Application rules
Application rules allow the Citrix SD-WAN™ appliance to parse incoming traffic and classify them as belonging to a particular application or application group. This classification enhances the Quality of Service (QoS) of individual application or application families by creating and applying application rules.
You can filter traffic flows based on application, application group, or application object match-types and apply application rules to them. The application rules are similar to the Internet Protocol (IP) rules. For information on IP rules see, IP Rules.
For every application rule, you can specify the traffic policy. The following are the available traffic policies:
- Load Balance Path: Application traffic for the flow is balanced across multiple paths. Traffic is sent through the best path until that path is used. The remaining packets are sent through the next best path.
- Persistent Path: Application traffic remains on the same path until the path is no longer available.
- Duplicate Path: Application traffic is duplicated across multiple paths, increasing reliability. The application rules are associated to classes.
How application rules are applied?
In the SD-WAN network, when the incoming packets reach the SD-WAN appliance, the initial few packets do not undergo DPI classification. At this point, the IP rule attributes such as Class, TCP termination are applied to the packets. After DPI classification, the application rule attributes such as Class, traffic policy override the IP rule attributes.
The IP rules have more number of attributes as compared to the application rules. The application rule overrides only a few IP rule attributes. The rest of the IP rule attributes remain processed on the packets.
For example, consider you have specified an application rule for a webmail application such as Google Mail that uses the SMTP protocol. The IP rule set for the SMTP protocol is applied initially before DPI classification. After parsing the packets and classifying it as belonging to the Google Mail application, the application rule specified for the Google Mail application is applied.
Create application rules
To create application rules, navigate to Configuration > QoS > QoS Policies > Application Rules. Select Global Rules tab for creating application rules at the global level or Site/Group Specific Rules for creating rules at a site level.
Click New Application Rule under the Application Rules section.
-
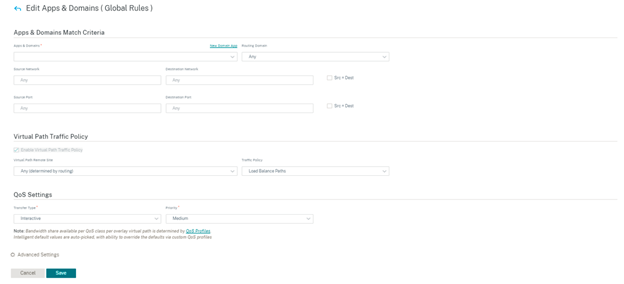
Apps and Domains Match Criteria
- Apps & Domains: Choose an application or domain from the drop-down list. You can also create a domain app by clicking + New Domain App. Enter a name and add domains.
- Routing Domain: Select a routing domain. You can select the default routing domain or select Any.
- Source Network: Source IP address and the subnet mask to match against the traffic.
- Destination Network: Destination IP address and the subnet mask to match against the traffic.
- Source Port: Source port number or port range to match against the traffic.
- Destination Port: Destination port number or port range to match against the traffic.
- Src = Dest: If selected, the source port is also used for the destination port.
-
Virtual Path Traffic Policy
Select the Enable Virtual Path Traffic Policy check box.
- Virtual Path Remote Site: Select the virtual path for the remote site.
-
Traffic Policy: Choose one of the following traffic policies as needed.
- Load Balance Paths: Application traffic for the flow is balanced across multiple paths. Traffic is sent through the best path until that path is used. The remaining packets are sent through the next best path.
-
Persistent Path: Application traffic remains on the same path until the path is no longer available. Select one of the following Persistence Policies:
- Persist on the originating link: The application traffic remains on the originating link until the path is no longer available.
- Persist on MPLS link if available, else on the originating link: The application traffic remains on the MPLS link. If the MPLS link is unavailable, then the traffic remains on the originating link.
- Persist on Internet link if available, else on the originating link: The application traffic remains on the internet link. If the internet link is unavailable, then the traffic remains on the originating link.
- Persist on Private Intranet link if available, else on the originating link: The application traffic remains on the private intranet link. If the private intranet link is unavailable, then the traffic remains on the originating link.
Persistence Impedance is the time (in ms) until which the application traffic remains on the link.
- Duplicate Paths: Application traffic is duplicated across multiple paths, increasing reliability.
-
QoS Settings (QoS Class)
-
Transfer Type: Choose one of the following transfer types:
- Realtime: Used for low latency, low bandwidth, time-sensitive traffic. Real-time applications are time-sensitive but don’t really need high bandwidth (for example voice over IP). Real-time applications are sensitive to latency and jitter but can tolerate some loss.
- Interactive: Used for interactive traffic with low to medium latency requirements and low to medium bandwidth requirements. The interaction is typically between a client and a server. The communication might not need high bandwidth but is sensitive to loss and latency.
- Bulk: Used for high bandwidth traffic and applications that can tolerate high latency. Applications that handle file transfer and need high bandwidth are categorized as a bulk class. These applications involve little human interference and are mostly handled by the systems themselves.
- Priority: Choose a priority for the selected transfer type.
-
Transfer Type: Choose one of the following transfer types:
Advanced Settings
-
WAN General
- Retransmit Lost Packets: Sends traffic that matches this rule to the remote appliance over a reliable service and retransmits lost packets.
- Enable Packet Aggregation: Aggregates small packets into larger packets.
-
LAN to WAN
- Drop Depth(bytes): Queue depth threshold after which packets are dropped.
- Drop Limit: Time after which packets waiting in the class scheduler are dropped. Not applicable for a bulk class.
- Enable RED: Random Early Detection (RED) ensures fair sharing of class resources by discarding packets when congestion occurs.
- Duplicate Packet Disable Depth(bytes): The queue depth of the class scheduler at which point the duplicate packets are not generated.
- Duplicate Packet Disable Limit: Time for which duplication can be disabled to prevent duplicate packets from consuming bandwidth.
-
WAN to LAN
- DSCP Tag: DSCP tag applied to the packets that match this rule on WAN to LAN, before sending them to the LAN.
- Enable Packets Resequencing: The traffic flows that match the rule gets tagged for sequence order, and the packets gets reordered (if necessary) at the WAN to LAN appliance.
-
Hold Time: Time interval for which the packets are held for resequencing, after which the packets are sent to the LAN. When the timer expires, the packets are sent to the LAN without waiting any further for the prerequisite sequence numbers.
If the rule has a traffic policy as duplicate path, the default hold time is 80 ms. Otherwise, the default is 900 ms for TCP rules and 250 ms for non-TCP rules.
- Discard Late Resequencing Packets: Discards out-of-order packets that arrived after the packets needed for resequencing have been sent to the LAN.
Click Save to save the configuration settings.
Click Verify Configuration on the Configuration > QoS > QoS Policies page to validate any audit error.to validate any audit error.

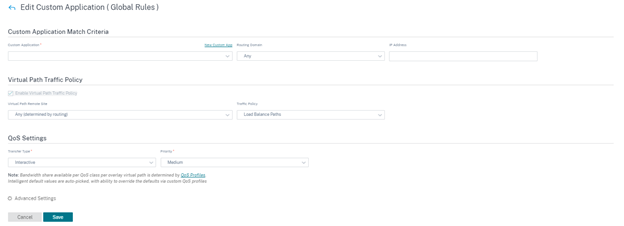
Create custom application rules
You can also create custom application rules. To create a custom application rule, navigate to Configuration > QoS > QoS Policies > Custom Application Rules. Select Global Rules tab for creating custom application rules at the global level or Site/Group Specific Rules for creating rules at a site level.
Click New Custom Application Rule under the Custom Application Rules section. Click New Custom App next to the Custom Application field name. Enter a name for the custom application. In the Match Criteria section, select the application, protocol, DSCP tag and enter the network IP and port number. Click Save.
Enter details in the other fields as needed. For information on field descriptions, refer Create application rules.
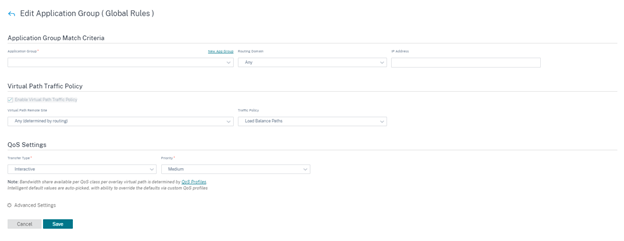
Create application group rules
You can create rules for a group of applications. To create application group rules, navigate to Configuration > QoS > QoS Policies > Application Group Rules. Select Global Rules tab for creating application group rules at the global level or Site/Group Specific Rules for creating rules at a site level.
Click New Application Group Rule under the Application Group Rules section. Click New App Group next to Application Group field name. Enter a name for the application group. Search and add applications as needed. Click Save.
Enter details in the other fields as needed. For information on field descriptions, refer Create application rules.
Verify application rules
To verify application rules, navigate to Reports > Real Time > Flows. Select the site for which you want to view the flow information and the number of flows to display. Click Customize Columns and select the check boxes corresponding to the flow information you want to view. Verify if the flow information is according to the configured rules.
Navigate to Reports > Real Time > Statistics and select Rules. Choose the site and click Retrieve latest data. Verify the configured rules.
For more information about reporting, see Flows.