Dynamic routing
After configuration and deployment of SD-WAN appliances in the network and once the connections are established, it is important to ensure that the traffic is properly redirected through the overlay SD-WAN network. You can check traffic redirection by using ping and traceroute diagnostic tools. If the ping and traceroute tests indicate that connectivity is established through the underlay paths, traffic redirection can be achieved by using the following dynamic routing protocols.
-
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF): It is an interior gateway protocol, used to redirect traffic within an autonomous system, like the enterprise network. OSPF uses a link state routing algorithm to detect changes in the network topology and reroute packets by computing the shortest path first for each route. Use this protocol to redirect MPLS traffic. For more information, see OSPF section.
-
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP): It is an exterior gateway protocol designed to redirect traffic routing and reachability information among different autonomous systems on the internet. It is capable of making routing decisions based on paths determined by ISPs. Use this protocol to redirect Internet traffic. For more information, see Configure BGP section.
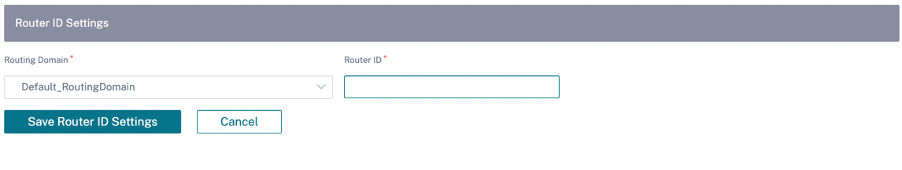
Earlier, the dynamic routing capability was available only for a single router ID. You were able configure a unique router ID either globally for all the configured routing domains (one for OSPF and BGP) or provide no router ID. From Citrix SD-WAN 11.3.1 release onwards, you can not only configure a router ID for the entire protocol but also configure a router ID for each routing domain. With this enhancement, you can enable stable dynamic routing across multiple instances with different router ID’s converging in a stable manner.
If you configure a router ID for a specific routing domain, the specific router ID overrides the protocol level routing domain.
OSPF
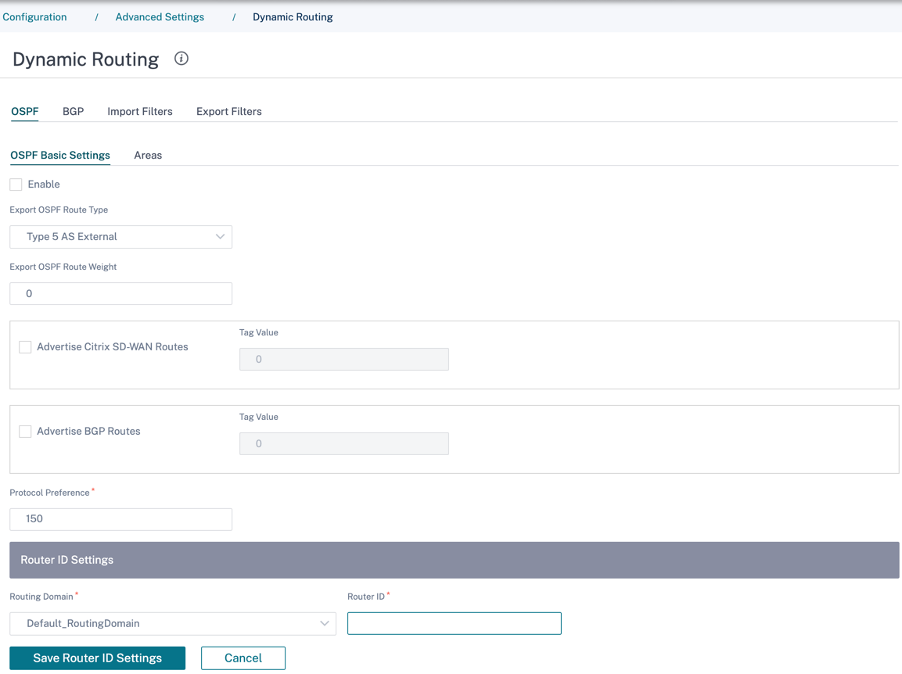
To configure OSFF, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > Dynamic Routing > OSPF.
OSPF basic settings
Here are the parameters to be configured:
-
Enable: Allow the OSPF routing protocol on the SD-WAN appliance to start exchanging Hello packets between neighboring routers.
-
Router ID: The IPv4 address used for OSPF advertisements. This field is optional. If it is not specified, the lowest virtual IPv4 address of the virtual interfaces participating in routing is chosen. For the IPv6 interface, it is mandatory to specify the router ID in IPv4 format. For example, 1.1.1.1.
Note
-
The router ID configuration is optional for an IPv4 network. But for an IPv6 network, the router ID configuration is mandatory. The router ID for an IPv6 network must be configured in the same IPv4 format (32-bit notation).
-
You must create separate IPv4 and IPv6 peering to the same router (if applicable) for learning and advertising.
-
-
Export OSPF Route Type: Advertise the SD-WAN route to OSPF neighbors as type 1 Intra-area route or type 5 External route.
-
Export OSPF Route Weight: The cost advertised to OSPF neighbors is the original route cost and the weight configured here.
-
Advertise SD-WAN Routes: To advertise SD-WAN routes to the peer network elements.
-
Advertise BGP Routes: To enable redistribution of BGP routes into the OSPF domain.
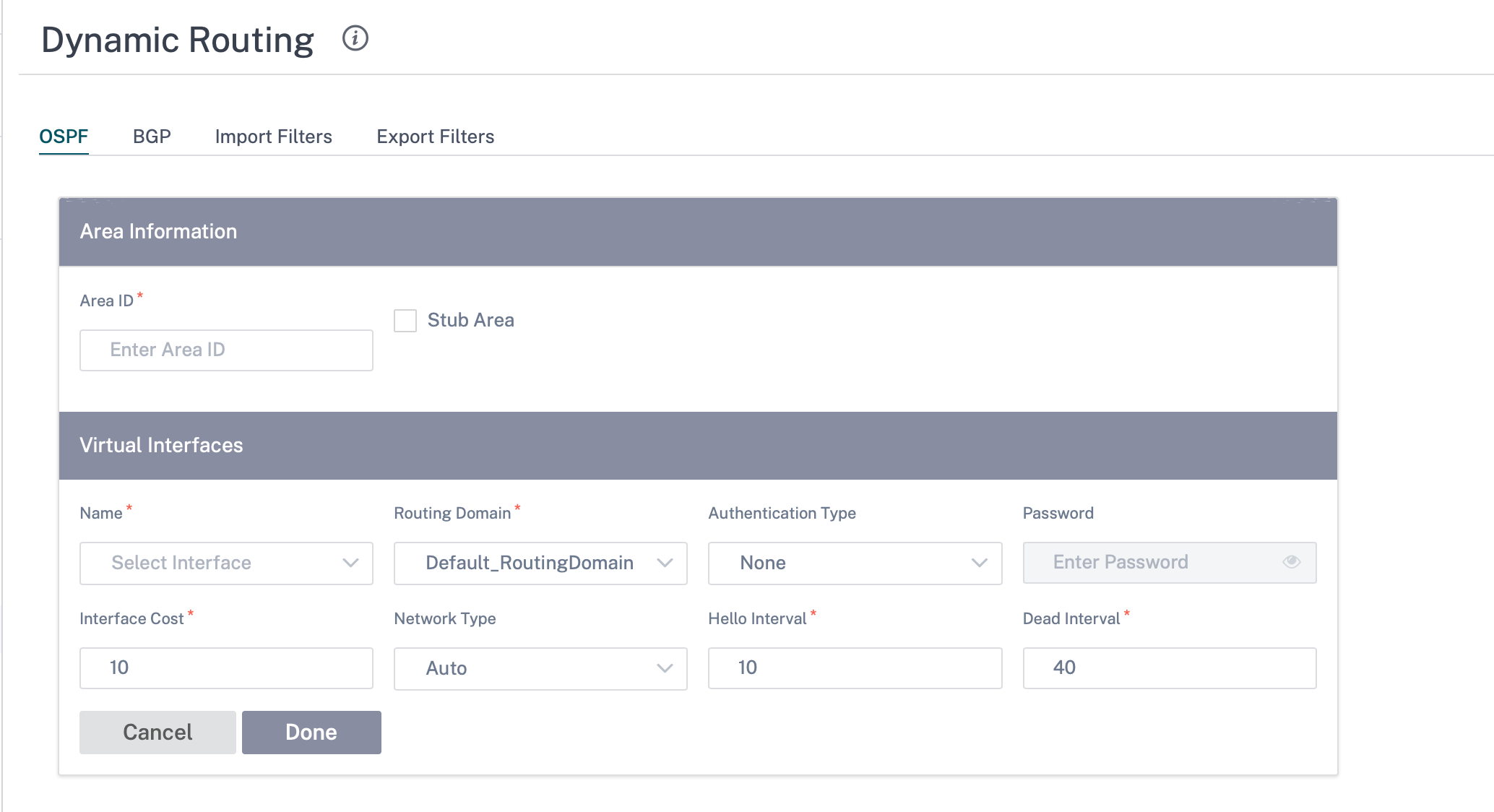
Areas
Click + Area and provide the Area ID of the network that OSPF will learn routes from and advertise routes. Stub area ensures that this area will not receive route advertisements from outside of the designated Autonomous System. Configure the virtual interface settings.
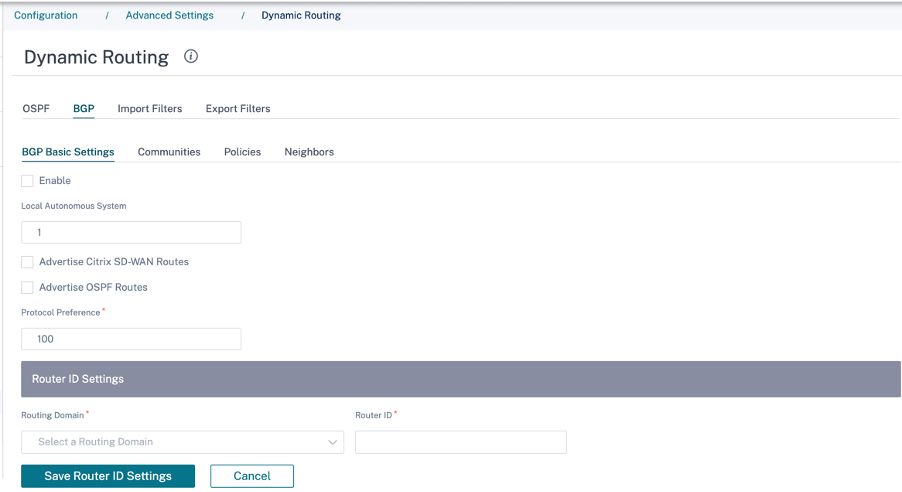
BGP
To configure BGP, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > Dynamic Routing > BGP.
BGP basic settings
The following are the parameters to be configured:
-
Enable: Allow the BGP routing protocol on the SD-WAN appliance to start sending an open message as part of BGP peering.
-
Router ID: The IPv4 address used for BGP advertisements. If the router ID is not specified the lowest virtual IPv4 address of the virtual interfaces participating in routing is chosen.
Note
-
The router ID configuration is optional for an IPv4 network. But for an IPv6 network, the router ID configuration is mandatory. The router ID for an IPv6 network must be configured in the same IPv4 format (32-bit notation).
-
You must create separate IPv4 and IPv6 peering to the same router (if applicable) for learning and advertising.
-
-
Local Autonomous System: Autonomous system number the BGP protocol is running in.
-
Advertise SD-WAN Routes: To advertise SD-WAN routes to the peer network elements.
-
Advertise OSPF Routes: To enable redistribution of OSPF routes into the BGP domain.
Communities
Click + Community to add a community. A collection of BGP communities that can be used for route filtering. The community list can also be used to set or modify the communities of a matching route.
For each policy, users can configure multiple community strings, AS-PATH-PREPEND, MED attribute. Users can configure up to 10 attributes for each policy.
Specify the name for the community and enter a community string to be advertised.
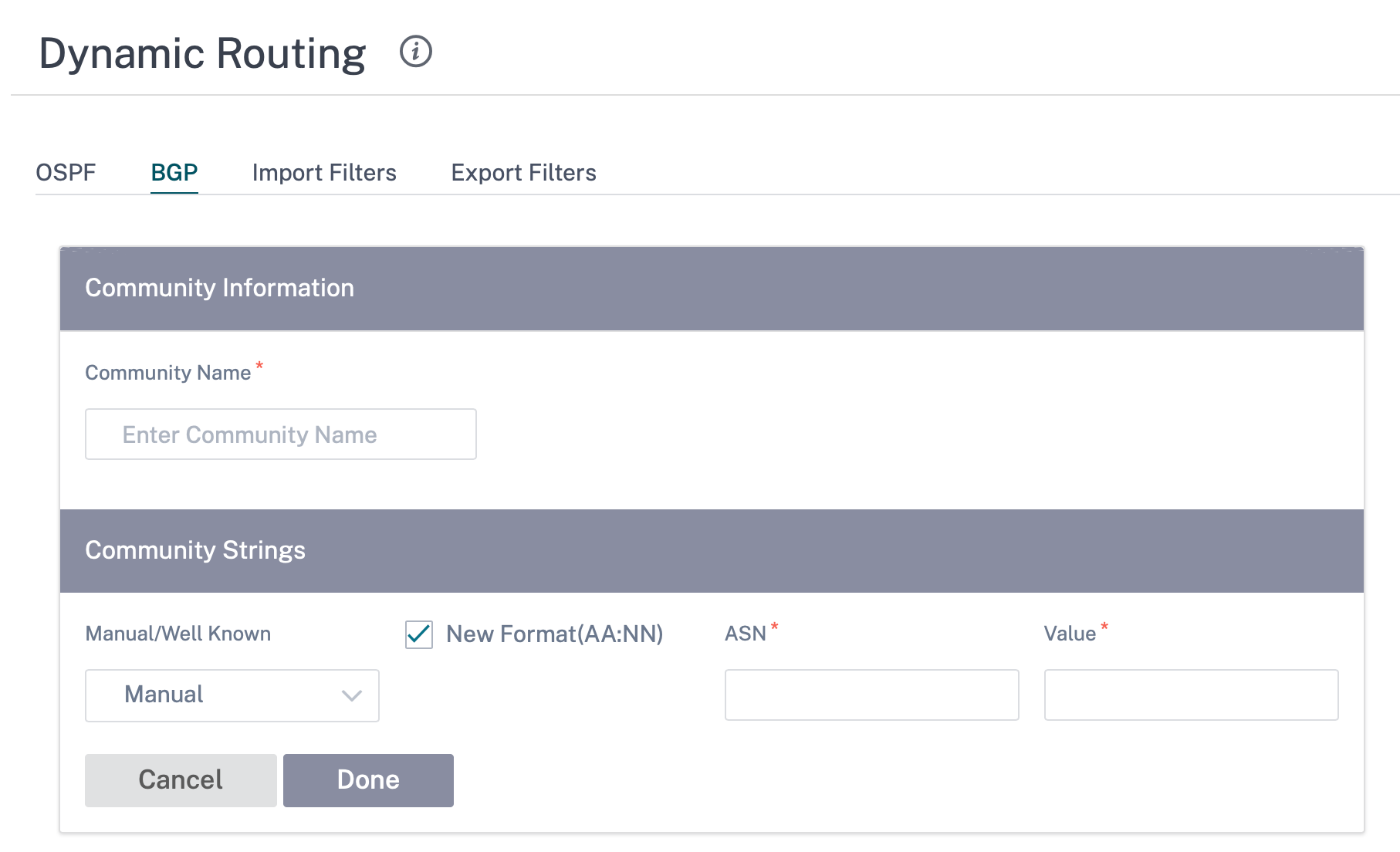
- Community Name: Enter a community name.
- Manual/Well Known: Configure BGP community manually or select a standard well known BGP community from the list.
- New Format (AA:NN): Select the check box to use the new format for configuring the BGP community.
- ASN: The first 16 digit of the BGP community when using the new format for configuration.
- Value: Enter the BGP community value.
Policies
A collection of BGP attributes which can be used to set or modify route attributes for each BGP Peer. Create BGP policies to be applied selectively to a set of networks on a per-neighbor basis, in either direction (import or export). An SD-WAN appliance supports eight policies per site, with up to eight network objects (or eight networks) associated with a policy.
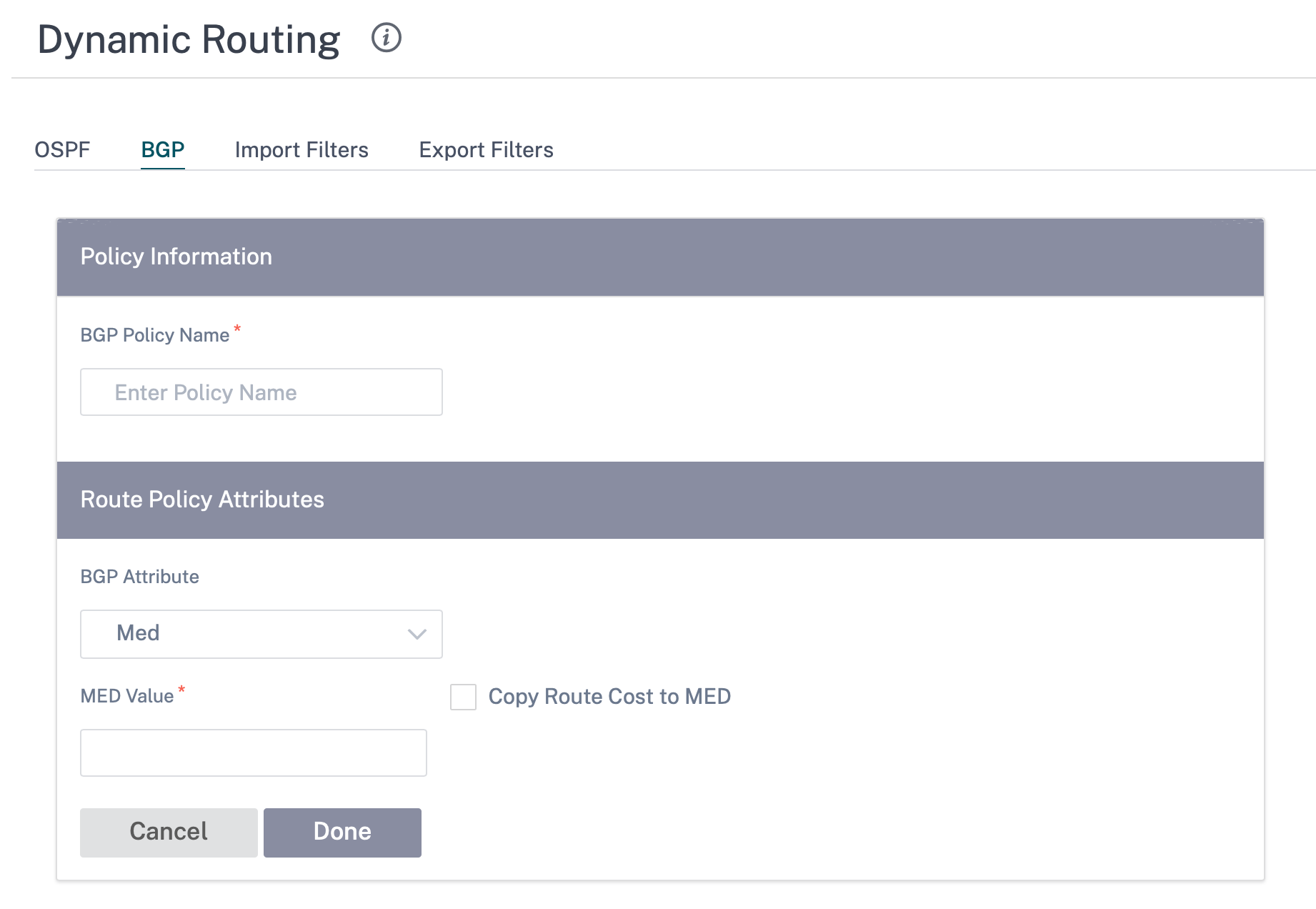
- BGP Policy Name: Enter the BGP policy name.
- BGP Attributes: Select the BGP attributes from the list and provide the necessary information.
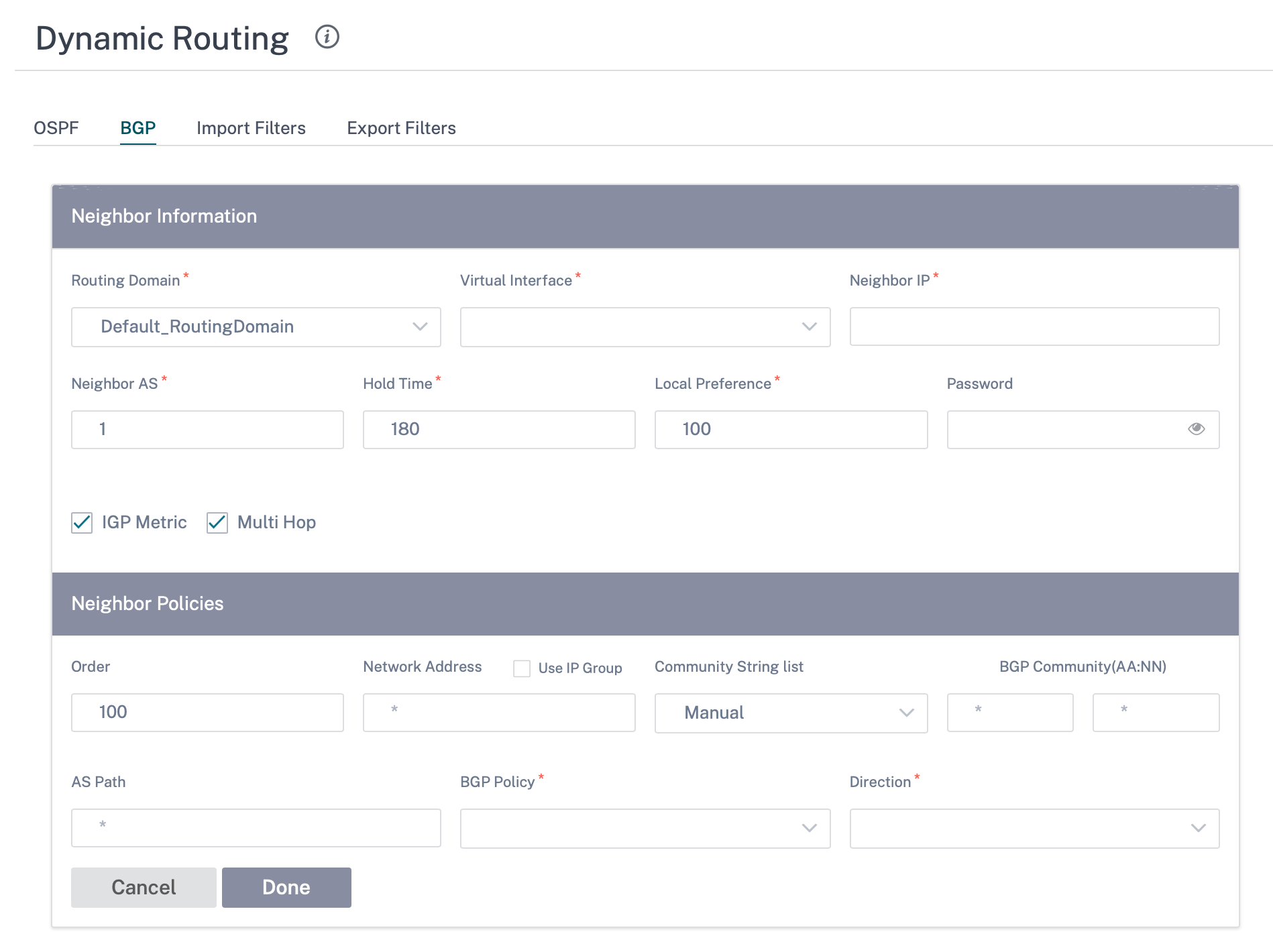
Neighbors
Neighbors are all of the configured BGP peer routers that are checked to find the shortest paths for routing. All the neighbors must be part of the same Autonomous System.
Click + Neighbor to add a configured BGP policy for neighboring routers. You can specify the direction to indicate if this policy is applied for incoming or outgoing routes.
Route filtering
For networks with Route Learning enabled, Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator™ provides more control over which SD-WAN routes are advertised to routing neighbors rather and which routes are received from routing neighbors, rather than advertising and accepting all or no routes.
Import filters
Import Filters are used to accept or not accept routes which are received using OSPF and BGP neighbors based on specific match criteria. Import filter rules are the rules that must be met before importing dynamic routes into the SD-WAN route database. No routes are imported by default.
You can configure Filters to fine-tune how route-learning takes place.
Click + Import Rule.
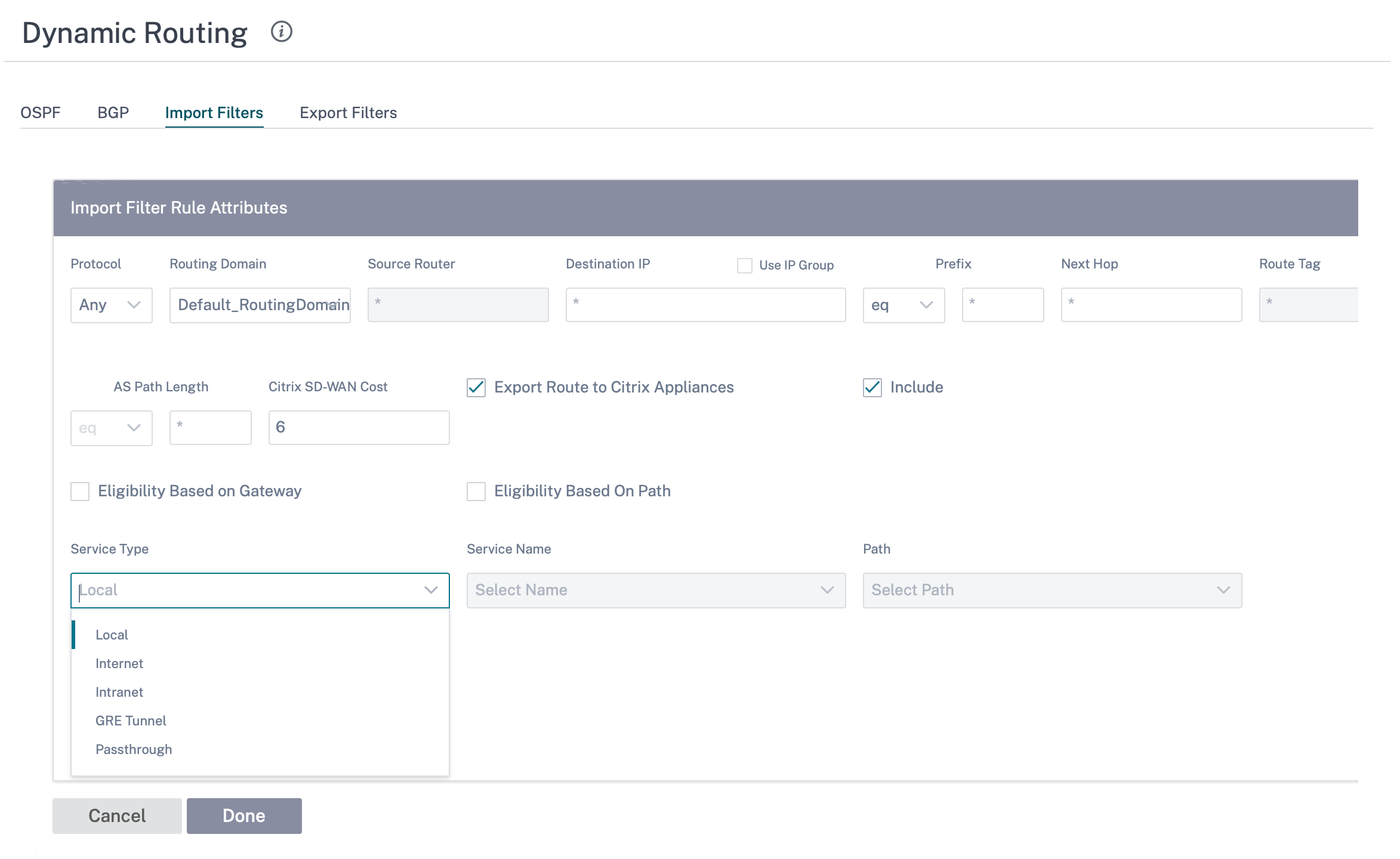
Use the following criteria to construct each Export Filter that you want to create.
| Field Criteria | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | The routing protocol using which a route is learned. Select the protocol from the drop-down list. | Any, OSPF, BGP |
| Routing Domain | Enter the routing domain from the drop-down list. |
|
| Source Router | The IP address of the source router, it is applicable for iBGP only |
|
| Destination IP | The IP address and subnet mask of a route’s destination |
|
| Use IP Group | Select the Use IP Group check box as needed. |
|
| Prefix | To match routes by prefix, choose a match predicate from the menu and enter a Route prefix in the adjacent field |
|
| Next Hop | The IP address of the next hop |
|
| Route Tag | The OSPF Route tag that the filter matches. OSPF route tags prevent routing loops during mutual redistributing between OSPF and other protocols | Numeric value |
| Cost | The route cost used to match OSPF routes for importing | Numeric value |
| AS Path Length | The AS path length used to match BGP routes for importing | Numeric value |
| Export Route to Citrix Appliances | Select the check box to enable this filter. Otherwise the filter is ignored | None |
| Include | Select the check box to Include routes that match this filter. Otherwise matching routes are ignored | None |
| Eligibility Based on Gateway | Select this check box and provide the Service Type, Service Name and Path from the drop-down list. | Service Type (Local, Internet, Intranet, GRE Tunnel, Passthrough), Service Name, and Path |
| Eligibility Based on Path | Select this check box and provide the Service Type, Service Name and Path from the drop-down list. | Service Type (Local, Internet, Intranet, GRE Tunnel, Passthrough), Service Name, and Path |
Click Done to save the settings.
Export filters
Export Filters are used to include or exclude routes for advertisement using OSPF and BGP protocols based on specific match criteria. Export filter rules are the rules that must be met when advertising SD-WAN routes over dynamic routing protocols. All the routes are advertised to peers by default.
Click + Export Rule.
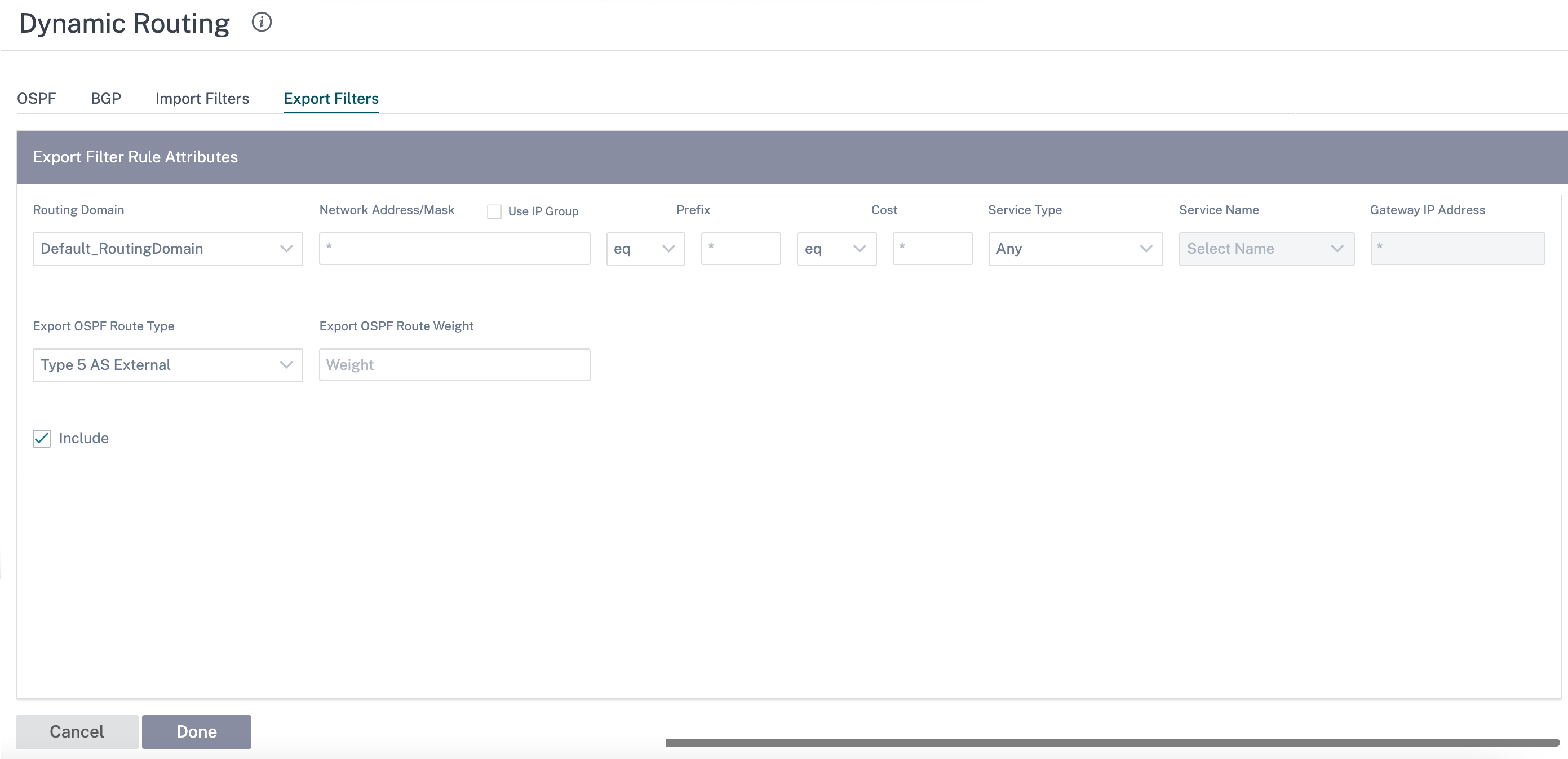
Use the following criteria to construct each Export Filter that you want to create.
| Field Criteria | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Routing Domain | Select the routing domain from the drop-down list. | Routing domain |
| Network Address/Mask | Enter the IP address and subnet mask of configured Network Object that describes the route’s network |
|
| Use IP Group | Select the check box if needed and enter the IP group from the drop-down list. |
|
| Prefix | To match routes by prefix, choose a match predicate from the menu and enter a Route prefix in the adjacent field |
|
| Cost | The method (predicate) and the SD-WAN Route Cost that are used to narrow the selection of routes exported | Numeric value |
| Service Type | Select the Service types that are assigned to matching routes from a list of Citrix SD-WAN Services | Any, Local, Virtual Path, Internet, Intranet, LAN GRE Tunnel, LAN IPsec Tunnel |
| Site/Service Name | For Intranet, LAN GRE Tunnel, and LAN IPsec Tunnel, specify the name of the configured Service Type to use | Text string |
| Gateway IP Address | If you choose LAN GRE Tunnel as the Service Type, enter the gateway IP for the tunnel | IP address |
| Export OSPF Route Type | Advertise the Citrix SD-WAN route to OSPF neighbors as type 1 Intra-area route or type 5 External route. Default route is always advertised as type - 5 external route to normal areas and type-3 summary route to stub areas. | Route type |
| Export OSPF Route Weight | When export Citrix SD-WAN routes to OSPF, and the weight to each route’s Citrix SD-WAN cost as total cost. | Weight |
| Include | Select the check box to Include routes that match this filter. Otherwise matching routes are ignored | None |
Route filtering is implemented on LAN routes and Virtual Path routes in an SD-WAN network (Data Center/Branch) and is advertised to a non-SD-WAN network through using BGP and OSPF.
You can configure up to 512 Export Filters and 512 Import Filters. This is the overall limit, not per routing domain limit.