-
Getting Started with NetScaler
-
Solutions for Telecom Service Providers
-
Load Balance Control-Plane Traffic that is based on Diameter, SIP, and SMPP Protocols
-
Provide Subscriber Load Distribution Using GSLB Across Core-Networks of a Telecom Service Provider
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing application traffic
-
Basic components of authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration
-
Web Application Firewall protection for VPN virtual servers and authentication virtual servers
-
On-premises NetScaler Gateway as an identity provider to Citrix Cloud™
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration for commonly used protocols
-
Troubleshoot authentication and authorization related issues
-
-
-
-
-
-
Persistence and persistent connections
-
Advanced load balancing settings
-
Gradually stepping up the load on a new service with virtual server–level slow start
-
Protect applications on protected servers against traffic surges
-
Retrieve location details from user IP address using geolocation database
-
Use source IP address of the client when connecting to the server
-
Use client source IP address for backend communication in a v4-v6 load balancing configuration
-
Set a limit on number of requests per connection to the server
-
Configure automatic state transition based on percentage health of bound services
-
-
Use case 2: Configure rule based persistence based on a name-value pair in a TCP byte stream
-
Use case 3: Configure load balancing in direct server return mode
-
Use case 6: Configure load balancing in DSR mode for IPv6 networks by using the TOS field
-
Use case 7: Configure load balancing in DSR mode by using IP Over IP
-
Use case 10: Load balancing of intrusion detection system servers
-
Use case 11: Isolating network traffic using listen policies
-
Use case 12: Configure Citrix Virtual Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 13: Configure Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 14: ShareFile wizard for load balancing Citrix ShareFile
-
Use case 15: Configure layer 4 load balancing on the NetScaler appliance
-
-
-
-
Authentication and authorization for System Users
-
-
HTTP/3 Configuration
-
-
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between two Datacenters
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector between Datacenter and AWS Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a Datacenter and Azure Cloud
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between Datacenter and SoftLayer Enterprise Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a NetScaler Appliance and Cisco IOS Device
-
CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
HTTP/3 configuration and Stat summary
To configure a HTTP/3 protocol for sending multiple streams of HTTP/3 data using QUIC, you must complete the following steps:
- Enable SSL and load balancing features.
- Add load balancing and content switching (optional) virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC.
- Associate QUIC protocol parameters with the HTTP_QUIC virtual server.
- Enable HTTP/3 on the HTTP_QUIC virtual server.
- Bind SSL certificate-key pair with HTTP_QUIC virtual server.
- Associate SSL/TLS protocol parameters with the HTTP_QUIC virtual server.
Enable SSL and load balancing
Before you begin, make sure that the SSL and Load Balancing features are enabled on the appliance. At the command prompt type:
enable ns feature ssl lb
<!--NeedCopy-->
Add load balancing and content switching (optional) virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC for HTTP/3 service
You add a load balancing virtual server to accept HTTP/3 traffic over QUIC. Note: The load balancing virtual server of type HTTP_QUIC has built-in QUIC, SSL, and HTTP3 profiles. If you prefer to create user-define profiles, you can add new profiles and bind it with the load balancing virtual server.
add lb vserver <vserver-name> HTTP_QUIC <IP-address> <UDP-listening-port>
add cs vserver <vserver-name> HTTP_QUIC <IP-address> <UDP-listening-port>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add lb vserver lb-http3 HTTP_QUIC 1.1.1.1 443
add cs vserver cs-http3 HTTP_QUIC 10.10.10.10 443
Associate QUIC protocol parameters with HTTP_QUIC virtual server
You can create a QUIC profile and specify QUIC parameters for the QUIC service and associate it to the load balancing virtual server. You must either create a user-defined profile or use the in-built QUIC profile and bind the profile to the load balancing virtual server.
Step 1: configure a user-defined QUIC profile At the command prompt, type:
set quic profile <profile_name> -transport_param <value>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
set quic profile quic_http3 -ackDelayExponent 10 -activeConnectionIDlimit 4
The different QUIC transport parameters are as follows:
-ackDelayExponent. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, indicating an exponent that the remote QUIC endpoint should use, to decode the ACK Delay field in QUIC ACK frames sent by the NetScaler.
-activeConnectionIDlimit. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint. It specifies the maximum number of QUIC connection IDs from the remote QUIC endpoint, that the NetScaler is willing to store.
-activeConnectionMigration. Specify whether the NetScaler must allow the remote QUIC endpoint to perform active QUIC connection migration.
-congestionCtrlAlgorithm. Specify the congestion control algorithm to be used for QUIC connections.
-initialMaxData. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial value, in bytes, for the maximum amount of data that can be sent on a QUIC connection.
-initialMaxStreamDataBidiLocal. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial flow control limit, in bytes, for bi-directional QUIC streams initiated by the NetScaler.
-initialMaxStreamDataBidiRemote. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial flow control limit, in bytes, for bi-directional QUIC streams initiated by the remote QUIC endpoint.
-initialMaxStreamDataUni. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial flow control limit, in bytes, for uni-directional streams initiated by the remote QUIC endpoint.
-initialMaxStreamsBidi. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial maximum number of bi-directional streams the remote QUIC endpoint must initiate.
-initialMaxStreamsUni. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the initial maximum number of uni-directional streams the remote QUIC endpoint must initiate.
-maxAckDelay. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the maximum amount of time, in milliseconds, by which the NetScaler delays sending acknowledgments.
-maxIdleTimeout. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the maximum idle timeout, in seconds, for a QUIC connection. A QUIC connection that remains idle, for longer than the minimum of the idle timeout values advertised by the NetScaler and the remote QUIC endpoint, and three times the current Probe Timeout (PTO), will be silently discarded by the NetScaler.
-maxUDPPayloadSize. An integer value advertised by the NetScaler to the remote QUIC endpoint, specifying the size of the largest UDP datagram payload, in bytes, that the NetScaler is willing to receive on a QUIC connection.
-newTokenValidityPeriod. An integer value, specifying the validity period, in seconds, of address validation tokens issued through QUIC NEW_TOKEN frames sent by the NetScaler.
-retryTokenValidityPeriod. An integer value, specifying the validity period, in seconds, of address validation tokens issued through QUIC Retry packets sent by the NetScaler.
-statelessAddressValidation. Specify whether the NetScaler must perform stateless address validation for QUIC clients, by sending tokens in QUIC Retry packets during QUIC connection establishment, and by sending tokens in QUIC NEW_TOKEN frames after QUIC connection establishment.
Step 2: Associate the user-defined QUIC profile to a load balancing virtual server of type http_quic
At the command prompt, type:
set lb vserver <name>@ [-IPAddress <ip_addr|ipv6_addr|*>@] <serviceName>@] [-persistenceType <persistenceType>] [-quicProfileName <string>]
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
set lb vserver lb-http3 -quicProfileName quic_http3
Enable and bind HTTP/3 on a HTTP_QUIC virtual server
To enable HTTP/3 on an HTTP_QUIC virtual server, a set of configuration parameters is added to the HTTP profile configuration. To facilitate ease of configuration, when you add an HTTP_QUIC virtual server, a new default/built-in HTTP profile is available on the appliance. The profile has the HTTP/3 protocol support parameters set to ENABLED, and also bounded to the HTTP_QUIC virtual servers (applicable if you choose not to associate the HTTP_QUIC virtual server with a user-added HTTP profile). The value of the HTTP/3 parameters in the HTTP profile decides whether to select the HTTP/3 protocol and advertise when processing the TLS ALPN (Application Layer Protocol Negotiation) extension, during the QUIC protocol handshake.
You can create a HTTP/3 profile and specify HTTP parameters for the HTTP/3 service and load balancing virtual server. You must either create a user-defined profile or use the in-built HTTP/3 profile and bind the profile to the load balancing virtual server.
Step 1: configure a user-defined HTTP/3 profile At the command prompt, type:
Add ns httpProfile <profile_name> -http3 ENABLED
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add ns httpProfile http3_quic –http3 ENABLED
Step 2: Bind the user-defined HTTP/3 profile to a load balancing virtual server of type http_quic At the command prompt, type:
set lb vserver <name>@ [-IPAddress <ip_addr|ipv6_addr|*>@] <serviceName>@] [-persistenceType <persistenceType>] [-httpProfileName <string>]
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
set lb vserver lb-http3 –httpProfileName http3_quic
Bind SSL certificate-key pair with HTTP_QUIC virtual server
For processing encrypted traffic, you must add an SSL certificate-key pair and bind it to the HTTP_QUIC virtual server.
At the command prompt, type:
bind ssl vserver <vServerName> -certkeyName <certificate-KeyPairName>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
bind ssl vserver lb-http3 -certkeyName rsa_certkeypair
For more information, see Bind SSL certificate topic.
Bind SSL/TLS protocol parameters with a HTTP_QUIC virtual server
Virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC has in-built TLS 1.3 server functionality because the QUIC protocol uses TLS 1.3 as a mandatory security component. To facilitate the configuration when adding a HTTP_QUIC virtual server, a new default or built-in SSL profile of type - QUIC-FrontEnd is added. The SSL profile has TLS 1.3 version enabled with TLS 1.3 cipher suites (and elliptic curves) configured. The SSL profile must then be bound to the newly added HTTP_QUIC virtual servers. You can create an SSL profile and specify SSL encryption parameters for the TLP 1.1 service and load balancing virtual server. You must either create a user-defined profile or use the in-built SSL profile and bind the profile to the load balancing virtual server.
Step 1: configure a user-defined SSL profile At the command prompt, type:
add ssl profile <name> -sslprofileType QUIC-FrontEnd
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add ssl profile ssl_profile1 -sslprofileType QUIC-FrontEnd -tls13 ENABLED -tls12 DISABLED -tls11 DISABLED -tls1 DISABLED
Step 2: Bind the user-defined SSL profile to a load balancing virtual server of type HTTP_QUIC At the command prompt, type:
set ssl vserver <name>@ [-sslProfile <string>]
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
set ssl vserver lb-http3 -sslprofile ssl_profile1
Enable SSL and load balancing features by using the GUI
Complete the following steps to enable SSL and load balancing features:
- On the navigation pane, expand System and then click Settings.
- On the Configure Basic Features page, select the SSL and Load Balancing.
- Click OK, and then click Close.

Add load balancing and content switching (optional) virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC by using the GUI
- Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers.
- Click Add to create a load balancing virtual server of type HTTP_QUIC.
- In Load Balancing Virtual Server page, click Profiles.
- In the Profiles section, select the profile type as QUIC. Note: QUIC, HTTP/3 and SSL profiles are built-in ones.
- Click OK and then Done.
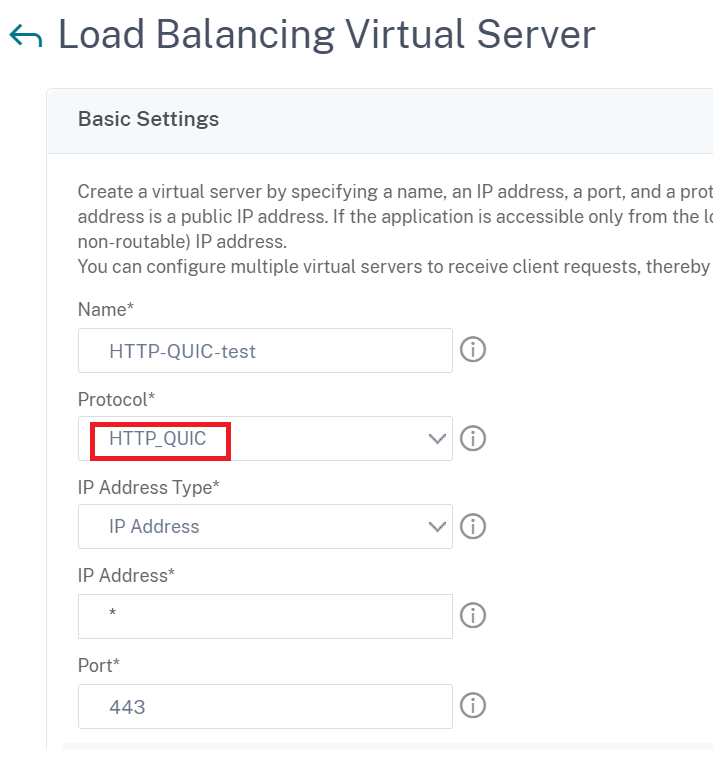
Associate QUIC protocol parameters with the HTTP_QUIC virtual server by using the GUI
Step 1: Add QUIC profile
- Navigate to System > Profiles > QUIC Profile.
- Click Add.
-
In the QUIC Profile page, set the following parameters. For detailed description of each parameter, see the Associate QUIC protocol CLI section.
-
Ack DelayExponent - Active Connection ID Limit
- Active Connection Migration
- Congestion Control Algorithm
- Initial Maximum Data
- Initial Maximum Stream Data Bidi Local
- Initial Maximum Stream Data Bidi Remote
- Initial Maximum Stream Data Unit
- Initial Maximum Stream bidi
- Initial Maximum Stream Uni
- Maximum Acknowledgment Delay
- Maximum Idle Timeout
- Maximum UDP Data GramsperBurst
- New Token Validity Period
- Retry Token Validity Period
- Stateless Address Validation
-
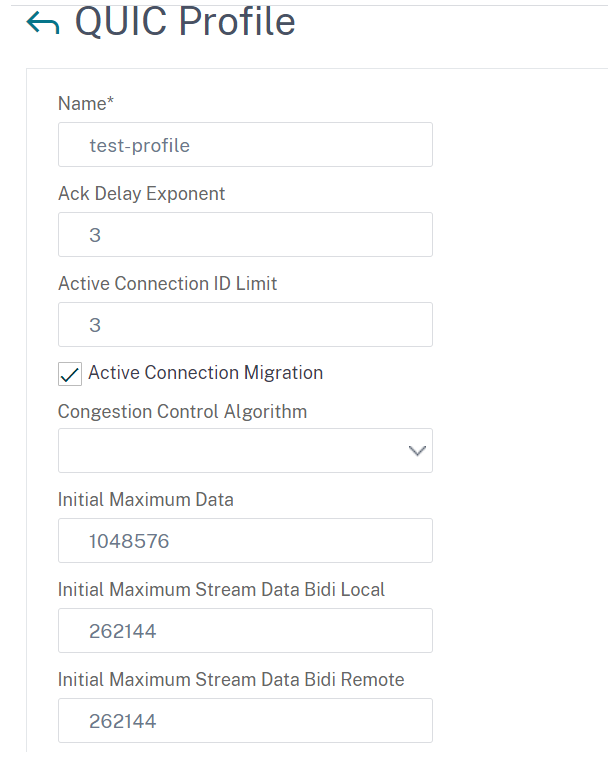
Step 2: Associate QUIC profile with load balancing virtual server of type HTTP_QUIC
- In the Profiles section, select the QUIC profile. Note: QUIC, HTTP/3 and SSL profiles are built-in ones.
- Click OK and then Done.
Associate SSL/TLS protocol parameters with the virtual server of type SSL by using the GUI
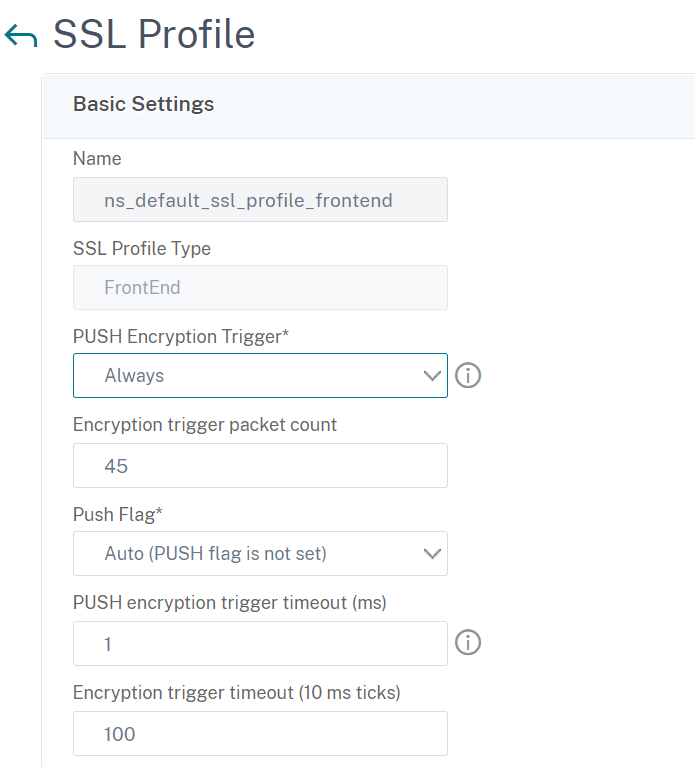
Step 1: Add SSL profile
- Navigate to System > Profiles > SSL Profile.
- Click Add.
- In the QUIC Profile page, set the SSL parameters. For detailed description see, SSL Profile configuration topic.
- Click OK and Close.
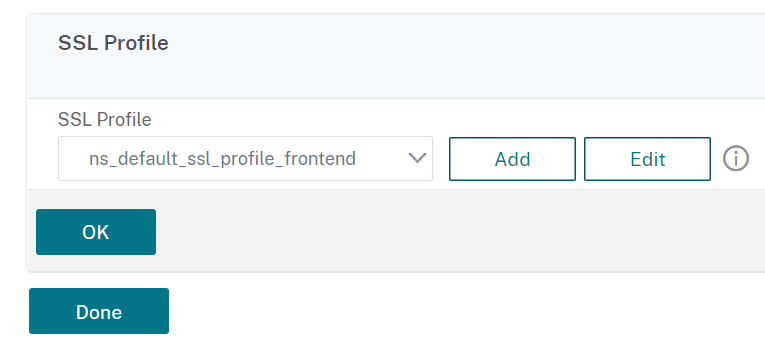
Step 2: Associate SSL profile with load balancing virtual server of type SSL.
- In the Profiles section, select the SSL profile.
- Click OK and then Done.
View QUIC, and HTTP/3 statistics
The following commands display a detailed summary of QUIC, and HTTP3 statistics. At the command prompt, type the following:
> stat quic
> stat quic –detail
<!--NeedCopy-->
To clear the statistics display, type one of the following:
> stat quic -clearstats basic
> stat quic -clearstats full
<!--NeedCopy-->
To display a detailed summary of HTTP/3 statistics:
> stat http3
> stat http3 –detail
<!--NeedCopy-->
To clear the statistics display, type one of the following:
> stat http3 -clearstats basic
> stat http3 -clearstats full
<!--NeedCopy-->
Share
Share
In this article
- Enable SSL and load balancing
- Add load balancing and content switching (optional) virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC for HTTP/3 service
- Associate QUIC protocol parameters with HTTP_QUIC virtual server
- Enable and bind HTTP/3 on a HTTP_QUIC virtual server
- Bind SSL certificate-key pair with HTTP_QUIC virtual server
- Bind SSL/TLS protocol parameters with a HTTP_QUIC virtual server
- Enable SSL and load balancing features by using the GUI
- Add load balancing and content switching (optional) virtual servers of type HTTP_QUIC by using the GUI
- Associate QUIC protocol parameters with the HTTP_QUIC virtual server by using the GUI
- Associate SSL/TLS protocol parameters with the virtual server of type SSL by using the GUI
- View QUIC, and HTTP/3 statistics
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.