-
Getting Started with NetScaler
-
Licensing
-
Solutions for Telecom Service Providers
-
Load Balance Control-Plane Traffic that is based on Diameter, SIP, and SMPP Protocols
-
Provide Subscriber Load Distribution Using GSLB Across Core-Networks of a Telecom Service Provider
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing application traffic
-
Basic components of authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration
-
Web Application Firewall protection for VPN virtual servers and authentication virtual servers
-
On-premises NetScaler Gateway as an identity provider to Citrix Cloud™
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration for commonly used protocols
-
Troubleshoot authentication and authorization related issues
-
-
-
-
-
-
Persistence and persistent connections
-
Advanced load balancing settings
-
Gradually stepping up the load on a new service with virtual server–level slow start
-
Protect applications on protected servers against traffic surges
-
Retrieve location details from user IP address using geolocation database
-
Use source IP address of the client when connecting to the server
-
Use client source IP address for backend communication in a v4-v6 load balancing configuration
-
Set a limit on number of requests per connection to the server
-
Configure automatic state transition based on percentage health of bound services
-
-
Use case 2: Configure rule based persistence based on a name-value pair in a TCP byte stream
-
Use case 3: Configure load balancing in direct server return mode
-
Use case 6: Configure load balancing in DSR mode for IPv6 networks by using the TOS field
-
Use case 7: Configure load balancing in DSR mode by using IP Over IP
-
Use case 10: Load balancing of intrusion detection system servers
-
Use case 11: Isolating network traffic using listen policies
-
Use case 12: Configure Citrix Virtual Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 13: Configure Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 14: ShareFile wizard for load balancing Citrix ShareFile
-
Use case 15: Configure layer 4 load balancing on the NetScaler appliance
-
-
-
-
Authentication and authorization for System Users
-
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between two Datacenters
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector between Datacenter and AWS Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a Datacenter and Azure Cloud
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between Datacenter and SoftLayer Enterprise Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a NetScaler Appliance and Cisco IOS Device
-
CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Licensing overview
Important:
File based licensing system (also referred to as manually managed entitlements), traditionally used for activating various on-premises components, will be End of Life (EOL) on April 15, 2026. License Activation Service (LAS) is the next generation technology for product activations across the suite of Citrix products. LAS will be the only way to activate and license NetScaler instances after April 15, 2026, supporting NetScaler Flexed licenses (CPL/UHMC), legacy NetScaler Pooled licenses, and NetScaler Fixed term Bandwidth licenses. To remain supported, your NetScaler and NetScaler Console deployments must be on a LAS compatible version.
The minimum required NetScaler® versions that are LAS compatible are:
NetScaler ADCs: 14.1-51.80, 13.1-60.29, 13.1-37.247 (FIPS)
NetScaler SVM: 14.1-51.83, 13.1-60.30
NetScaler Console Service: Supported from early September 2025
NetScaler Console on-prem: 14.1-51.83
Note: LAS support for Console on-prem is from release 14.1-51.83 onwards. However, file-based licensing is deprecated from Console on-prem releases 14.1-51.83 onwards and 13.1-60.26 onwards, and goes EOL on April 15th, 2026. That is, even if you upgrade to Console on-prem release 14.1-51.83 or release 13.1-60.26 or later, you can continue using file-based licensing. However you must upgrade to Console on-prem release 14.1-51.83 or later, and switch to LAS before 15th April 2026 because file-based licensing reaches EOL.
All the other forms of legacy NetScaler licenses such as Pooled vCPU, CICO, perpetual will not be supported with LAS. NetScaler instances leveraging perpetual licenses without an active maintenance will become unlicensed upon upgrade to the above mentioned software versions.
LAS based licenses may not be available to customers where prohibited by law or regulations.
If you have questions or concerns, contact Customer Care. Citrix® may limit or suspend your Citrix Maintenance for non-compliance with these requirements without liability in addition to any other remedies Citrix may have at law or equity. These requirements don’t apply where prohibited by law or regulation.
NetScaler offers a wide range of product editions and licensing models for MPX and VPX appliances, to meet your organization’s need.
For proper operation of a NetScaler appliance, it must have one of the NetScaler family edition licenses. The ADC product line has three family editions:
- Standard Edition
Note:
Standard edition has reached End-of-Sale (EOS) and is only available for renewal.
- Advanced Edition
- Premium Edition
For more information, see the data sheet. The data sheet is available on www.netscaler.com.
Select a NetScaler edition. Then select an MPX or a VPX license offering based on the following criteria:
- Perpetual and subscription (yearly and hourly subscription)
- vCPU and bandwidth
- on-premises and cloud
Important:
Starting from NetScaler release 13.1-60.x, there are some changes related to perpetual licensing. For details, see Changes related to perpetual licensing.
NetScaler VPX Express license
VPX Express for on-premises and cloud deployments does not require a license file, and it offers the following features:
- 20 Mbps bandwidth
- Starting with NetScaler release 13.1 build 56.x, VPX Express includes all the advanced features that are available with the Premium license.
- Maximum 250 SSL sessions
- 20 Mbps SSL throughput
Important
Clustering is available in Standard edition for VPX public cloud, and in VPX Express license.
NetScaler fixed bandwidth (throughput) license
Fixed bandwidth perpetual licenses are EOS and you must now use fixed bandwidth subscription licenses. Fixed bandwidth subscription allows you to run a fixed throughput deployment in any form factor (MPX/SDX/VPX/BLX). After deploying your NetScaler, you must fetch your license files from the license server and download a license manually to each device (on-premises or cloud).
Notes:
- NetScaler instance stops its normal operations after the license expiry, including configuration loss and complete shutdown of traffic processing.
- Only advanced and premium editions are supported.
- Edition and bandwidth upgrades are not supported.
- Migration to pooled capacity license is not supported.
NetScaler Pooled Capacity license
Use NetScaler Application Delivery Management (ADM) to create a licensing framework that comprises a common bandwidth and an instance pool. For more information, see NetScaler Pooled Capacity.
Note:
NetScaler Console can host both Pooled and Self Managed Pool licenses. To use the required license, configure the license server on NetScaler and check out the capacity from the appropriate pool. The ADC CLI and GUI configuration steps for the Pooled and Self Managed Pool license are the same.
NetScaler Self Managed Pool license
From NetScaler release 13.1 build 30.x onwards, NetScaler instances support the Self Managed Pool license. With this license, you can simplify and automate license file uploads to a license server. Use NetScaler Console to create a licensing framework that comprises a common bandwidth or vCPU and instance pool.
To use the Self Managed Pool license, configure the license server to the SelfManagedPool license mode on NetScaler and check out the required capacity. Use the show ns license command after rebooting the NetScaler appliance to find out the license that is configured.
Important
If your system is configured with Pooled Capacity license but want to migrate to Self Managed Pool license without impacting the traffic flow, ensure that the target server has the required Self Managed Pool license.
You can migrate only between the following compatible licenses:
- Pooled Capacity to Self Managed Pool, and conversely.
- vCPU to Self Managed vCPU, and conversely.
To migrate the license, run the following command:
add ns licenseserver (<licenseServerIP> | <serverName>) -forceUpdateIP -licensemode [CICO | Pooled | SelfManagedPool | VCPU | SelfManagedvCPU]Example:
add licenseserver 192.0.2.246 -forceUpdateIP -licensemode selfManagedvcPU
Configure Self Managed Pool license using the CLI
To add the license server config to the NetScaler appliance, run the following command:
add ns licenseserver (<licenseServerIP> | <serverName>) [-port <positive_integer>] -licensemode [CICO | Pooled | SelfManagedPool | VCPU | SelfManagedvCPU]
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add ns licenseserver 192.0.2.246 -port 27000 -licensemode SelfManagedPool
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
The
show ns licenseserverpoolcommand displays only licenses based on the specified license mode. Hence, the licenses are fetched faster. To get an inventory of all the licenses, run theshow ns licenseserverpool -getallLicensescommand. If the license mode is not specified, the Pooled Capacity licenses are displayed by default.
To modify the system capacity, run the following command:
set ns capacity ((-bandwidth <positive_integer> -unit ( Gbps | Mbps )) | -platform <platform>) [-Edition <Edition>]
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
set ns capacity -bandwidth 3 -unit gbps -edition enterprise
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
Capacity is checked out from the license pool of the license server.
To reboot the NetScaler appliance, run the following command:
reboot [-warm]
<!--NeedCopy-->
To display the state of all the licensed features and configured license mode, run the following command:
show ns license
<!--NeedCopy-->
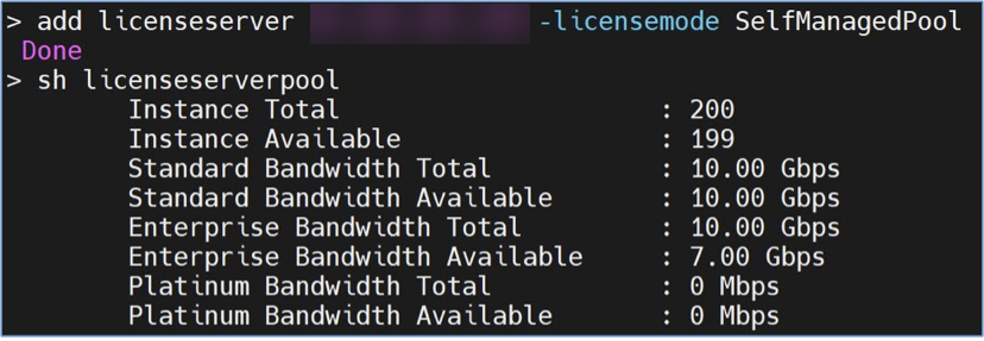
Sample output of show ns licenseserverpool command:
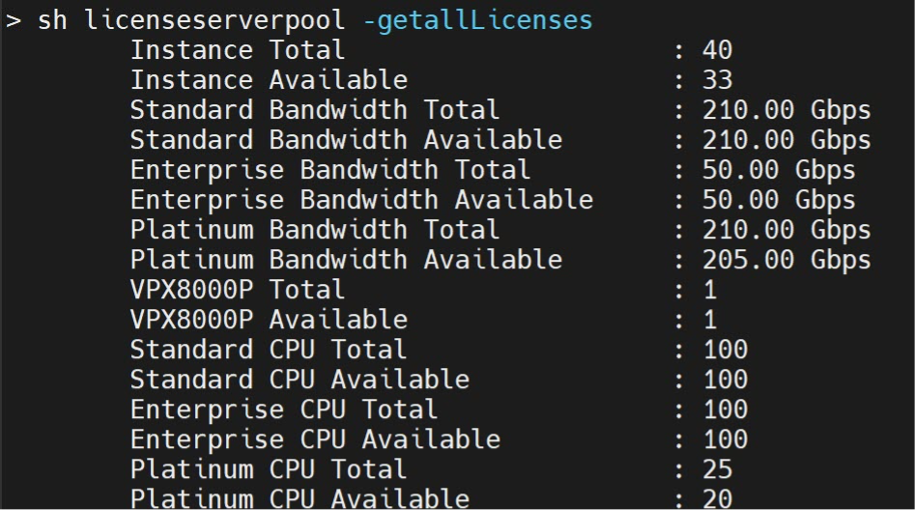
Sample output of show ns licenseserverpool -getallLicenses command:
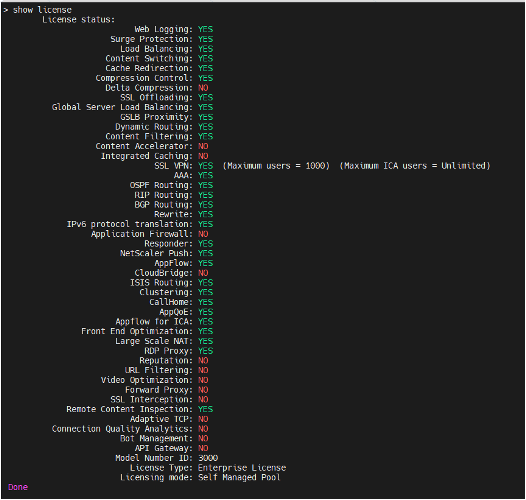
Sample output of show license command:
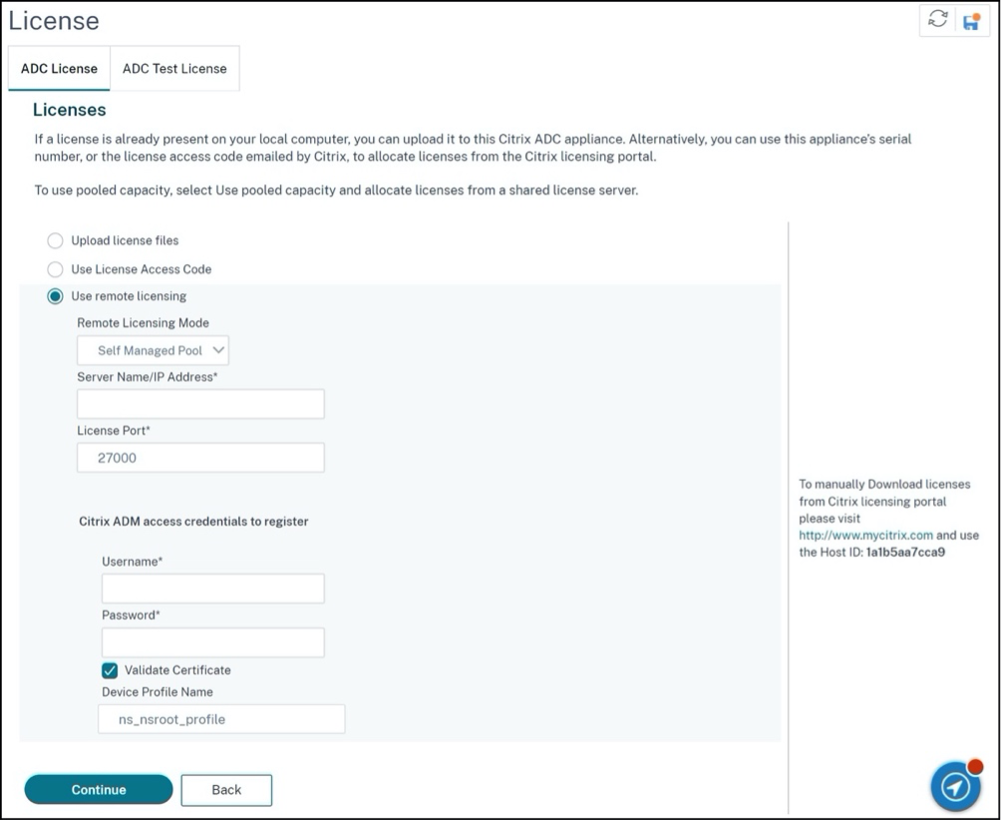
Configure Self Managed Pool license using the GUI
Complete the following steps to configure the Self Managed Pool license:
- Navigate to System > Licenses > ADC License > Manage Licenses > Add New License.
- In the Licenses page, select the Use remote licensing radio button, and choose your license mode from Remote Licensing Mode.
- Enter the server IP address and the license port details.
- Provide the NetScaler Console access credentials.
- Click Continue.
Changes related to perpetual licensing
Terminology description:
- Subscription Advantage (SA) Date: A date present in perpetual license files, introduced to limit upgrades to NetScaler versions released only up to a certain date.
- Burn-In Date (BID): A date associated with every NetScaler version and build.
The following changes are introduced in Perpetual licensing:
Change 1: SA Date check and enforcement:
This check and enforcement is introduced to block NetScaler customers who are running NetScaler instances on perpetual licenses with expired maintenance, resulting in unsupported deployments.
If the Burn-In Date of the NetScaler build to which you are trying to upgrade to is later than the SA date in the perpetual license file used on your NetScaler instance, your NetScaler instance becomes unlicensed after the upgrade. Some NetScaler VPX™ versions already had this check and enforcement. It is now introduced for NetScaler form-factors: VPX, MPX, and SDX starting from the following NetScaler releases:
- NetScaler ADC: 14.1 51.x, 13.1-60.x, 13.1-37.x (FIPS)
- NetScaler SVM: 14.1 51.x, 13.1-60.x
To find the SA date of the perpetual license used on your NetScaler instance, see your perpetual license file for the SA date in YYYY.MMDD format as shown in the following sample image.

This check occurs during boot up after a NetScaler upgrade. To avoid your NetScaler instance becoming unlicensed, obtain a supported NetScaler license with active maintenance.
Note:
If you are using a perpetual license on your NetScaler instance and have active maintenance, but have not replaced the old perpetual license file with the license file provided with your latest maintenance renewal (that is, you did not use the latest license file with updated SA date and are still using the older license file with old SA date), your NetScaler becomes unlicensed if you upgrade to NetScaler builds that have the SA date check and enforcement. To avoid this impact, use the latest file that you received during your most recent maintenance renewal.
Change 2: Burn-In Date specific to each build:
Earlier, the Burn-In Date for all builds across a major NetScaler version used to be the same. For example, all builds under NetScaler version 13.1 used to have the same Burn-In Date. Now, each unique NetScaler build has its own Burn-In Date (approximately based on its release date) starting from the following NetScaler releases:
- NetScaler ADC: 14.1-51.x, 13.1-60.x, 13.1 37.x (FIPS)
- NetScaler SVM: 14.1-51.x, 13.1-60.x
For example, from NetScaler version 13.1 build 60.x onwards, each build has a different Burn-In Date.
Related resources
VPX licensing on cloud
VPX deployment is supported on public cloud providers such as Azure, AWS, and Google. For more information, see the following documents:
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.