Zscaler Integration by using GRE tunnels and IPsec tunnels
The Zscaler Cloud Security Platform acts as a series of security check posts in more than 100 data centers around the world. By simply redirecting your internet traffic to Zscaler, you can immediately secure your stores, branches, and remote locations. Zscaler connects users and the internet, inspecting every byte of traffic, even if it is encrypted or compressed.
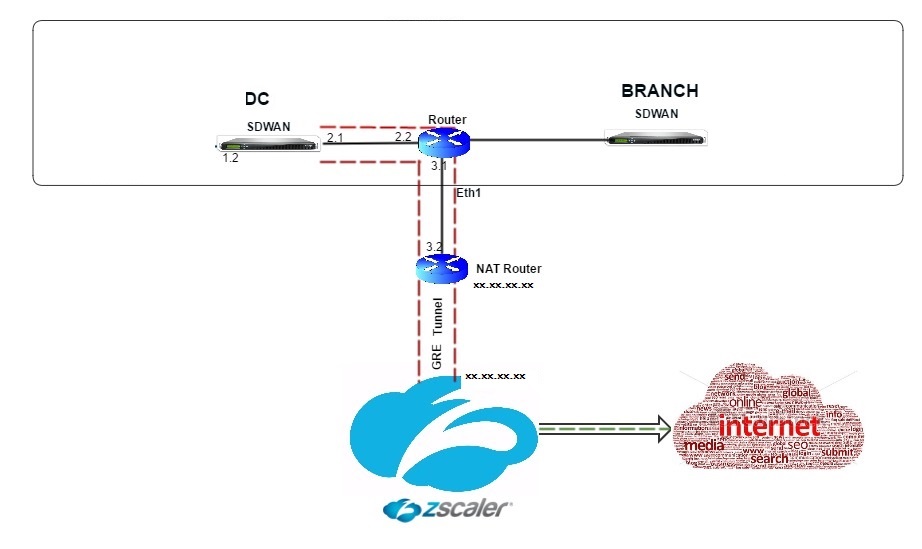
Citrix SD-WAN™ appliances can connect to a Zscaler cloud network through GRE tunnels at the customer’s site. A Zscaler deployment using SD-WAN appliances supports the following functionality:
- Forwarding all GRE traffic to Zscaler, thereby enabling direct Internet breakout.
- Direct internet access (DIA) using Zscaler on a per customer site basis.
- On some sites, you might want to provide DIA with on-premises security equipment and not use Zscaler.
- On some sites, you might choose to backhaul the traffic another customer site for internet access.
- Virtual routing and forwarding deployments.
- One WAN link as part of internet services.
Zscaler is a cloud service. You must set it up as a service and define the underlying WAN links:
- Configure an internet service at the data center and branch through GRE.
- Configure a trusted Public internet link at the data center and the branch sites.
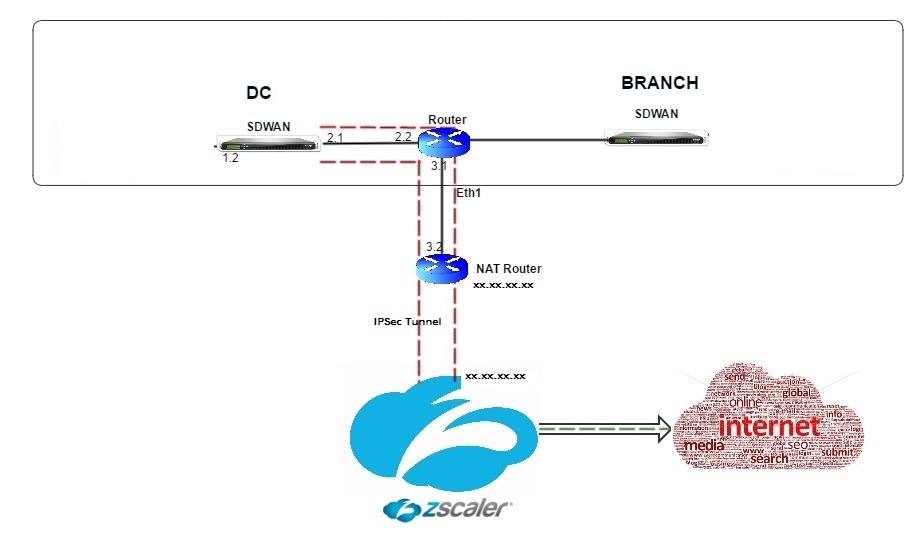
Topology
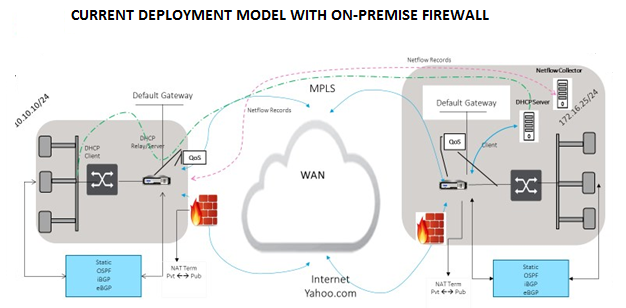
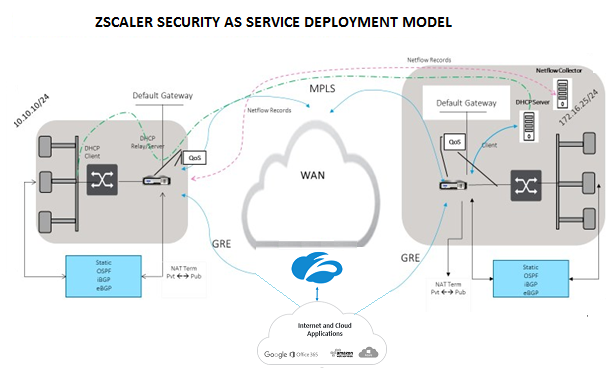
To use GRE tunnel or IPsec Tunnel traffic forwarding:
-
Log into the Zscaler help portal at: https://help.zscaler.com/submit-ticket.
-
Raise a ticket and provide the static public IP address, which is used as the GRE tunnel or IPsec tunnel source IP address.
Zscaler uses the source IP address to identify the customer IP address. The source IP needs to be a static public IP. Zscaler responds with two ZEN IP addresses (Primary and Secondary) to transmit traffic to. GRE keep alive messages can be used to determine the health of the tunnels.
Zscaler uses the source IP address value to identify the customer IP address. This value must be a static public IP address. Zscaler responds with two ZEN IP addresses [DR1] to which to redirect traffic. GRE keep-alive messages can be used to determine the health of the tunnels.
Sample IP addresses
Primary
Internal Router IP address: 172.17.6.241/30 Internal ZEN IP address: 172.17.6.242/30
Secondary
Internal Router IP address: 172.17.6.245/30 Internal ZEN IP address: 172.17.6.246/30
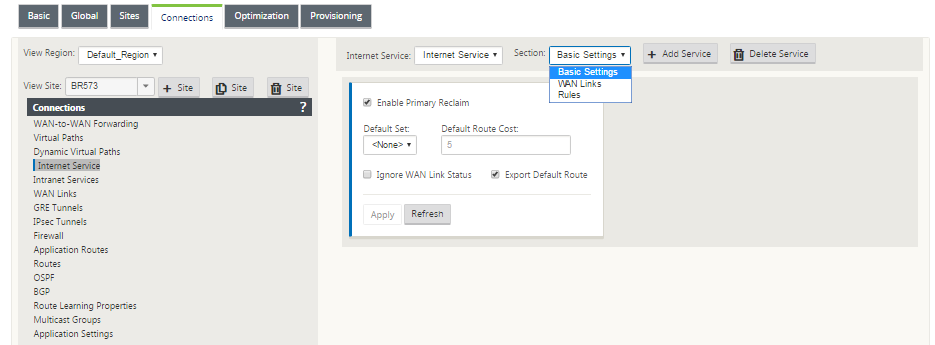
Configuring an Internet Service
To configure an internet service:
-
Navigate to Connections- Internet Services. Configure internet service.
-
Select + Service and enable the settings (Basic settings, WAN Links, and Rules) as required.
-
Select Apply.
For more information about enabling Internet service for a site, see Direct Internet Breakout at Branch with Integrated Firewall.
You can configure the following settings on an Internet Service:
Basic settings
A Firewall zone setting is not configurable for an Internet Service. If the Internet Service is trusted, it is assigned to Internet_Zone. If the Internet Service is untrusted, it is assigned to Untrusted_Internet_Zone.
The basic settings that are configurable are described below:
-
Enable Primary Reclaim: If enabled, the (use = primary) usage associated with this service on a WAN Link forcefully reclaims status as the active service on that WAN link.
-
Default Set: Name of the Internet default set that populates rules for the Internet service on the Site.
-
Default Route Cost: Route cost associated with the default (0.0.0.0/0) internet route.
-
Ignore WAN Link Status: If enabled, packets destined for this service still choose this service even if all WAN links for this service are unavailable.
-
Export Default Route: If enabled, the default route for the Internet Service, 0.0.0.0/0, is exported to other Sites if WAN-to-WAN forwarding is enabled.
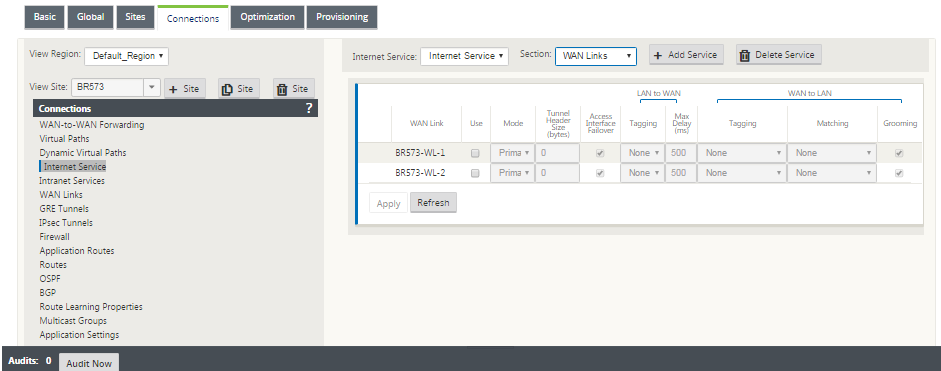
WAN links
The WAN link settings that are configurable are described below:
- Use: Allow the Service to use this WAN Link. When Use is disabled, all the other options are unavailable.
- Mode: The mode of Service – Primary, Secondary, or Balance, for traffic redundancy or load balancing.
- Tunnel Header Size (bytes): The size of the tunnel header, in bytes, if applicable.
- Access Interface Failover: If enabled, the Internet or Intranet packets with mismatched VLANs can still use the service.
LAN to WAN
- Tagging: The DSCP tag to apply to LAN to WAN packets on the Service.
- Max Delay (ms): The maximum time, in milliseconds, to buffer packets when the WAN Links bandwidth is exceeded.
WAN to LAN
-
Tagging: The DSCP tag to apply to WAN to LAN packets on the service.
-
Matching: Internet WAN to LAN packets matching this tag are assigned to the service.
-
Grooming: If enabled, packets are randomly dropped to prevent WAN to LAN traffic from exceeding the provisioned bandwidth of the service.
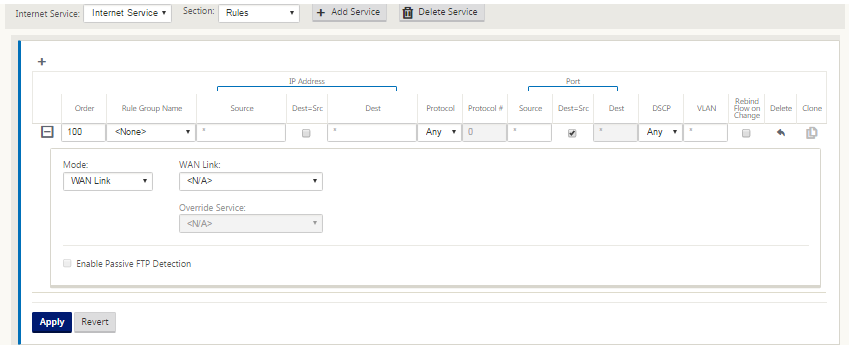
Rules
Internet traffic is identified based on the rules defined. A rule definition is used to match a specific traffic flow. Once matched, you must define the action to apply for the traffic flow.
The list of available rules is described below:
- Order: The sequence in which rules are applied and automatically redistributed.
- Rule group Name: Name given to a rule that allows rule statistics to be summed in groups when they are displayed. All the statistics for rules with the same rule group name can be viewed together.
- Source: The source IP address and subnet mask that matches with the rule.
- Dest-Src: If enabled, the source IP address is also used as the destination IP address.
- Dest: The destination IP address and subnet mask that matches with the rule.
- Protocol: The protocol name that matches with the filter.
- Protocol #: The protocol number that matches with the filter.
- DSCP: The DSCP tag in the IP header that matches with the rule.
The list of available actions is described below:
-
WAN Link: The WAN link to be used by flows matching the rule when Internet load balancing is enabled.
-
Override Service: The destination service for flows matching the rule.
-
Discard: Drop the traffic.
-
Passthrough: Map the flow to pass-through and allow the traffic to flow through the appliance unchanged.
-
Configure GRE Tunnel
-
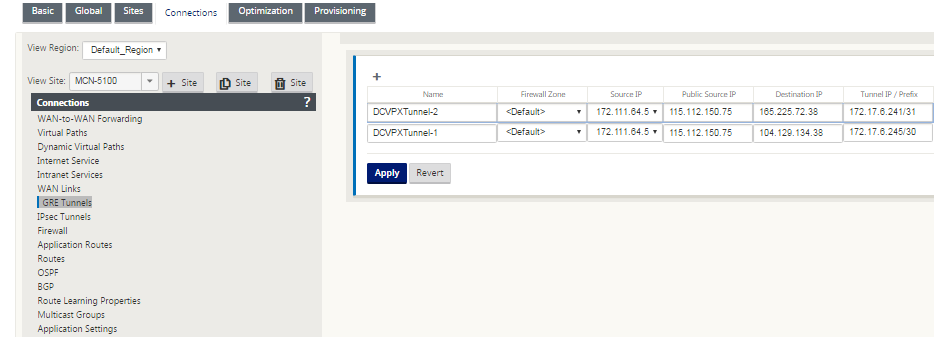
Source IP address is the Tunnel Source IP address. If the Tunnel Source IP address is NATted, the Public Source IP address is the public Tunnel Source IP address, even if it is NATted on a different intermediate device.
-
Destination IP address is the ZEN IP address that Zscaler provides.
-
The Source IP address and the Destination IP address are the router GRE headers when the original payload is encapsulated.
-
Tunnel IP address and Prefix are the IP addressing on the GRE tunnel itself. This is useful for routing traffic over the GRE tunnel. The traffic needs this IP address as the gateway address.
To configure GRE Tunnel:
-
In the configuration editor, navigate to Connections > Site > GRE Tunnels, and configure routes to forward internet prefix services to the Zscaler GRE Tunnels.
The source IP address can only be chosen from the Virtual network interface on trusted links. See, How to configure GRE tunnel.
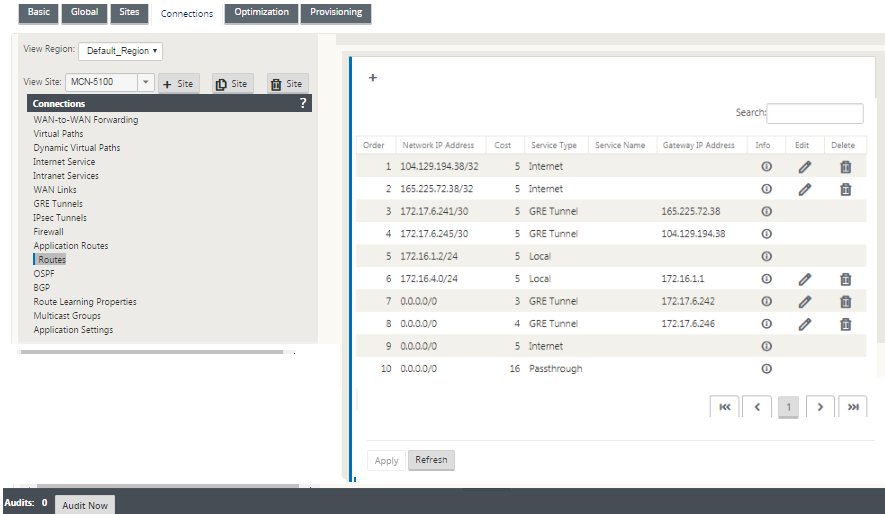
Configure routes for GRE tunnels
Configure routes to forward internet prefix services to the Zscaler GRE Tunnels.
- The ZEN IP address (Tunnel destination IP, shown as 104.129.194.38 in the above figure) must be set to service-type Internet. This is required so that traffic destined to Zscaler is accounted from the Internet service.
- All traffic destined to Zscaler must match the default route 0/0 and be transmitted over the GRE tunnel. Ensure that the 0/0 route used for [DR1 the GRE tunnel has a lower Cost than Passthrough or any other Service type.
- Similarly, the backup GRE tunnel to Zscaler must have a higher cost than that of the Primary GRE tunnel.
- Ensure that nonrecursive routes exist for the ZEN IP address.
To configure routes for GRE Tunnel:
-
Navigate to Connections > Site > Routes, and follow the procedures described in Configuring Routes for instructions about creating routes.
Note
If you do not have specific routes for the Zscaler IP address, configure the route prefix 0.0.0.0/0 to match the ZEN IP address and route it through a GRE tunnel encapsulation loop. This configuration uses the tunnels in an active-backup mode. With the values shown in the above figure, traffic automatically switches over to the tunnel with gateway IP address 172.17.6.242. If desired, configure a backhaul virtual path route. Otherwise, set the keep-alive interval of the backup tunnel to zero. This enables secure internet access to a site even if both the tunnels to Zscaler fail.
GRE keep-alive messages are supported. A new field called Public Source IP that provides the NAT address of the GRE Source address is added to the Citrix SD-WAN GUI interface (in the case when SD-WAN appliance Tunnel Source is NATted by an intermediate device). The Citrix SD-WAN GUI includes a field called Public Source IP, which provides the NAT address of the GRE Source address when the Citrix SD-WAN appliance’s Tunnel Source is NATted by an intermediate device.
Limitations
- Multiple VRF deployments are not supported.
- Primary backup GRE tunnels are supported for a high-availability design mode only.
Configure IPsec Tunnels
To configure IPsec Tunnels for intranet or LAN services in the Citrix SD-WAN appliance GUI:
-
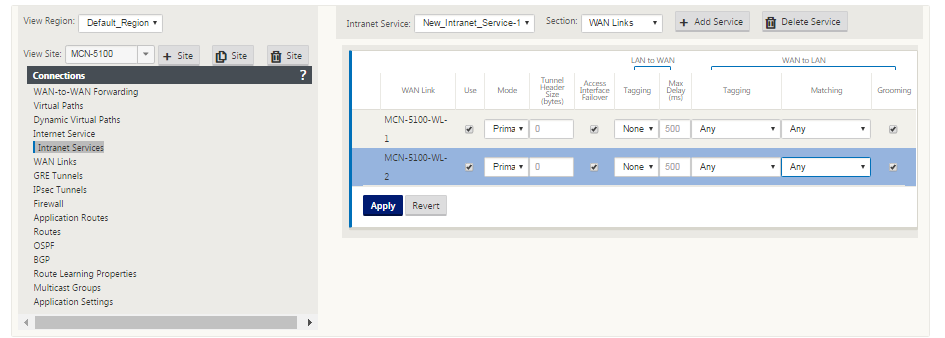
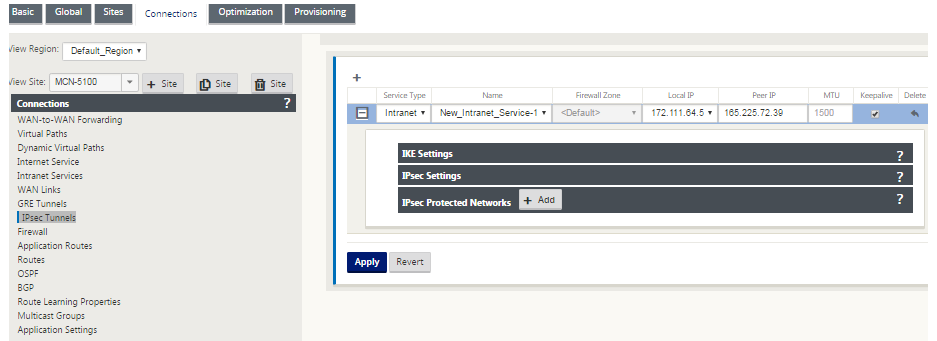
In the Configuration Editor, navigate to Connections > <siteName> > IPsec Tunnels and choose a service type (LAN or Intranet).
-
Enter a Name for the service type. For Intranet service type, the configured intranet server determines which Local IP addresses are available.
-
Select the available Local IP address and enter the Peer IP address for the virtual path to the remote peer.
-
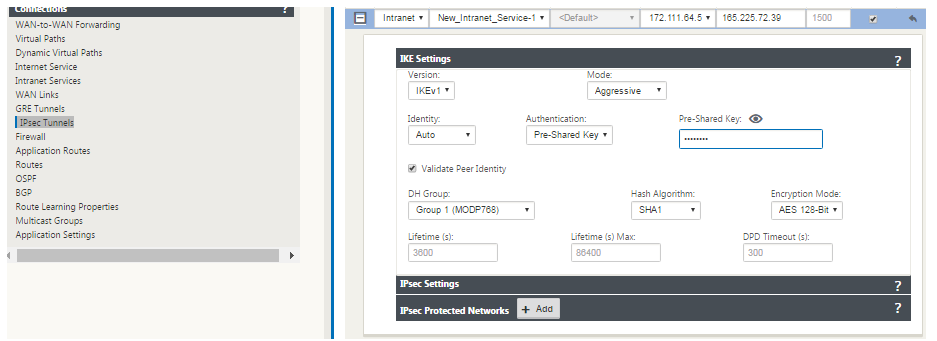
Select IKEv1 for IKE Settings. Zscaler supports only IKEv1.
-
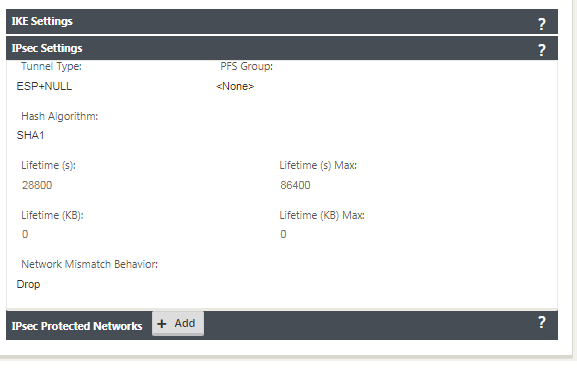
Under IPsec Settings, select ESP-NULL for Tunnel type, to redirect traffic to Zscaler through the IPsec tunnel. The IPsec tunnel does not encrypt the traffic.
-
Because internet traffic is redirected, the destination IP/Prefix can be any IP address.
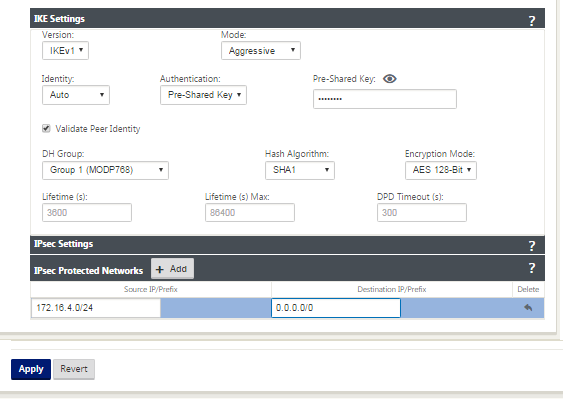
For more information about configuring IPsec Tunnels by using the Citrix SD-WAN web interface, see; the IPsec Tunnels topic.
Configure routes for IPsec tunnels
To configure IPsec routes:
- Navigate to Connections > DC > Routes and follow the procedures described in Configuring Routes for instructions about creating routes.
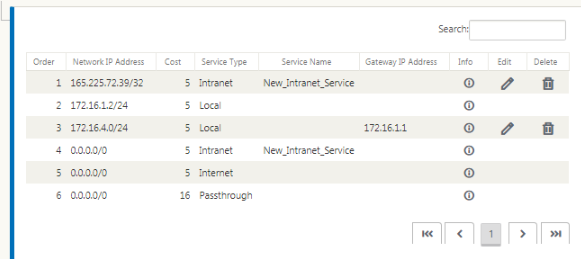
To monitor GRE and IPsec tunnel statistics:
| In the SD-WAN web interface, navigate to Monitoring > Statistics > [GRE Tunnel | IPsec Tunnel]. |
For more information, see; monitoring IPsec tunnels and GRE tunnels topics.