-
Getting Started with Citrix ADC
-
Deploy a Citrix ADC VPX instance
-
Install a Citrix ADC VPX instance on Microsoft Hyper-V servers
-
Install a Citrix ADC VPX instance on Linux-KVM platform
-
Prerequisites for Installing Citrix ADC VPX Virtual Appliances on Linux-KVM Platform
-
Provisioning the Citrix ADC Virtual Appliance by using OpenStack
-
Provisioning the Citrix ADC Virtual Appliance by using the Virtual Machine Manager
-
Configuring Citrix ADC Virtual Appliances to Use SR-IOV Network Interface
-
Configuring Citrix ADC Virtual Appliances to use PCI Passthrough Network Interface
-
Provisioning the Citrix ADC Virtual Appliance by using the virsh Program
-
Provisioning the Citrix ADC Virtual Appliance with SR-IOV, on OpenStack
-
Configuring a Citrix ADC VPX Instance on KVM to Use OVS DPDK-Based Host Interfaces
-
-
Deploy a Citrix ADC VPX instance on Microsoft Azure
-
Network architecture for Citrix ADC VPX instances on Microsoft Azure
-
Configure multiple IP addresses for a Citrix ADC VPX standalone instance
-
Configure a high-availability setup with multiple IP addresses and NICs
-
Configure a high-availability setup with multiple IP addresses and NICs by using PowerShell commands
-
Configure HA-INC nodes by using the Citrix high availability template with Azure ILB
-
Configure address pools (IIP) for a Citrix Gateway appliance
-
-
Upgrade and downgrade a Citrix ADC appliance
-
Solutions for Telecom Service Providers
-
Load Balance Control-Plane Traffic that is based on Diameter, SIP, and SMPP Protocols
-
Provide Subscriber Load Distribution Using GSLB Across Core-Networks of a Telecom Service Provider
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing application traffic
-
Configuring authentication, authorization, and auditing policies
-
Configuring Authentication, authorization, and auditing with commonly used protocols
-
Use an on-premises Citrix Gateway as the identity provider for Citrix Cloud™
-
Troubleshoot authentication issues in Citrix ADC and Citrix Gateway with aaad.debug module
-
-
-
-
-
DataStream
-
-
Persistence and persistent connections
-
Advanced load balancing settings
-
Gradually stepping up the load on a new service with virtual server–level slow start
-
Protect applications on protected servers against traffic surges
-
Retrieve location details from user IP address using geolocation database
-
Use source IP address of the client when connecting to the server
-
Use client source IP address for backend communication in a v4-v6 load balancing configuration
-
Set a limit on number of requests per connection to the server
-
Configure automatic state transition based on percentage health of bound services
-
-
Use case 2: Configure rule based persistence based on a name-value pair in a TCP byte stream
-
Use case 3: Configure load balancing in direct server return mode
-
Use case 6: Configure load balancing in DSR mode for IPv6 networks by using the TOS field
-
Use case 7: Configure load balancing in DSR mode by using IP Over IP
-
Use case 10: Load balancing of intrusion detection system servers
-
Use case 11: Isolating network traffic using listen policies
-
Use case 12: Configure Citrix Virtual Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 13: Configure Citrix Virtual Apps™ for load balancing
-
Use case 14: ShareFile wizard for load balancing Citrix ShareFile
-
-
-
-
-
Authentication and authorization
-
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between two Datacenters
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector between Datacenter and AWS Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a Datacenter and Azure Cloud
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between Datacenter and SoftLayer Enterprise Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a Citrix ADC Appliance and Cisco IOS Device
-
CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
DataStream
The Citrix® ADC DataStream feature provides an intelligent mechanism for request switching at the database layer by distributing requests based on the SQL query being sent.
When deployed in front of database servers, a Citrix ADC appliance ensures optimal distribution of traffic from the application servers and Web servers. Administrators can segment traffic according to information in the SQL query and based on database names, user names, character sets, and packet size.
You can configure load balancing to switch requests based on load balancing algorithms. Alternately, you can elaborate the switching criteria by configuring content switching to make a decision based on an SQL query parameter. You can further configure monitors to track the state of database servers.
Note:
Citrix ADC DataStream is supported only for MySQL and MS SQL databases. For information about the supported protocol version, character sets, special queries, and transactions, see DataStream Reference.
How DataStream works
In DataStream, the ADC appliance is placed in-line between the application or web servers and the database servers. On the appliance, the database servers are represented by services.
A typical DataStream deployment consists of the entities described in the following diagram.
Figure 1. DataStream Entity Model
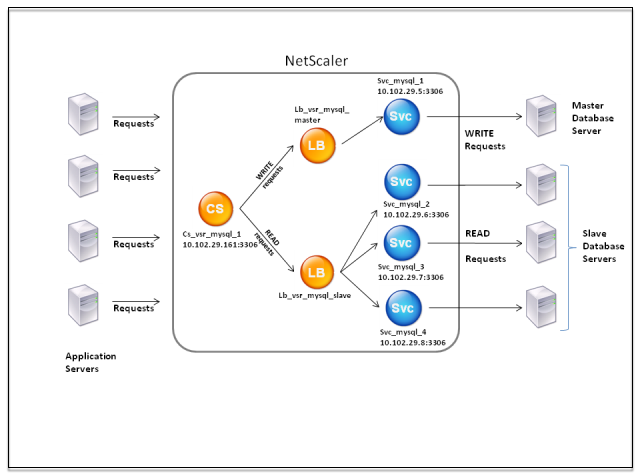
As shown in this figure, a DataStream configuration can consist of:
- An optional content switching virtual server (CS).
- A load balancing setup consisting of load balancing virtual servers (LB1 and LB2).
- Services (Svc1, Svc2, Svc3, and Svc4).
- Content switching policies (optional).
The clients (application or Web servers) send requests to the IP address of a content switching virtual server (CS) configured on the Citrix ADC appliance. The appliance, then, authenticates the clients using the database user credentials configured on the appliance. The content switching virtual server (CS) applies the associated content switching policies to the requests. After evaluating the policies, the content switching virtual server (CS) routes the requests to the appropriate load balancing virtual server (LB1 or LB2). Then, the load balancing virtual server distributes the requests to the appropriate database servers (represented by services on the appliance) based on the load balancing algorithm. The Citrix ADC appliance uses the same database user credentials to authenticate the connection with the database server.
If a content switching virtual server is not configured on the appliance, the clients (application or Web servers) send their requests to a load balancing virtual server configured on the appliance. The Citrix ADC appliance authenticates the client by using the database user credentials configured on the appliance, and then uses the same credentials to authenticate the connection with the database server. The load balancing virtual server distributes the requests to the database servers according to the load balancing algorithm. The most effective load balancing algorithm for database switching is the least connection method.
DataStream uses connection multiplexing to enable multiple client-side requests to be made over the same server-side connection. The following connection properties are considered:
- User name
- Database name
- Packet size
- Character set
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.