This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Deploy appliances for Use with plug-ins
Client acceleration requires special configuration on the WANOP Client Plug-in appliance. Other considerations include appliance placement. Plug-ins are typically deployed for VPN connections.
Use a dedicated appliance when possible
Attempting to use the same appliance for both plug-in acceleration and link acceleration is often difficult, because the two uses sometimes call for the appliance to be at different points in the data center, and the two uses can call for different service-class rules.
In addition, a single appliance can serve as an endpoint for plug-in acceleration or as an endpoint for site-to-site acceleration, but cannot serve both purposes for the same connection at the same time. Therefore, when you use an appliance for both plug-in acceleration for your VPN and for site-to-site acceleration to a remote data center, plug-in users do not receive site-to-site acceleration. The seriousness of this problem depends on how much of the data used by plug-in users comes from remote sites.
Finally, because a dedicated appliance’s resources are not divided between plug-in and site-to-site demands, they provide more resources and thus higher performance to each plug-in user.
Use inline mode when possible
An appliance should be deployed on the same site as the VPN unit that it supports. Typically, the two units are in line with each other. An inline deployment provides the simplest configuration, the most features, and the highest performance. For best results, the appliance should be directly in line with the VPN unit.
However, appliances can use any deployment mode, except group mode or high availability mode. These modes are suitable for both appliance-to-appliance and client-to-appliance acceleration. They can be used alone (transparent mode) or in combination with redirector mode.
Place the appliances in a secure part of your network
An appliance depends on your existing security infrastructure in the same way that your servers do. It should be placed on the same side of the firewall (and VPN unit, if used) as the servers.
Avoid NAT problems
Network address translation (NAT) at the plug-in side is handled transparently and is not a concern. At the appliance side, NAT can be troublesome. Apply the following guidelines to ensure a smooth deployment:
-
Put the appliance in the same address space as the servers, so that whatever address modifications are used to reach the servers are also applied to the appliance.
-
Never access the appliance by using an address that the appliance does not associate with itself.
-
The appliance must be able to access the servers by using the same IP addresses at which plug-in users access the same servers.
-
In short, do not apply NAT to the addresses of servers or appliances.
Select softboost mode
On the Configure Settings: Bandwidth Management page, select Softboost mode. Softboost is the only type of acceleration supported with the WANOP Client Plug-in Plug-in.
Define plug-in acceleration rules
The appliance maintains a list of acceleration rules that tell the clients which traffic to accelerate. Each rule specifies an address or subnet and a port range that the appliance can accelerate.
What to Accelerate-The choice of what traffic to accelerate depends on the use the appliance is being put to:
-
VPN accelerator - If the appliance is being used as a VPN accelerator, with all VPN traffic passing through the appliance, all TCP traffic should be accelerated, regardless of destination.
-
Redirector mode - Unlike with transparent mode, an appliance in redirector mode is an explicit proxy, causing the plug-in to forward its traffic to the redirector-mode appliance even when doing so is not desirable. Acceleration can be counterproductive if the client forwards traffic to an appliance that is distant from the server, especially if this “triangle route” introduces a slow or unreliable link. Therefore, Citrix® recommends that acceleration rules be configured to allow a given appliance to accelerate its own site only.
-
Other uses - When the plug-in is used neither as a VPN accelerator nor in redirector mode, the acceleration rules should include addresses that are remote to the users and local to datacenters.
Define the Rules- Define acceleration rules on appliance, on the Configuration: WANOP Client Plug-in: Acceleration Rules tab.
Rules are evaluated in order, and the action (Accelerate or Exclude) is taken from the first matching rule. For a connection to be accelerated, it must match an Accelerate rule.
The default action is to not accelerate.
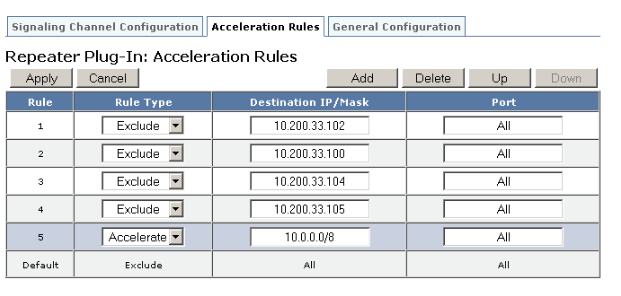
Figure 1. Setting Acceleration Rules
-
On the Configuration: WANOP Plug-in: Acceleration Rules tab:
-
Add an Accelerated rule for each local LAN subnet that can be reached by the appliance. That is, click Add, select Accelerate, and type the subnet IP address and mask.
-
Repeat for each subnet that is local to the appliance.
-
-
If you need to exclude some portion of the included range, add an Exclude rule and move it above the more general rule. For example, 10.217.1.99 looks like a local address. If it is really the local endpoint of a VPN unit, create an Exclude rule for it on a line above the Accelerate rule for 10.217.1.0/24.
-
If you want to use acceleration for only a single port (not recommended), such as port 80 for HTTP, replace the wildcard character in the Ports field with the specific port number. You can support additional ports by adding additional rules, one per port.
-
In general, list narrow rules (usually exceptions) before general rules.
-
Click Apply. Changes are not saved if you navigate away from this page before applying them.
IP port usage
Use the following guidelines for IP port usage:
-
Ports used for communication with WANOP Client Plug-in Plug-in–The plug-in maintains a dialog with the appliance over a signaling connection, which by default is on port 443 (HTTPS), which is allowed through most firewalls.
-
Ports used for communication with servers–Communication between the WANOP Client Plug-in Plug-in and the appliance uses the same ports that the client would use for communication with the server if the plug-in and appliance were not present. That is, when a client opens an HTTP connection on port 80, it connects to the appliance on port 80. The appliance in turn contacts the server on port 80.
In redirector mode, only the well-known port (that is, the destination port on the TCP SYN packet) is preserved. The ephemeral port is not preserved. In transparent mode, both ports are preserved.
The appliance assumes that it can communicate with the server on any port requested by the client, and the client assumes that it can communicate with the appliance on any desired port. This works well if appliance is subject to the same firewall rules as the servers. When such is the case, any connection that would succeed in a direct connection succeeds in an accelerated connection.
TCP option usage and firewalls
WANOP Client Plug-in parameters are sent in the TCP options. TCP options can occur in any packet and are guaranteed to be present in the SYN and SYN-ACK packets that establish the connection.
Your firewall must not block TCP options in the range of 24-31 (decimal), or acceleration cannot take place. Most firewalls do not block these options. However, a Cisco PIX or ASA firewall with release 7.x firmware might do so by default, and therefore you might have to adjust its configuration.
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.