-
Getting Started with NetScaler
-
Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance
-
Optimize NetScaler VPX performance on VMware ESX, Linux KVM, and Citrix Hypervisors
-
Apply NetScaler VPX configurations at the first boot of the NetScaler appliance in cloud
-
Configure simultaneous multithreading for NetScaler VPX on public clouds
-
Install a NetScaler VPX instance on Microsoft Hyper-V servers
-
Install a NetScaler VPX instance on Linux-KVM platform
-
Prerequisites for installing NetScaler VPX virtual appliances on Linux-KVM platform
-
Provisioning the NetScaler virtual appliance by using OpenStack
-
Provisioning the NetScaler virtual appliance by using the Virtual Machine Manager
-
Configuring NetScaler virtual appliances to use SR-IOV network interface
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX on KVM hypervisor to use Intel QAT for SSL acceleration in SR-IOV mode
-
Configuring NetScaler virtual appliances to use PCI Passthrough network interface
-
Provisioning the NetScaler virtual appliance by using the virsh Program
-
Provisioning the NetScaler virtual appliance with SR-IOV on OpenStack
-
Configuring a NetScaler VPX instance on KVM to use OVS DPDK-Based host interfaces
-
-
Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on AWS
-
Deploy a VPX high-availability pair with elastic IP addresses across different AWS zones
-
Deploy a VPX high-availability pair with private IP addresses across different AWS zones
-
Protect AWS API Gateway using the NetScaler Web Application Firewall
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX instance to use SR-IOV network interface
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX instance to use Enhanced Networking with AWS ENA
-
Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on Microsoft Azure
-
Network architecture for NetScaler VPX instances on Microsoft Azure
-
Configure multiple IP addresses for a NetScaler VPX standalone instance
-
Configure a high-availability setup with multiple IP addresses and NICs
-
Configure a high-availability setup with multiple IP addresses and NICs by using PowerShell commands
-
Deploy a NetScaler high-availability pair on Azure with ALB in the floating IP-disabled mode
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX instance to use Azure accelerated networking
-
Configure HA-INC nodes by using the NetScaler high availability template with Azure ILB
-
Configure a high-availability setup with Azure external and internal load balancers simultaneously
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX standalone instance on Azure VMware solution
-
Configure a NetScaler VPX high availability setup on Azure VMware solution
-
Configure address pools (IIP) for a NetScaler Gateway appliance
-
Deploy a NetScaler VPX instance on Google Cloud Platform
-
Deploy a VPX high-availability pair on Google Cloud Platform
-
Deploy a VPX high-availability pair with external static IP address on Google Cloud Platform
-
Deploy a single NIC VPX high-availability pair with private IP address on Google Cloud Platform
-
Deploy a VPX high-availability pair with private IP addresses on Google Cloud Platform
-
Install a NetScaler VPX instance on Google Cloud VMware Engine
-
-
Solutions for Telecom Service Providers
-
Load Balance Control-Plane Traffic that is based on Diameter, SIP, and SMPP Protocols
-
Provide Subscriber Load Distribution Using GSLB Across Core-Networks of a Telecom Service Provider
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing application traffic
-
Basic components of authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration
-
Web Application Firewall protection for VPN virtual servers and authentication virtual servers
-
On-premises NetScaler Gateway as an identity provider to Citrix Cloud™
-
Authentication, authorization, and auditing configuration for commonly used protocols
-
Troubleshoot authentication and authorization related issues
-
-
-
-
-
-
Configure DNS resource records
-
Configure NetScaler as a non-validating security aware stub-resolver
-
Jumbo frames support for DNS to handle responses of large sizes
-
Caching of EDNS0 client subnet data when the NetScaler appliance is in proxy mode
-
Use case - configure the automatic DNSSEC key management feature
-
Use Case - configure the automatic DNSSEC key management on GSLB deployment
-
-
-
Source IP address whitelisting for GSLB communication channels
-
Use case: Deployment of domain name based autoscale service group
-
Use case: Deployment of IP address based autoscale service group
-
-
Persistence and persistent connections
-
Advanced load balancing settings
-
Gradually stepping up the load on a new service with virtual server–level slow start
-
Protect applications on protected servers against traffic surges
-
Retrieve location details from user IP address using geolocation database
-
Use source IP address of the client when connecting to the server
-
Use client source IP address for backend communication in a v4-v6 load balancing configuration
-
Set a limit on number of requests per connection to the server
-
Configure automatic state transition based on percentage health of bound services
-
-
Configure load balancing for commonly used protocols
-
Load balance a group of SIP servers
-
Use case 2: Configure rule based persistence based on a name-value pair in a TCP byte stream
-
Use case 3: Configure load balancing in direct server return mode
-
Use case 6: Configure load balancing in DSR mode for IPv6 networks by using the TOS field
-
Use case 7: Configure load balancing in DSR mode by using IP Over IP
-
Use case 10: Load balancing of intrusion detection system servers
-
Use case 11: Isolating network traffic using listen policies
-
Use case 12: Configure Citrix Virtual Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 13: Configure Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops for load balancing
-
Use case 14: ShareFile wizard for load balancing Citrix ShareFile
-
Use case 15: Configure layer 4 load balancing on the NetScaler appliance
-
-
-
-
Authentication and authorization for System Users
-
-
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between two Datacenters
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector between Datacenter and AWS Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a Datacenter and Azure Cloud
-
Configuring CloudBridge Connector Tunnel between Datacenter and SoftLayer Enterprise Cloud
-
Configuring a CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Between a NetScaler Appliance and Cisco IOS Device
-
CloudBridge Connector Tunnel Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Load balance a group of SIP servers
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is designed to initiate, manage, and terminate multimedia communications sessions. It has emerged as the standard for Internet telephony (VoIP). SIP messages can be transmitted over TCP or UDP. SIP messages are of two types: request messages and response messages.
The traffic in a SIP based communication system is routed through dedicated devices and applications (entities). In a multimedia communication session, these entities exchange messages. The following figure shows a basic SIP based communication system:
Figure 1. SIP Based Communication System
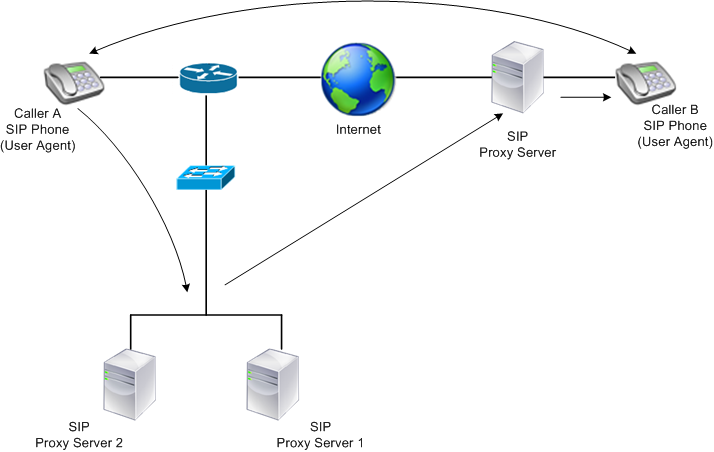
A NetScaler enables you to load balance SIP messages over UDP or over TCP (including TLS). You can configure the NetScaler to load balance SIP requests to a group of SIP proxy servers. To do so, you create a load balancing virtual server with the load balancing method and the type of persistence set to one of the following combinations:
- Call-ID hash load balancing method with no persistence setting
- Call-ID based persistence with least connection or round robin load balancing method
- Rule based persistence with least connection or round robin load balancing method
Also, by default, the NetScaler appends RPORT via the header of the SIP request, so that the server sends the response back to the source IP address and port from which the request originated.
Note: For load balancing to work, you must configure the SIP proxies so that they do not add private IP addresses or private domains to the SIP header/payload. SIP proxies must add to the SIP header a domain name that resolves to the IP address of the SIP virtual server. Also, the SIP proxies must communicate with a common database to share registration information.
Server Initiated Traffic
For SIP-server initiated outbound traffic, configure RNAT on the NetScaler so that the private IP addresses used by the clients are translated into public IP addresses.
If you have configured SIP parameters that include the RNAT source or destination port, the appliance compares the values of the source and destination ports of the request packets with the RNAT source port and RNAT destination port. If one of the values matches, the appliance updates the VIA header with RPORT. The SIP response from the client then traverses the same path as the request.
For server-initiated SSL traffic, the NetScaler uses a built-in certificate-key pair. If you want to use a custom certificate-key pair, bind the custom certificate-key pair to the NetScaler internal service named nsrnatsip-127.0.0.1-5061.
Support for Policies and Expressions
The NetScaler default expressions language contains several expressions that operate on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) connections. These expressions can be bound only to SIP based (sip_udp, sip_tcp or sip_ssl) virtual servers, and to global bind points. You can use these expressions in content switching, rate limiting, responder, and rewrite policies.
Configuring Load Balancing for SIP Signaling Traffic over TCP or UDP
The NetScaler can load balance SIP servers that send requests over UDP or TCP, including TCP traffic secured by TLS. The ADC provides the following service types to load balance the SIP servers:
- SIP_UDP – Used when SIP servers send SIP messages over UDP.
- SIP_TCP – Used when SIP servers send SIP messages over TCP.
- SIP_SSL – Used to secure SIP signaling traffic over TCP by using SSL or TLS. The NetScaler supports the following modes:
- End-to-end TLS connection between the client, the ADC, and the SIP server.
- TLS connection between the client and the ADC, and TCP connection between the ADC and the SIP server.
- TCP connection between the client and the ADC, and TLS connection between the ADC and the SIP server.
The following figure shows the topology of a setup configured to load balance a group of SIP servers sending SIP messages over TCP or UDP.
Figure 2. SIP Load Balancing Topology
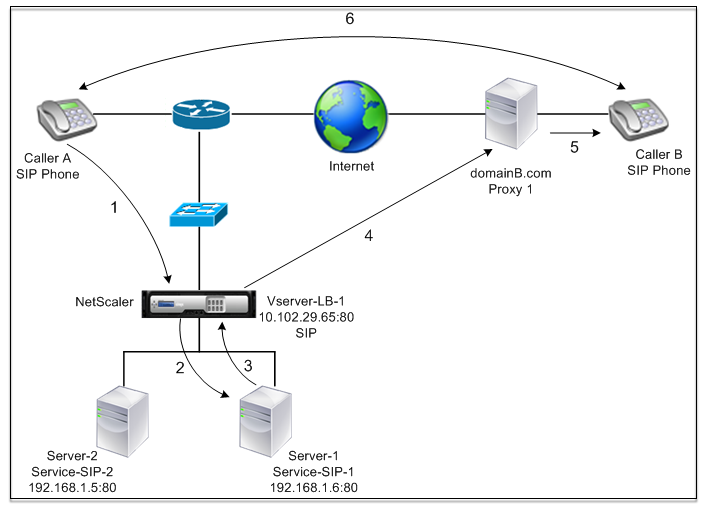
| Entity type | Name | IP address | Port | Service type / Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Server | Vserver-LB-1 | 10.102.29.65 | 80 | SIP_UDP / SIP_TCP / SIP_SSL |
| Services | Service-SIP-1 | 192.168.1.6 | 80 | SIP_UDP / SIP_TCP / SIP_SSL |
| Service-SIP-2 | 192.168.1.5 | 80 | SIP_UDP / SIP_TCP / SIP_SSL | |
| Monitors | Default | None | 80 | SIP_UDP / SIP_TCP / SIP_SSL |
Following is an overview of configuring basic load balancing for SIP traffic:
-
Configure services, and configure a virtual server for each type of SIP traffic that you want to load balance:
- SIP_UDP – If you are load balancing the SIP traffic over UDP.
- SIP_TCP – If you are load balancing the SIP traffic over TCP.
- SIP_SSL – If you are load balancing and securing the SIP traffic over TCP.
Note: If you use SIP_SSL, be sure to create an SSL certificate-key pair. For more information, see Adding a Certificate Key Pair.
-
Bind the services to the virtual servers.
-
If you want to monitor the states of the services with a monitor other than the default (tcp-default), create a custom monitor and bind it to the services. The NetScaler provides two custom monitor types, SIP-UDP and SIP-TCP, for monitoring SIP services.
-
If using a SIP_SSL virtual server, bind an SSL certificate-key pair to the virtual server.
-
If you are using the NetScaler as the gateway for the SIP servers in your deployment, configure RNAT.
-
If you want to append RPORT to the SIP messages that are initiated from the SIP server, configure the SIP parameters.
To configure a basic load balancing setup for SIP traffic by using the command line interface
Create one or more services. At the command prompt, type:
add service <name> <serverName> (SIP_UDP | SIP_TCP | SIP_SSL) <port>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add service Service-SIP-UDP-1 192.0.2.5 SIP_UDP 80
<!--NeedCopy-->
Create as many virtual servers as necessary to handle the services that you created. The virtual server type must match the type of services that you bind to it. At the command prompt, type:
add lb vserver <name> <serverName> (SIP_UDP | SIP_TCP | SIP_SSL) <port>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add lb vserver Vserver-LB-1 SIP_UDP 10.102.29.60 80
<!--NeedCopy-->
Bind each service to a virtual server. At the command prompt, type:
bind lb vserver <name> <serverName>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
bind lb vserver Vserver-LB-1 Service-SIP-UDP-1
<!--NeedCopy-->
(Optional) Create a custom monitor of type SIP-UDP or SIP-TCP, and bind the monitor to the service. At the command prompt, type:
add lb monitor <monitorName> <monitorType> [<interval>]
bind lb monitor <monitorName> <ServiceName>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add lb monitor mon1 sip-UDP -sipMethod REGISTER -sipuRI sip:mon@test.com -sipregURI sip:mon@test.com -respcode 200
bind monitor mon1 Service-SIP-UDP-1
<!--NeedCopy-->
If you created a SIP_SSL virtual server, bind an SSL certificate key pair to the virtual server. At the command prompt, type: At the command prompt, type:
bind ssl vserver <vServerName> -certkeyName <certificate-KeyPairName> -CA –skipCAName
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
bind ssl vserver Vserver-LB-1 -certkeyName CertKey-SSL-1
<!--NeedCopy-->
Configure RNAT as required by your network topology. At the command prompt, type one of the following commands to create, respectively, an RNAT entry that uses a network address as the condition and SNIP as the NAT IP address, an RNAT entry that uses a network address as the condition and a unique IP address as the NAT IP address, an RNAT entry that uses an ACL as the condition and a SNIP as the NAT IP address, or an RNAT entry that uses an ACL as a condition and a unique IP address as the NAT IP address:
add rnat <name> (<network> | (<aclname> [-redirectPort <port>]))
bind rnat <name> <natIP>@ …
show rnat
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add rnat RNAT-1 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
bind rnat RNAT-1 -natip 10.102.29.50
<!--NeedCopy-->
If you want to use a custom certificate-key pair, bind the custom certificate-key pair to the NetScaler internal service named nsrnatsip-127.0.0.1-5061.
add ssl certKey <certkeyName> -cert <string> [-key <string>]
bind ssl service <serviceName> -certkeyName <string>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Example:
add ssl certKey c1 -cert cert.epm -key key.ky
bind ssl service nsrnatsip-127.0.0.1-5061 -certkeyName c1
<!--NeedCopy-->
If you want to append RPORT to the SIP messages that the SIP server initiates, type the following command at the command prompt:
set lb sipParameters -rnatSrcPort <rnatSrcPort> -rnatDstPort<rnatDstPort> -retryDur <integer> -addRportVip <addRportVip> - sip503RateThreshold <sip503_rate_threshold_value>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Sample Configuration for load balancing the SIP traffic over UDP
add service service-UDP-1 10.102.29.5 SIP_UDP 80
Done
add lb vserver vserver-LB-1 SIP_UDP 10.102.29.60 80
Done
bind lb vserver vserver-LB-1 service-UDP-1
Done
add lb mon mon1 sip-udp -sipMethod REGISTER -sipuRI sip:mon@test.com -sipregURI sip:mon@test.com -respcode 200
Done
bind mon mon1 service-UDP-1
Done
add rnat RNAT-1 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
Done
set lb sipParameters -rnatSrcPort 5060 -rnatDstPort 5060 -retryDur 1000 -addRportVip ENABLED -sip503RateThreshold 1000
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
Sample Configuration for load balancing the SIP traffic over TCP
add service service-TCP-1 10.102.29.5 SIP_TCP 80
Done
add lb vserver vserver-LB-1 SIP_TCP 10.102.29.60 80
Done
bind lb vserver vserver-LB-1 service-TCP-1
Done
add lb mon mon1 sip-tcp -sipMethod REGISTER -sipuRI sip:mon@test.com -sipregURI sip:mon@test.com -respcode 200
Done
bind mon mon1 service-TCP-1
Done
add rnat RNAT-1 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
Done
set lb sipParameters -rnatSrcPort 5060 -rnatDstPort 5060 -retryDur 1000 -addRportVip ENABLED -sip503RateThreshold 1000
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
Sample Configuration for load balancing and securing SIP traffic over TCP
add service service-SIP-SSL-1 10.102.29.5 SIP_SSL 80
Done
add lb vserver vserver-LB-1 SIP_SSL 10.102.29.60 80
Done
bind lb vserver vserver-LB-1 service-SIP-SSL
Done
add lb mon mon1 sip-tCP -sipMethod REGISTER -sipuRI sip:mon@test.com -sipregURI sip:mon@test.com -respcode 200
Done
bind mon mon1 service-SIP-SSL
Done
bind ssl vserver Vserver-LB-1 -certkeyName CertKey-SSL-1
Done
add rnat RNAT-1 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
Done
set lb sipParameters -rnatSrcPort 5060 -rnatDstPort 5060 -retryDur 1000 -addRportVip ENABLED -sip503RateThreshold 1000
Done
<!--NeedCopy-->
To configure a basic load balancing setup for SIP traffic by using the GUI
-
Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers, and add a virtual server of type SIP_UDP, SIP_TCP, or SIP_SSL.
-
Click the Service section, and add a service of type SIP_UDP, SIP_TCP, or SIP_SSL.
-
(Optional) Click the Monitor section, and add a monitor of the type: SIP-UDP or SIP-TCP.
-
Bind the monitor to the service, and bind the service to the virtual server.
-
If you created a SIP_SSL virtual server, bind an SSL certificate key pair to the virtual server. Click the Certificates section, and bind a certificate key pair to the virtual server.
-
Configure RNAT as required by your network topology. To configure RNAT:
- Navigate to System > Network > Routes.
- On the Routes page, click the RNAT tab.
- In the details pane, click Configure RNAT.
- In the Configure RNAT dialog box, do one of the following:
- If you want to use the network address as a condition for creating an RNAT entry, click Network and set the following parameters:
- Network
- Netmask
- If you want to use an extended ACL as a condition for creating an RNAT entry, click ACL and set the following parameters:
- ACL Name
- Redirect Port
- If you want to use the network address as a condition for creating an RNAT entry, click Network and set the following parameters:
- To set a SNIP address as a NAT IP address, skip to step 7.
- To set a unique IP address as a NAT IP, in the Available NAT IP (s) list, select the IP address that you want to set as the NAT IP, and then click Add. The NAT IP you selected appears in the Configured NAT IPs’ list.
- Click Create, and then click Close.
If you want to use a custom certificate-key pair, bind the custom certificate-key pair to the NetScaler internal service named nsrnatsip-127.0.0.1-5061. To bind the pair:
- Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Services and click the Internal Services tab.
- Select nsrnatsip-127.0.0.1-5061 and click Edit.
- Click the Certificates section and bind a certificate key pair to the internal service.
-
If you want to append RPORT to the SIP messages that the SIP server initiates, configure the SIP parameters. Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing and click Change SIP settings, set the various SIP parameters.
SIP Expression and Policy Example: Compression Enabled in Client Requests
A NetScaler cannot process compressed client SIP requests, so the client SIP request fails.
You can configure a responder policy that intercepts the SIP NEGOTIATE message from the client and looks for the compression header. If the message includes a compression header, the policy responds with “400 Bad Request,” so that the client resends the request without compressing it.
At the command prompt, type the following commands to create the responder policy:
add responder action sipaction1 respondwith q{"SIP/2.0 400 Bad Requestrnrn"}
Done
add responder policy sippol1
add responder policy sippol1 "SIP.REQ.METHOD.EQ("NEGOTIATE")&&SIP.REQ.HEADER("Compression").EXISTS" sipaction1
<!--NeedCopy-->
Share
Share
In this article
- Server Initiated Traffic
- Support for Policies and Expressions
- Configuring Load Balancing for SIP Signaling Traffic over TCP or UDP
- To configure a basic load balancing setup for SIP traffic by using the command line interface
- Sample Configuration for load balancing the SIP traffic over UDP
- Sample Configuration for load balancing the SIP traffic over TCP
- Sample Configuration for load balancing and securing SIP traffic over TCP
- To configure a basic load balancing setup for SIP traffic by using the GUI
- SIP Expression and Policy Example: Compression Enabled in Client Requests
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.