This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Hairpin Mode
With hairpin deployment, you can implement use of a Remote Hub site for internet access through backhaul or hairpin when local internet services are unavailable or are experiencing slower traffic. You can apply high bandwidth routing between client sites by allowing backhauling from specific sites.
The purpose of a hairpin deployment from a non-WAN to a WAN forwarding site is to provide more efficient deployment process and more streamlined technical implementation. You can use a remote hub site for internet access when needs arise, and can route flows through the virtual path to the SD-WAN network.
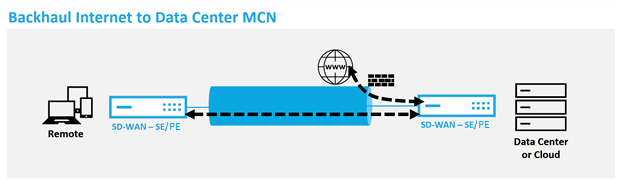
For example, consider an administrator with multiple SD-WAN Sites, A and B. Site A has poor internet service. Site B has usable internet service, with which you want to backhaul traffic from site A to site B only. You can try to accomplish this without the complexity of strategically weighted route costs and propagation to sites that should not receive the traffic.
Also, the route table is not shared across all sites in a Hairpin deployment. For example, if traffic is hairpin’ned between Site A and Site B through Site C, then only Site C would be aware of site A’s and B’s routes. Site A and Site B do not share each other’s route table unlike in WAN-to-WAN forwarding.
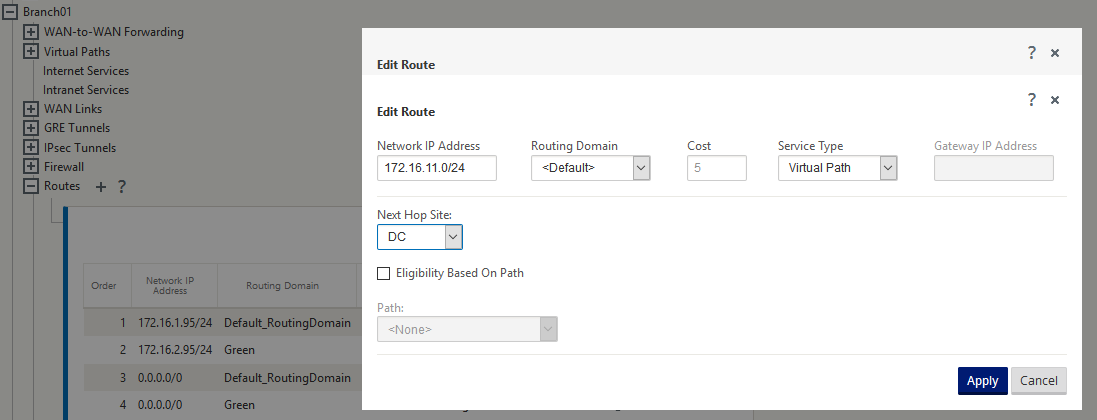
When traffic is Hairpin’ned between Site A and Site B through Site C, the static routes are required to be added in Site A and Site B indicating that the next hop for both the sites is the intermediate Site C.
WAN-to-WAN Forwarding and Hairpin deployment have certain differences, namely:
-
Dynamic Virtual Paths are not configured. Always, the intermediate site sees all the traffic between the two sites.
-
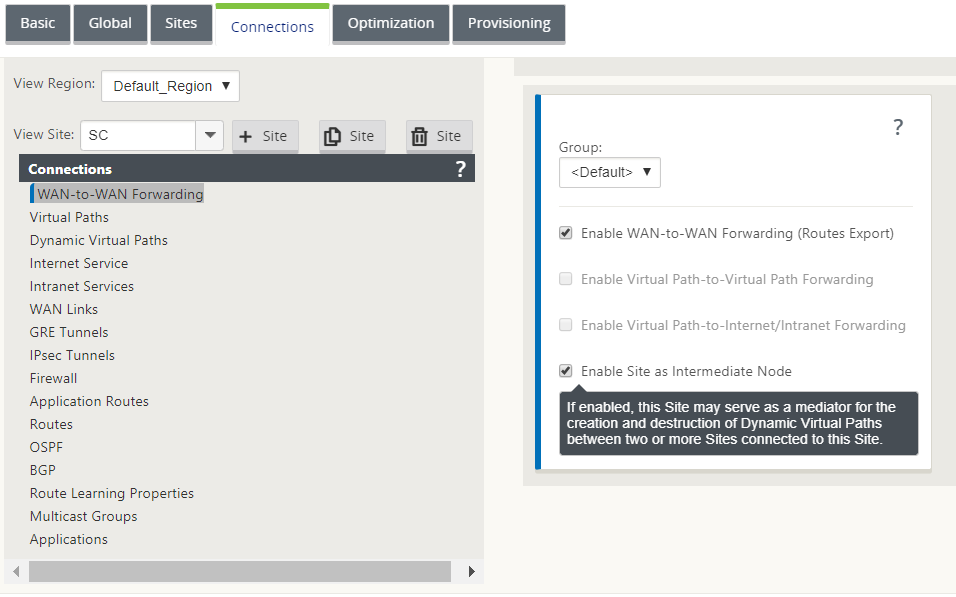
Does not participate in WAN-to-WAN Forwarding groups.
WAN-to-WAN Forwarding and Hairpin deployment are mutually exclusive. Only one of them can be configured at any given point in time.
Citrix SD-WAN SE/PE and VPX (virtual) appliances support hairpin deployment. You can now configure a 0.0.0.0/0 route to hairpin traffic between two locations without affecting any additional locations. If hairpinning used for intranet traffic, specific Intranet routes are added to the client site to forward intranet traffic through the virtual path to the hairpin site. Enabling WAN-to-WAN forwarding to accomplish hairpin functionality is no longer required.
You can configure hairpin deployment through the Citrix SD-WAN™ web management interface from the configuration editor.
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.