Network address translation
Network Address Translation (NAT) on the SD-WAN appliance performs IP address conservation to preserve the limited number of registered IP addresses. It translates the private addresses in the internal network into a legal public address and connects your private SD-WAN network with the public internet. The public IP address is used for communication over the internet. NAT also ensures extra security by advertising only one address for the entire network to the internet, hiding the entire internal network.
You can configure the following types of NAT:
- Dynamic source NAT
- Static NAT
- Destination NAT
Note
The NAT capability can only be configured at the site level. There is no global configuration (templates) for NAT.
To configure NAT for a site using the Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator for On-premises, from site level, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > NAT.
Inbound and Outbound NAT
The direction for a connection can either be inside to outside or outside to inside. When a NAT rule is created, you can define the direction using the On Receive check box. When the check box is selected, the direction is configured as Inbound and when the check box is cleared, the direction is configured as Outbound.
- Inbound: The source address is translated for packets received on the service. The destination address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. For example, Internet service to LAN service – For packets received (Internet to LAN), the source IP address is translated. For packets transmitted (LAN to Internet), the destination IP address is translated.
- Outbound: The destination address is translated for packets received on the service. The source address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. For example, LAN service to Internet service – for packets transmitted (LAN to Internet) the source IP address is translated. For packets received (Internet to LAN) the destination IP address is translated.
Zone Derivation
The source and destination firewall zones for the inbound or outbound traffic must not be the same. If both the source and destination firewall zones are the same, NAT is not performed on the traffic.
For outbound NAT, the outside zone is automatically derived from the service. Every service on SD-WAN is associated to a zone by default. For example, Internet service on a trusted internet link is associated with the trusted internet zone. Similarly, for an inbound NAT, the inside zone is derived from the service.
For a Virtual path service NAT zone derivation does not happen automatically, you have to manually enter the inside and outside zone. NAT is performed on traffic belonging to these zones only. Zones cannot be derived for virtual paths because there might be multiple zones within the Virtual path subnets.
Dynamic source NAT
Dynamic Source NAT is a many-to-one mapping of a private IP address or subnets inside the SD-WAN network to a public IP address or subnet outside the SD-WAN network. It allows multiple hosts to have their source IP addresses translated to the same public IP address with different port numbers. Port restricted NAT uses the same outside port for all translations related to an Inside IP address and port pair. The traffic from different zones and subnets over trusted (inside) IP addresses in the LAN segment is sent over a single public (outside) IP address.
Note
Dynamic NAT translations allow all reciprocal traffic for a session initiated from the Inside Network. To filter these connections, add filter Policies for the outbound traffic.
Port Address Translation
Dynamic NAT does Port Address Translation (PAT) along with IP address translation. Port numbers are used to distinguish which traffic belongs to which IP address. A single public IP address is used for all internal private IP addresses, but a different port number is assigned to each private IP address. PAT is a cost effective way to allow multiple hosts to connect to the Internet using a single Public IP address.
The Symmetric check box defines the PAT configuration. While configuring NAT rules, if the check box is selected, Symmetric NAT is configured and when cleared, Port Restricted NAT gets configured in the back-end.
- Port Restricted: Port Restricted NAT uses the same outside port for all translations related to an Inside IP Address and Port pair. This mode is typically used to allow Internet P2P applications.
- Symmetric: Symmetric NAT uses the same outside port for all translations related to an Inside IP Address, Inside Port, Outside IP Address, and Outside Port tuple. This mode is typically used to enhance security or expand the maximum number of NAT sessions.
Port Forwarding
Dynamic NAT with port forwarding allows traffic from an Outside network to access specific hosts and ports on the Inside network without the session being initiated from the inside. This is typically used for inside hosts like web servers.
Once the dynamic NAT is configured you can define the port forwarding policies. Configure dynamic NAT for IP address translation and define the port forwarding policy to map an outside port to an inside port. Dynamic NAT port forwarding is typically used to allow remote hosts to connect to a host or server on your private network.
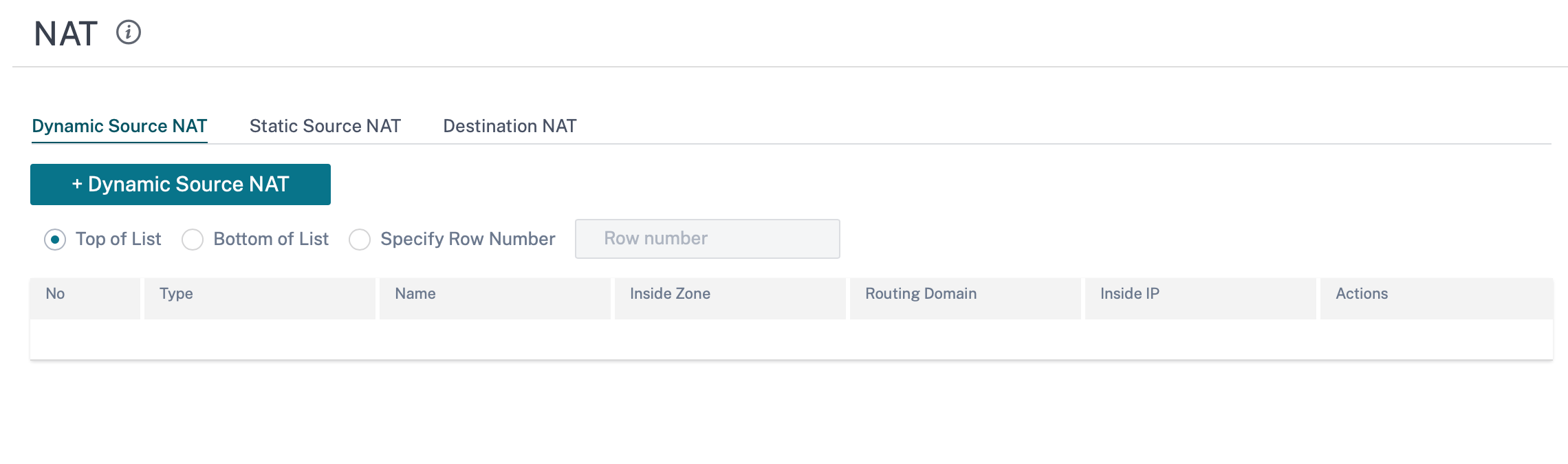
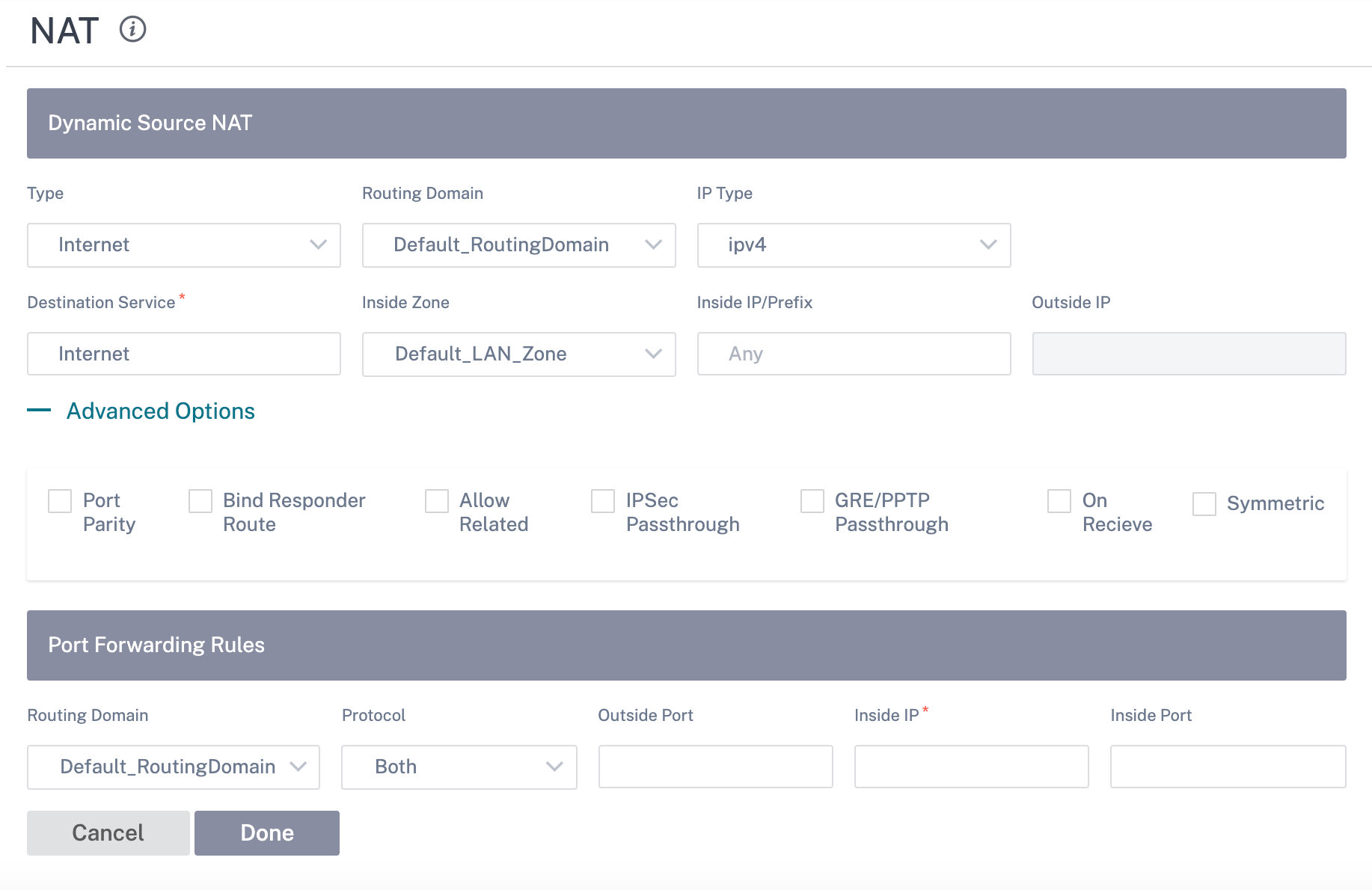
Configure Dynamic Source NAT
To configure dynamic NAT for a site using the Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator for On-premises, from site level, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > NAT > Dynamic Source NAT tab. Click + Dynamic Source NAT.
- Type: The SD-WAN service types on which the NAT policy is applied. For static NAT, the service types supported are Local, Virtual Paths, Internet, Intranet, and Inter-routing domain services.
- Routing Domain: Select the routing domain for which the selected translation applies to.
- IP Address Type: Select the IPv4 or IPv6 address type based on your preference.
- Destination Service: Provide a name for the service that corresponds to the Service Type.
- Inside Zone: The Inside firewall zone match-type that the packet must be from to allow translation.
- Inside IP/Prefix: The inside IP address and prefix that has to be translated to if the match criteria is met.
- Outside IP: The outside IP address and prefix that the inside IP address is translated to if the match criteria is met. For outbound traffic using Internet and Intranet services, the configured WAN link IP address is dynamically chosen as the outside IP address.
- Port Parity: If enabled, outside ports for NAT connections maintain parity (even if inside port is even, odd if outside port is odd).
- Bind Responder Route: Ensures that the response traffic is sent over the same service that it is received on, to avoid asymmetric routing.
- Allow Related: Allow traffic related to the flow matching the rule. For example, ICMP redirection related to the specific flow that matched the policy, if there was some type of error related to the flow.
- IPSec Passthrough: Allow an IPsec (AH/ESP) session to be translated.
- GRE/PPTP Passthrough: Ensures that the response traffic is sent over the same service that it is received on, to avoid asymmetric routing.
- On Receive: When this check box is selected, inbound NAT is configured. When cleared, outbound NAT is configured.
- Symmetric: When this check box is selected, Symmetric NAT is configured. When cleared, port restricted NAT is configured.
Port Forwarding Rules:
- Routing Domain: Select the routing domain for which the selected translation applies to.
- Protocol: TCP, UDP, or both.
- Outside Port: The Outside port that is port forward into the inside port.
- Inside IP: The inside address to forward matching packets.
- Inside Port: The Inside port that the outside port will be port forwarded into.
Every port forwarding rule has a parent NAT rule. The outside IP address is taken from the parent NAT rule.
Note
The Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator for On-premises UI displays auto-created NAT rules when the following conditions are fulfilled:
Internet service is enabled on the site.
IPv4 outbound Internet dynamic source NAT rule is not configured at the site.
At least 1 WAN link is on an untrusted interface or Internet is enabled on all routing domains.
Static source NAT
Static NAT is a one-to-one mapping of a private IP address or subnet inside the SD-WAN network to a public IP address or subnet outside the SD-WAN network. Configure Static NAT by manually entering the inside IP address and the outside IP address to which it has to translate. You can configure Static NAT for the Local, Virtual Paths, Internet, Intranet, and Inter-routing domain services.
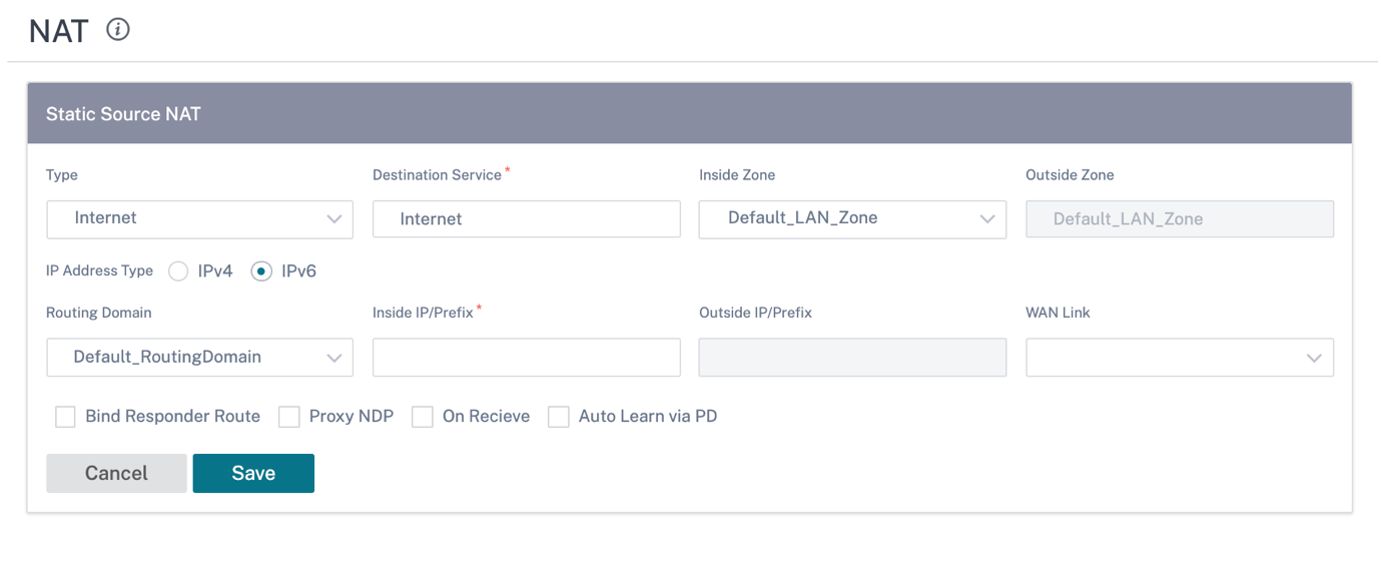
Configure Static source NAT
To configure static NAT for a site using the Citrix SD-WAN Orchestrator for On-premises, from site level, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > NAT > Static Source NAT tab. Click + Static Source NAT.
- Type: The SD-WAN service types on which the NAT policy is applied. For static NAT, the service types supported are Local, Virtual Paths, Internet, Intranet, and Inter-routing domain services
- Destination Service: Provide a name for the service that corresponds to the Service Type.
- Inside Zone: The Inside firewall zone match-type that the packet must be from to allow translation.
- Outside Zone: The outside firewall zone match-type that the packet must be from to allow translation.
- IP Address Type: Select the IPv4 or IPv6 address type based on your preference.
- Routing Domain: Select the routing domain for which the selected translation applies to.
- Inside IP/Prefix: The inside IP address and prefix that has to be translated to if the match criteria is met.
- Outside IP/Prefix: The outside IP address and prefix that the inside IP address is translated to if the match criteria is met.
- Bind Responder Route: Ensures that the response traffic is sent over the same service that it is received on, to avoid asymmetric routing.
- Proxy ARP: Ensures that the appliance responds to local ARP requests for the outside IP address.
- Proxy NDP: Ensures that the appliance responds to local NDP requests for the outside IP address.
- On Receive: When this check box is selected, inbound NAT is configured. When cleared, outbound NAT is configured.
- Auto Learn via PD: This check box gets enabled only when you select IPv6 as the IP Address Type. When selected, Citrix SD-WAN™ requests a prefix from the upstream delegating router and the delegating router responds with a prefix to Citrix SD-WAN.
Static NAT Policies for IPv6 Internet service
Citrix SD-WAN supports static NAT policies for the IPv6 Internet service from release 11.4.0 onwards. A static NAT policy for the IPv6 Internet service specifies the mapping of an inside network prefix to an outside network prefix. The number of static NAT policies required depends on the number of inside networks and the number of outside networks (WAN links). If there are M number of inside networks and N number of WAN links, then the number of static NAT policies required is M x N.
From Citrix SD-WAN release 11.4.0 onwards, while creating a static NAT policy, you can either enter the outside IP address manually or enable Auto Learn via PD. When Auto Learn via PD is enabled, the SD-WAN appliance receives delegated prefixes from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation. Before Citrix SD-WAN release 11.4.0, the outside IP address was derived from the service automatically and there was no option to enter the outside IP address manually. If you are upgrading an appliance to 11.4.0 or a later release and have static NAT policies configured for IPv6 Internet service, then you must manually update the policies.
Configuration example
In the following topology, the Citrix SD-WAN appliance is configured with 2 inside networks and 2 WAN links:
- Inside network 1 resides in the CORPORATE routing domain with network prefix FD01:0203:6561::/64
- Inside network 2 resides in the Wi-Fi routing domain with network prefix FD01:0203:1265::/64
- Through WAN Link 1, the SD-WAN appliance receives from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, 2 delegated prefixes 2001:0D88:1261::/64 and 2001:0D88:1265::/64. These 2 delegated prefixes are used as the outside network prefixes when the traffic from the inside networks transits WAN link 1.
- Through WAN Link 2, the SD-WAN appliance receives from the upstream delegating router through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, 2 delegated prefixes 2001:DB8:8585::/64 and 2001:DB8:8599::/64. These 2 delegated prefixes are used as the outside network prefixes when the traffic from the inside networks transits WAN link 2.
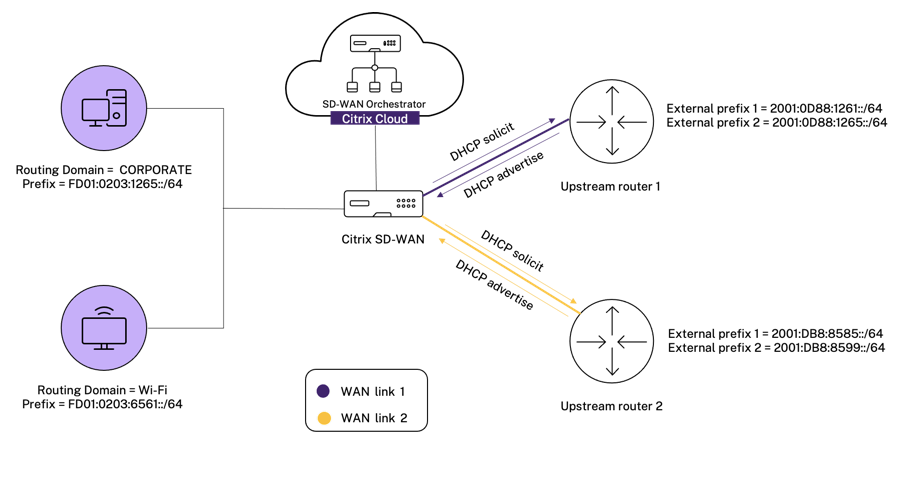
In this scenario, there are M=2 inside networks and N=2 WAN links. Therefore, the number of static NAT policies required for proper deployment of the IPv6 Internet service is 2 x 2 = 4. These 4 static NAT policies specify the address translation for:
- Inside network 1 through WAN link 1
- Inside network 1 through WAN link 2
- Inside network 2 through WAN link 1
- Inside network 2 through WAN link 2
To configure these static NAT policies, from site level, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > NAT > Static Source NAT. Click +Static Source NAT.
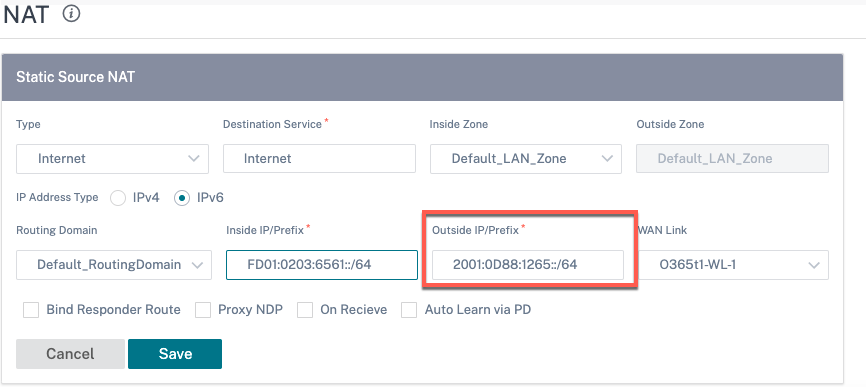
While creating NAT policies, ensure that you select the Type as Internet and IP Address Type as IPv6. Select the WAN link and in the Inside IP/Prefix field, enter the inside network prefix (only /64 prefixes are allowed). In the Outside IP/Prefix field, you can either manually enter the outside network prefix or select the Auto Learn via PD check box.
The following is an example where the outside IP address is entered manually in the static NAT policy.
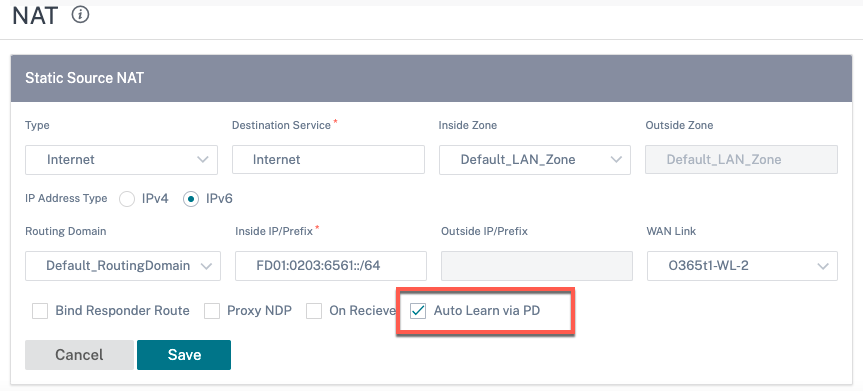
If you select the Auto Learn via PD check box, ensure that the upstream router supports DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation. Citrix SD-WAN requests a prefix from the upstream delegating router and the delegating router responds with a prefix to Citrix SD-WAN. Citrix SD-WAN uses this delegated prefix to translate the inside IP address to the outside IP address.
The following is an example where Auto Learn via PD is enabled, so that the outside network prefix is obtained through DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation.
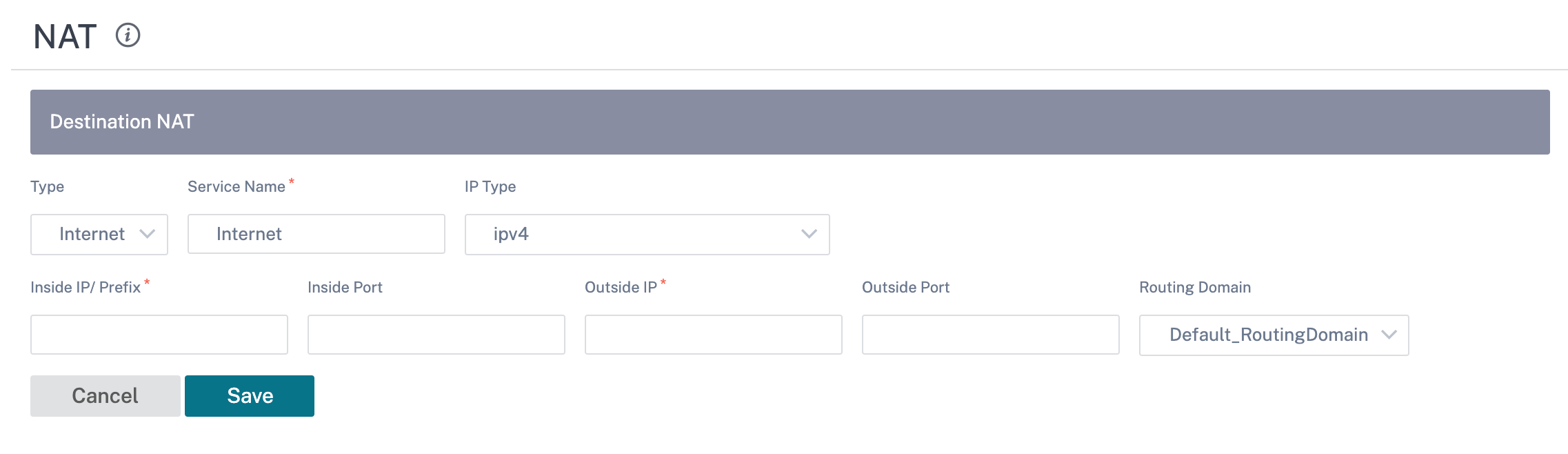
Destination NAT
Destination NAT Policies allow for the configuration of Network Address Translation policies between individual hosts or subnets.
Note
- While both Inbound and Outbound translations can be configured simultaneously for a Service, only the first to match will be used. Multiple translations can occur if a rule exists on the Service a packet is received on and the Service a packet is sent on.
- Destination NAT translations are applicable only for traffic originating from Local Service.
To configure these destination NAT policies, from site level, navigate to Configuration > Advanced Settings > NAT > Destination NAT. Click + Destination NAT.
- Type: The SD-WAN service types on which the NAT policy is applied. For static NAT, the service types supported are Local, Virtual Paths, Internet, Intranet, and Inter-routing domain services
- Service Name: Provide a name for the service that corresponds to the Service Type.
- IP Type: Select the IPv4 or IPv6 address type based on your preference.
- Inside Port: The Inside port that the outside port will be port forwarded into.
- Outside IP: The outside IP address and prefix that the inside IP address is translated to if the match criteria is met. For outbound traffic using Internet and Intranet services, the configured WAN link IP address is dynamically chosen as the outside IP address.
- Outside Port: The Outside port that is port forward into the inside port.
- Routing Domain: Select the routing domain for which the selected translation applies to.
- On Receive: When this check box is selected, inbound NAT is configured. When cleared, outbound NAT is configured.