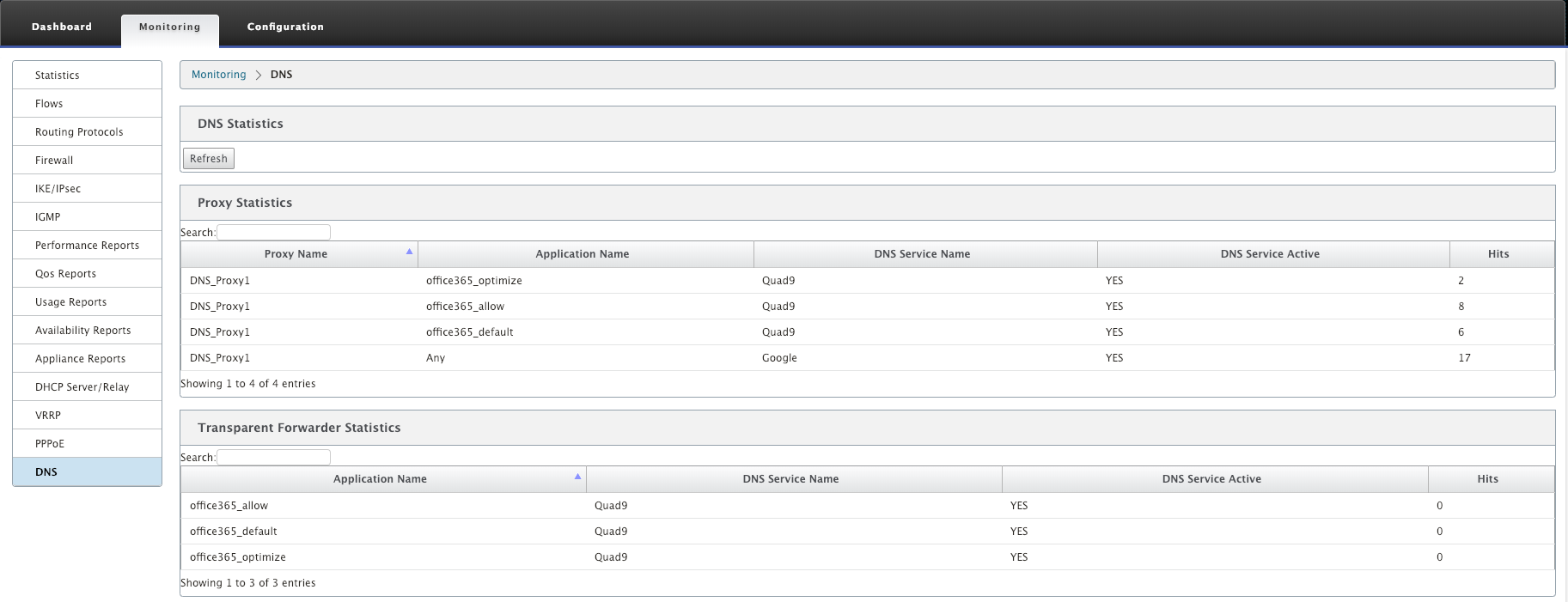
Transparent Forwarder Statistics
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.