MPLS queues
This feature simplifies creating SD-WAN configurations when adding a Multiprotocol Layer Switching (MPLS) WAN Link. Previously, each MPLS queue required one WAN Link to be created. Each WAN Link required a unique Virtual IP Address (VIP) to create the WAN Link and a unique Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) tag corresponding to the provider’s queuing scheme. After defining a WAN Link for each MPLS queue, the Intranet Service to map to a specific queue is defined.
Currently, a new MPLS specific WAN Link definition (that is, Access Type) is available. When a new Private MPLS Access Type is selected, you can define an MPLS queues associated with the WAN Link. This allows a single VIP with multiple DSCP tags that correspond to the provider’s queuing implementation for the MPLS WAN Link. This maps the Intranet Service to multiple MPLS Queues on a single MPLS WAN Link.
Allows MPLS providers to identify traffic based on DSCP markings so that the class of service can be applied by the provider.
Note
If you have existing MPLS configurations and would like to implement the Private MPLS Access Type, contact Citrix® Support for assistance.
Configure private MPLS WAN links
- Define the WAN Link Access Type as Private MPLS.
- Define the MPLS Queues corresponding to the Service Provider MPLS queues.
- Enable the WAN Link for virtual path service (enabled by default for Private MPLS WAN Links).
-
From the virtual path on a WAN Link, assign an Autopath group.
Note
If the Autopath Group is assigned from the WAN Link level, SD-WAN creates paths automatically between the MCN and Client MPLS Queues based on matching DSCP tags. If the Autopath Group is assigned from the MPLS Queue level, SD-WAN creates paths automatically regardless of whether the DSCP tags match.
-
Ensure that the same Autopath Group is configured at the MCN and Client.
-
Verify that the Paths for the WAN Link are built automatically.
- Assign Intranet Service to a specific queue, if needed.
Note
The SD-WAN configuration may not have a one-to-one mapping for provider-based queues. This is based on specific deployment scenarios. You cannot create Autopath Groups between different Private Access Types. For instance, you cannot create Autopath Groups between a Private Internet Access Type and a Private MPLS Access Type.
How to Add Private MPLS WAN LINK
To configure a new WAN Link Access Type for Private MPLS:
-
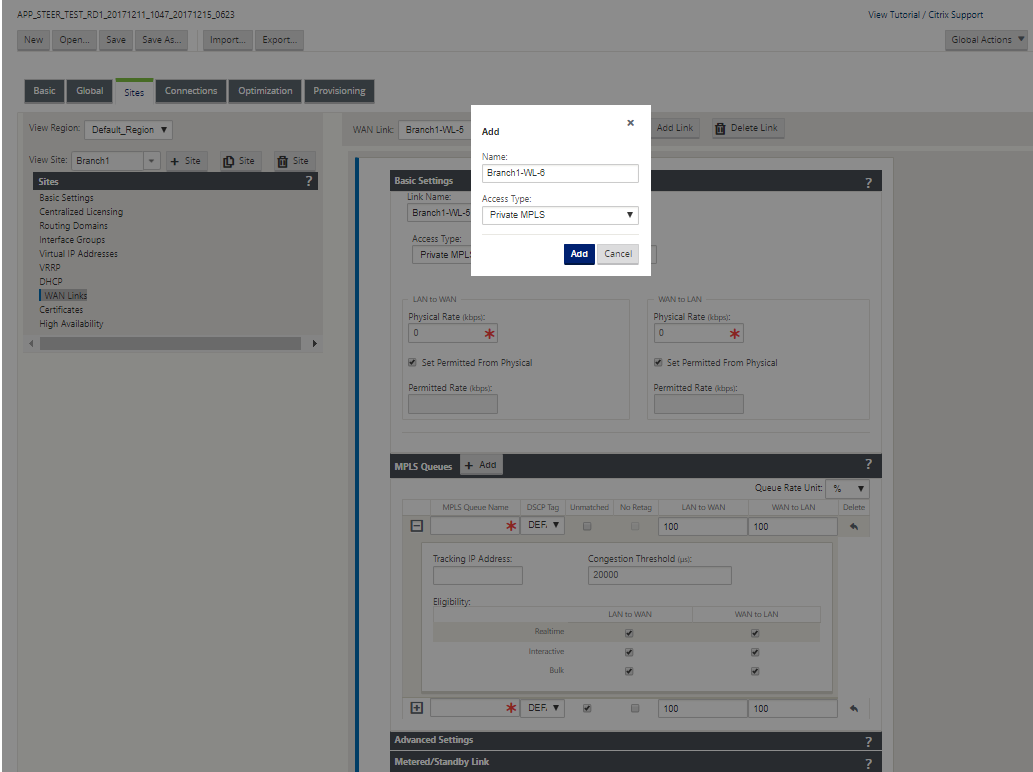
In the Configuration Editor, navigate to Sites > [Site Name] > WAN Links. Click Add Link. Enter WAN Link name and select Private MPLS as the Access Type.
-
Under the Basic Settings, there is now a new MPLS Queues tab. Click + Add to add specific MPLS Queues. These should correspond with the queues defined by the Service Provider.
Field Description MPLS Queue Name The MPLS queue name DSCP Tag Service Provider’s DSCP tag setting for the queue. Unmatched When enabled, any frames arriving that do not match the defined tags within the configuration file are mapped to this queue and the bandwidth defined for this queue. LAN to WAN Permitted Rate (kbps) The amount of bandwidth that SD-WAN devices are permitted to use for upload, which cannot exceed the defined physical upload rate of the WAN Link. WAN to WAN Permitted Rate (kbps) The amount of bandwidth that SD-WAN devices are permitted to use for download, which cannot exceed the defined physical download rate of the WAN Link. Expand the MPLS Queue definition (by clicking the +), and more options appear. These options include:
Field Description Tracking IP Address WAN Link tracking address Congestion Threshold The defined amount of time for congestion (in microseconds) after which the MPLS Queue throttles packet transmission to avoid more congestion. When congestion exceeds the set Threshold, SD-WAN backs off the sending rate. Eligibility The MPLS Queue’s eligibility to process specific classes of traffic. When eligibility is disabled for a specific class of traffic, that class of traffic is unlikely to route through the MPLS Queue unless network conditions require it. Configure the MPLS Queues that correspond to the existing Service Provider WAN Link queue definitions.
Note
Any existing MPLS WAN Links that are configured prior to SD-WAN 9.1 are not impacted.
Define WAN Link properties for private MPLS
Once the Private MPLS WAN Link with its MPLS Queues is defined, you should assign an Autopath Group for the WAN Link under a specific Virtual Path definition.
To assign autopath group:
-
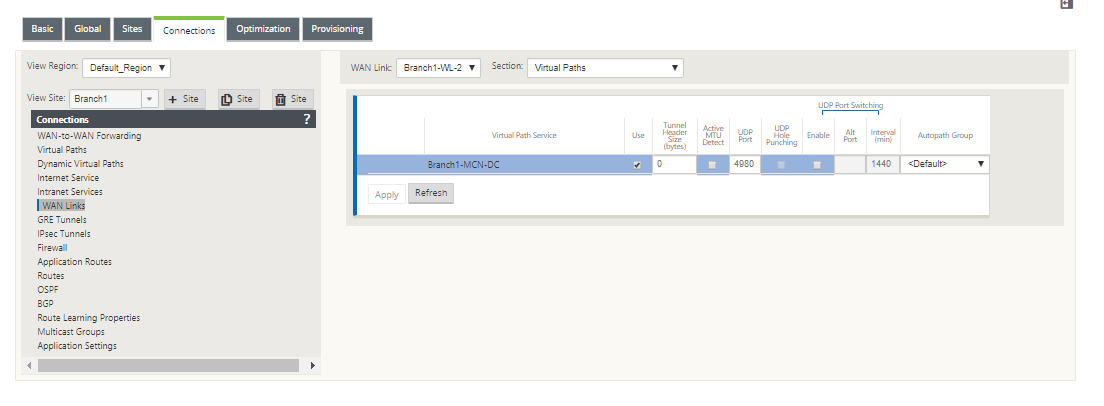
Go to Connections > [Site Name] > WAN Links >[MPLS WAN Link Name] > Virtual Paths> [Virtual Path Name] > [Local Site] > WAN Links and click Edit ().
-
Click the Autopath Group drop-down menu and choose from the available groups. By default, MPLS Queues inherit the Autopath Group assigned to the MPLS WAN Link. You can choose to set the individual MPLS Queues to Inherit the chosen Autopath Group or choose an alternate from the Autopath Group drop-down menu for each MPLS Queue.
Note
If there is no one-to-one mapping, based on the DSCP tag, between queues at the local site and the remote site, you must map MPLS Queues to specific Autopath Groups. Inheriting an Autopath Group from the MPLS WAN Link automatically generates paths between queues with matching DSCP tags.
Assign autopath group to virtual path-WAN Link
The Autopath Group defined is the same for the MCN and Client appliance. This allows the system to build the Paths automatically. At the MCN site, you can also expand the WAN Link associated with the virtual path.
View permitted rate and congestion for WAN links
The SD-WAN web interface now allows you to view the permitted rate for WAN Links and WAN Link Usages and whether a WAN Link, Path, or Virtual Path is in congested state. In the previous releases, this information was only available in SD-WAN log files and through the CLI. These options are now available in the web interface to help with troubleshooting.
View permitted rate
Permitted Rate is the amount of bandwidth that a particular WAN Link, Virtual Path Service, Intranet Service, or Internet Service is permitted to use at a given point in time. The permitted rate for a WAN Link is static, and is defined explicitly in the SD-WAN configuration. The permitted rate for a Virtual Path Service, Intranet Service, or Internet Service will fluctuate over time, in response to congestion, user demand, and Fair Shares, but will always be greater than or equal to the Minimum Reserved Bandwidth for the Service.
Monitor WAN link
Go to Monitor > Statistics, and select WAN Link from the Show drop-down list.
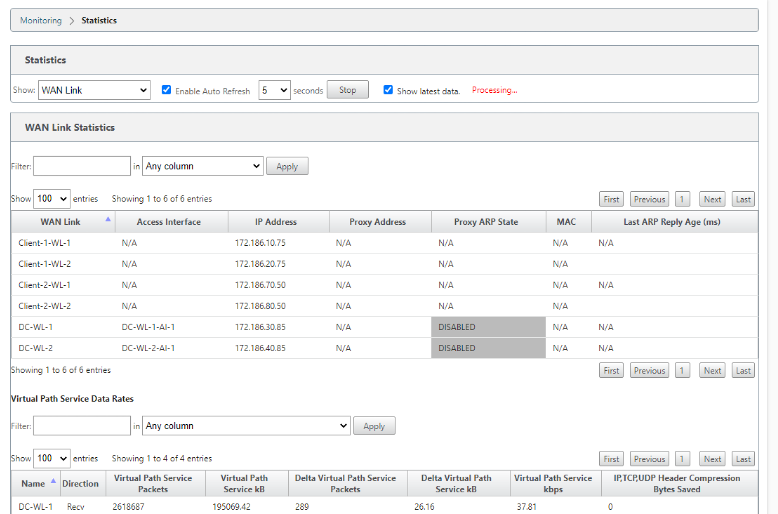
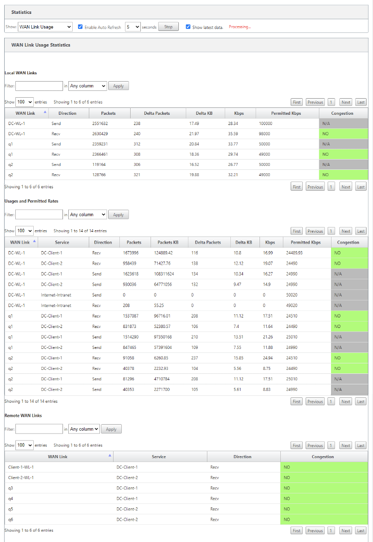
Go to Monitor > Statistics, and select WAN Link Usage from the Show drop-down list.
Monitor MPLS queues
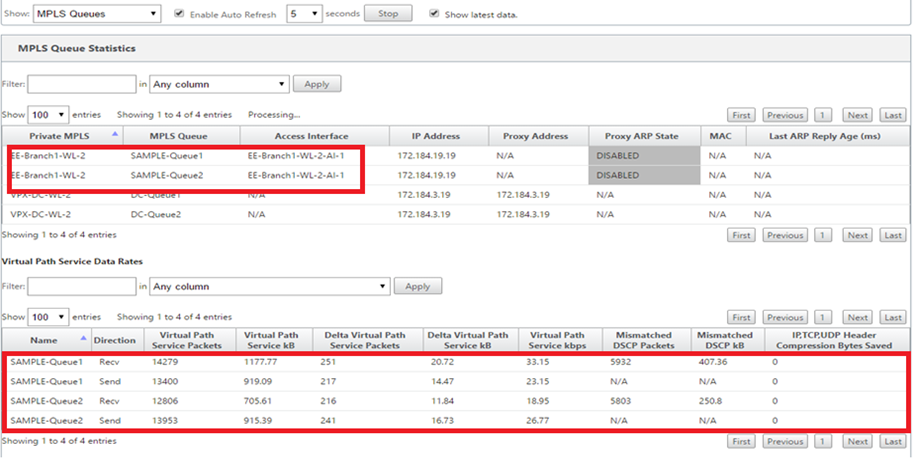
Go to Monitor > Statistics, and select MPLS Queues from the Show drop-down list.
Troubleshooting MPLS queues
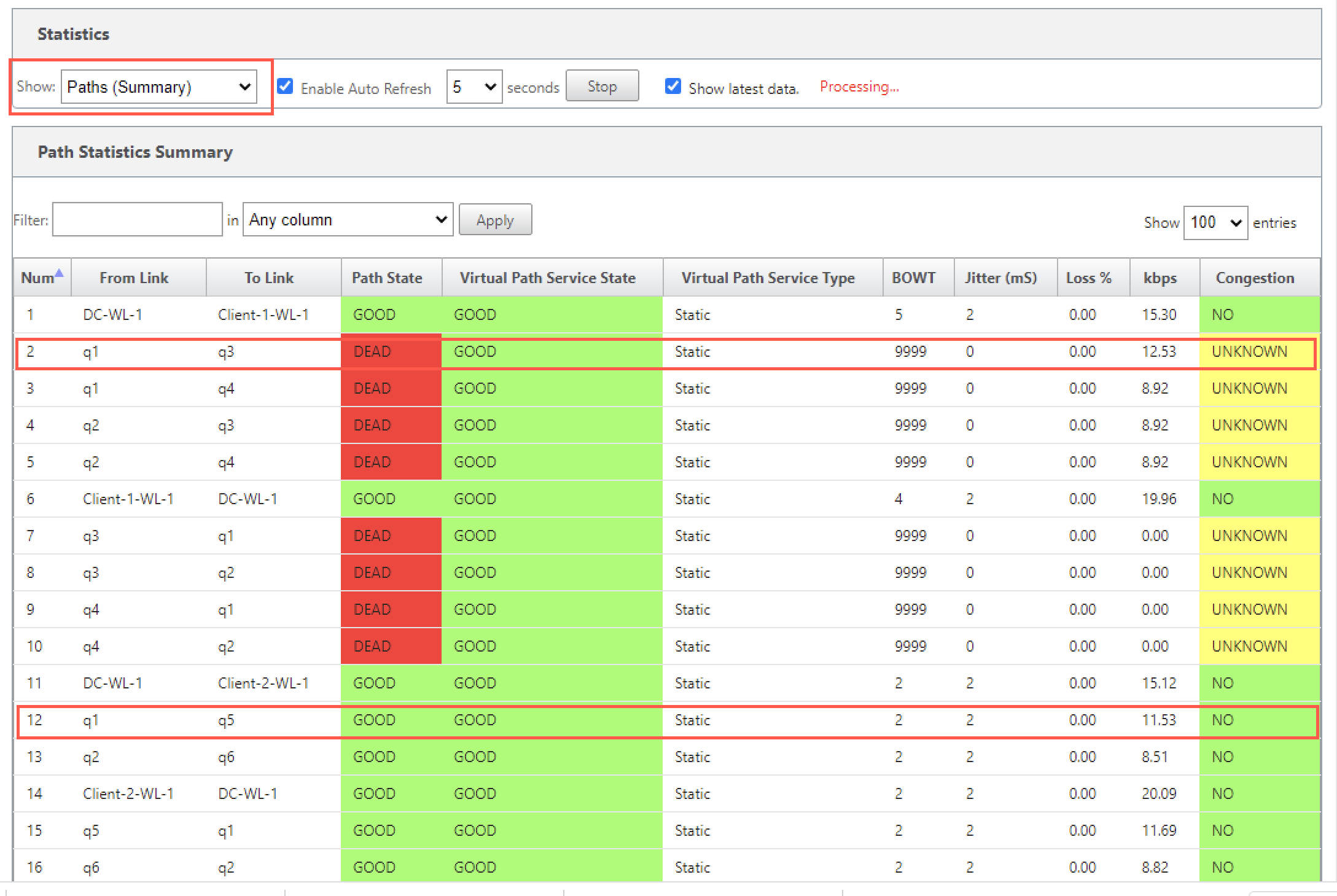
To check the status of MPLS queues, navigate to Monitor > Statistics and select Paths (summary) from the Show drop-down list. In the following example, the path from MPLS queue “q1” to “q3” is in DEAD state and shown in red. The path from MPLS queue “q1” to “q5” is in GOOD state and shown in green.
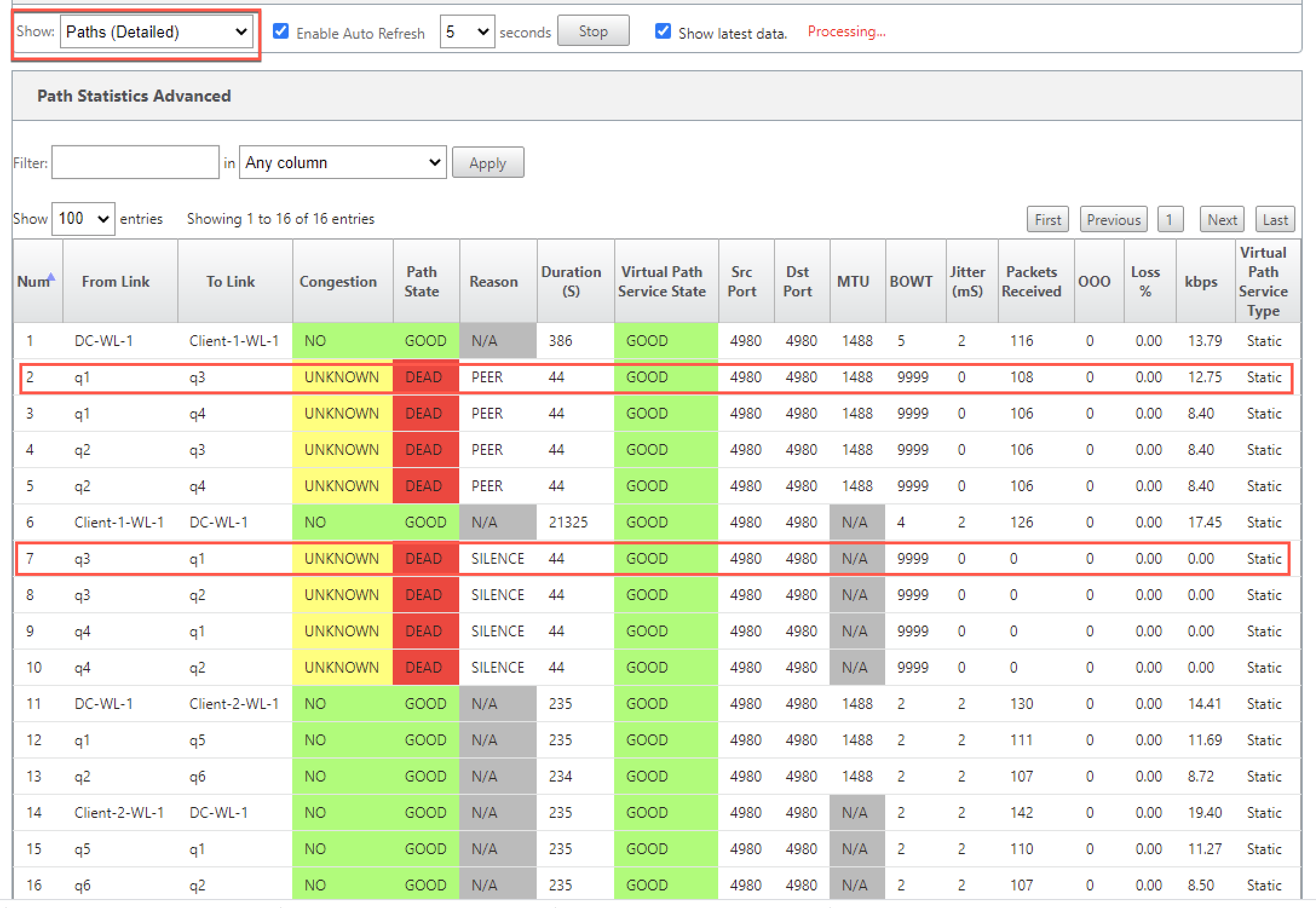
For detailed information on paths, select Paths (Detailed) from the Show drop-down list. The information on paths such as reason for the state, duration, source port, destination port, MTU are available
In the following example, the path from MPLS queue “q1” to “q3” is in DEAD state and the reason is PEER. The path from MPLS queue “q3” to “q1” is dead and the reason is SILENCE. The following table provides the list if available reasons and its descriptions.
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| GATEWAY | The path is DEAD as the appliance cannot reach or detect the gateway |
| SILENCE | The path is BAD or DEAD because the appliance has not received packets from the peer site |
| LOSS | The path is BAD due to packet loss |
| PEER | The peer site is reporting the path is BAD |
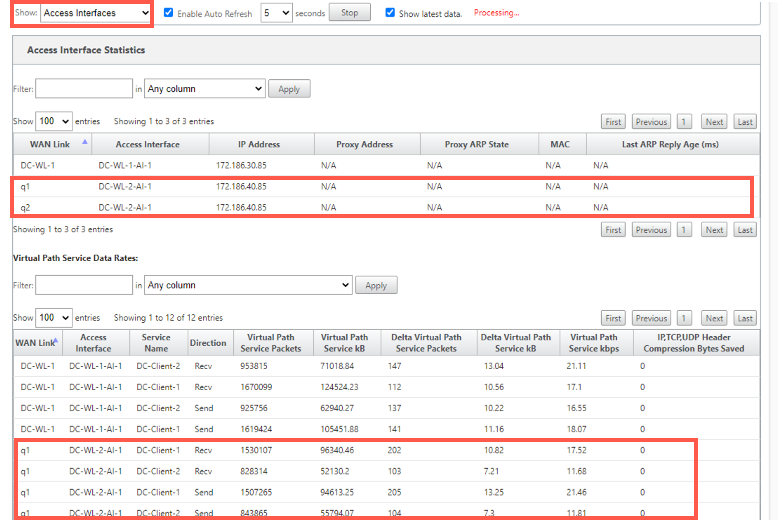
To check the access interface and IP address associated with the MPLS queues, select Access Interfaces from the Show drop-down list.
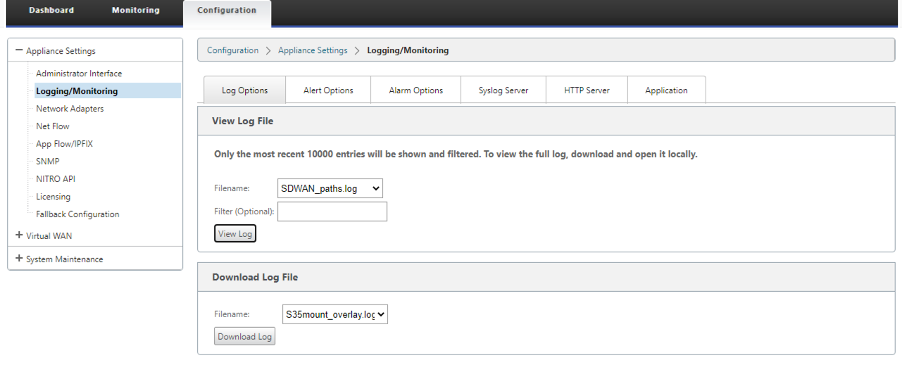
You can download the log files for further troubleshooting. Navigate to Configuration > Logging/Monitoring and select SDWAN_paths.log or SDWAN_common.log from the Log Options tab.